Pregnant gestosis: signs of early and late gestosis

Gestosis or late toxicosis are pathological conditions that develop in the third trimester of pregnancy.They are accompanied by violations of hemostasis and the functions of the nervous, endocrine and cardiovascular systems.Preeclampsia and their complications can pose a serious threat to the life of the mother and child.
In 20-30% of pregnant women after 18-20 weeks complications develop.Serious violations primarily affect the circulatory system.Gestosis is usually detected after 26-28 weeks.
Table of contents: Causes and mechanisms Classification Symptoms of gestosis Diagnosis Treatment of gestosis Preventing gestosisThe most severe course of gestosis is noted in the presence of the following concomitant pathologies:
- inflammation of the renal pelvis or glomeruli( pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis);
- biliary dyskinesia;
- hepatitis( including in the anamnesis);
- hypertension;
- endocrine disorders;
- dysmetabolic disorders( impaired lