Tuberculosis vaccine and Mantoux test
 Tuberculosis is a severe chronic disease that kills millions of lives each year, including children.Protect your child from tuberculosis infection by vaccinating him( BCG).In countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis, to which Russia belongs, this preventive measure is mandatory and strictly controlled by the state.
Tuberculosis is a severe chronic disease that kills millions of lives each year, including children.Protect your child from tuberculosis infection by vaccinating him( BCG).In countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis, to which Russia belongs, this preventive measure is mandatory and strictly controlled by the state.
About the BCG vaccine
BCG( the name of the vaccine comes from the first letters of the name and surname of its creator) is an immunobiological drug that contains live attenuated tubercle bacilli.This vaccine does not protect against infection with mycobacteria( the causative agent of tuberculosis), but it promotes the synthesis of specific antibodies in the child's body.The high concentration in the blood of these antibodies minimizes the likelihood of developing primary tuberculosis and, most importantly, does not allow the emergence of extremely dangerous and difficult to diagnose and treat forms of extrapulmonary tuberculosis( such as bone tuberculosis or tuberculous meningitis).
This should be remembered by parents who doubt whether to make BCG to their child .For certain categories of small patients, there is a special version of the vaccine against tuberculosis with a reduced number of microbial bodies - BCG-M. This drug is indicated for children who can not do routine BCG vaccine:
- Premature babies with a body weight of more than 2000 g( BCG is administered only to children weighing more than 2500 g).
- Newborns who underwent haemolytic disease, intrauterine infection, CNS lesions of varying severity.
 In addition, BCG-M is indicated if the inoculation against tuberculosis due to contraindications has not been carried out in the maternity hospital.
In addition, BCG-M is indicated if the inoculation against tuberculosis due to contraindications has not been carried out in the maternity hospital.
However, there are situations in which a child can not do either BCG or BCG-M.In particular, vaccination against tuberculosis is not carried out for children with immunodeficiencies and children who have severe reactions to BCG in their families from brothers and sisters.Also children who have recovered from tuberculosis or who have a positive Mantoux test can not be vaccinated and revaccinated.
Duration and rules for vaccination

In accordance with the national immunization calendar , TB vaccination is administered to children aged 3-7 days at the maternity hospital, that is, before the first contact with a tubercle bacillus.If, for some reason, the vaccine was not vaccinated in the hospital( for example, there were contraindications), it is done in a polyclinic.In this case, parents who are afraid of vaccination in the hospital, should know that after two months to exclude possible infection with mycobacteria, their baby before vaccination will have to put the test Mantoux.In addition, vaccination against tuberculosis, conducted not according to the vaccination schedule, will shift the entire immunization schedule( the interval between BCG or BCG-M and other vaccinations should be at least a month).
The vaccination against tuberculosis in accordance with the vaccination schedule is carried out at 6-7 years of and exclusively for children who have a negative Mantoux test( that is, they are not immune to the infection).
To be effective and safe, the drug must be injected intradermally into the child's left shoulder.Only in this case it is possible to achieve the development of a local infectious process and the development of specific immunity.
Scar after BCG
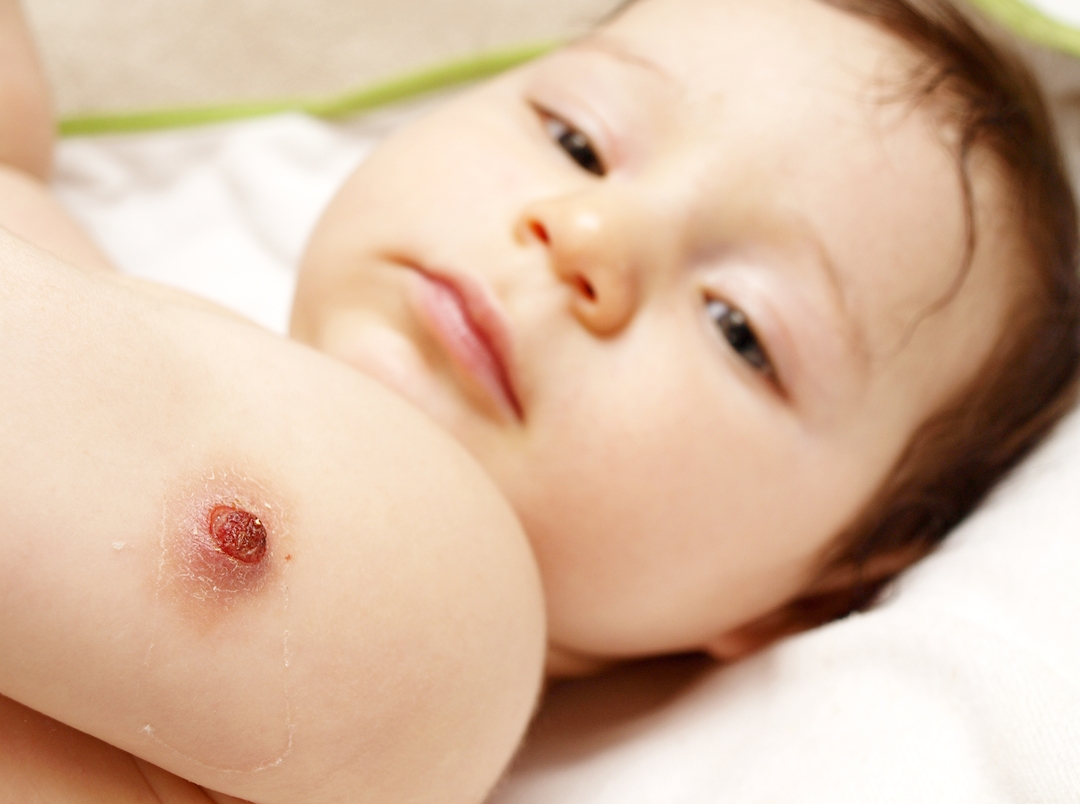 Limited inflammatory process and as a result a 3-10 mm hem in the place of introduction of the BCG vaccine is a normal reaction of the body to a vaccination against tuberculosis.The first signs of this reaction( redness and swelling) appear within 1-1,5 months after the vaccination or within a week after the revaccination.In the place of swelling, the pustule develops over time, after its resolution, a crust and a hem( somewhere in 5-6 months) is formed.Interfere with the local infectious and inflammatory process is impossible - you can not disinfect, bandage, open, rend the wound.
Limited inflammatory process and as a result a 3-10 mm hem in the place of introduction of the BCG vaccine is a normal reaction of the body to a vaccination against tuberculosis.The first signs of this reaction( redness and swelling) appear within 1-1,5 months after the vaccination or within a week after the revaccination.In the place of swelling, the pustule develops over time, after its resolution, a crust and a hem( somewhere in 5-6 months) is formed.Interfere with the local infectious and inflammatory process is impossible - you can not disinfect, bandage, open, rend the wound.
The situation is much worse with the absence of a hem after the introduction of BCG.This situation requires the consultation of a pediatric phthisiatrician, because it indirectly indicates that the child's immunity has not been formed.
Complications after BCG
After the BCG vaccination, the following complications may develop:
- Lymphadenitis( inflammation) of the axillary lymph nodes, this condition is also called BCG.
- Cold abscess - a cavity larger than 1 cm, filled with pus and mycobacteria, at the site of administration of the vaccine.
- Keloid scars.
- Inflammation of the humerus.
The development of these complications in most cases is associated with a violation of the rules for the introduction of the vaccine.A child with abnormal reaction to BCG is taken under the supervision of phthisiatricians and treated with anti-tuberculosis drugs.In the future, such children are not revaccinated from tuberculosis.
Consequences of the rejection of BCG
Refusing parents to vaccinate BCG to their baby in countries with a high incidence of tuberculosis and the inability to isolate themselves from contact with sick people expose the child to a high risk of infection with a tubercle bacillus and the development of severe disease.
This can be confirmed by statistics:
- Annually in Russia, about 60,000 cases of newly diagnosed tuberculosis are registered, of which more than 2,000 cases occur in children under 14 years of age.
- Data on tuberculosis of the year 2015 were no exception.For 9 months of the current year, the active form of the disease was diagnosed for the first time in 57,835 people, including 2,126 children.
- Among all those who fell ill in 2015, more than 23,000 patients have bacillary tuberculosis, that is, infectious.
All these people, as well as those who do not receive medical treatment or seek medical help in the presence of suspicious symptoms( chronic cough, hemoptysis) are potentially dangerous to others, especially for young children.
Mantoux test

Mantoux test( tuberculin diagnostics) is a diagnostic test for the presence of a tubercle bacillus in the human body.At its core, this test is a specific skin allergic reaction to the introduction of an allergen( tuberculin) into the body.
Vaccination Mantoux test is not and does not protect against tuberculosis. The main objectives of its implementation are the following :
- Timely detection of tuberculosis in children.
- Identify children who need to be vaccinated or revaccinated for tuberculosis infection.
Tuberculosis diagnosis is performed annually for all infants over 12 months of .Put Mantoux test intradermally in the forearm with a special syringe with tuberculin( a preparation containing individual protein particles of mycobacteria).The site of the injection can not be scratched, rubbed, damped, treated with antiseptics, sealed and bandaged.The result of the sample is removed after 72 hours.
Important: , using Mantoux test alone, to determine that a person is really infected and the more sick with tuberculosis it is impossible.This is only an indicative test, which in case of a positive result requires further examination of the patient and disproving the connection with a recent BCG vaccination or allergy.
To exclude the effect of tuberculin diagnostics on vaccination, an alternative to the Mantoux-Diaskintest trial was created in Russia.This test allows to detect the presence in the body of virulent strains of mycobacteria, which cause tuberculosis.Prevention and diagnosis of this pathology should be improved every year, so soon the Ministry of Health plans to use Diaskintest for a mass examination of children along with the Mantoux test.
Contraindications to tuberculin diagnostics :
- skin diseases;
- allergic conditions;
- acute infectious diseases;
- acute chronic diseases;
- quarantine in a children's institution that the patient visits.
After recovery or improvement of the condition of the child should pass at least a month, only then you can put the Mantoux test.In addition, it is impossible to carry out tuberculin diagnostics after vaccination( the interval should not be less than a month).
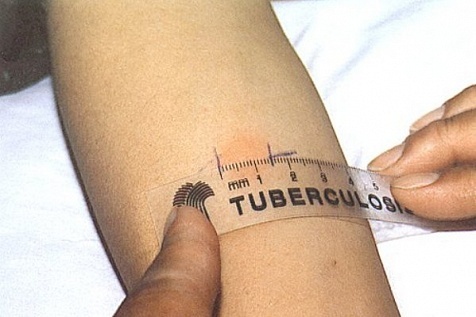
Assay Mantoux: decoding
Evaluate the mantue test for the size of the papule-seal that formed at the site of the injection.
 Reaction options:
Reaction options:
- negative - there is no trace on the skin at all or only a trace from the injection is visible;
- questionable - papule 2-4 mm or only hyperemia;
- positive - papule with a diameter of 5 to 16 mm;
- Hyperergic - seal more than 17 mm.
Normally, the first Mantoux samples in vaccinated children should be positive, and then the reaction may become questionable or negative, which indicates that the baby needs to be revaccinated, as the level of his antituberculous antibodies has dropped.In favor of the probable infection with tuberculosis the following signs testify:
- "turn" of tuberculin test( transition of negative result to positive);
- increasing the size of the papule by 6 mm or more in comparison with the previous positive result;
- Hyperergic reaction;
- positive response with a result of 12 mm, lasting more than 3 years.
Often there are also the so-called false positive reactions , in which there is no mycobacteria in the body of the patient, but the Mantoux test is positive.The cause of this may be an allergic reaction, for example, if the child is prone to allergic manifestations, or a recent infectious disease.
What if the Mantoux test is positive?
All children suspected of being infected with tuberculosis are referred to a TB clinic for children who carefully examines data on vaccinations, revaccinations from tuberculosis, Mantoux test results and, if necessary, gives directions for studies: chest X-ray, sputum examination, blood tests( bloodOn tuberculosis is investigated by a method of PTSR and IFA).In addition, a survey of family members of the child is conducted to identify possible contacts with tuberculosis infection.Subsequently, children with newly diagnosed infection are followed up, and if there are indications, specific chemoprophylaxis is performed.
For more information about TB in children and BCG vaccination, please refer to this video:
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist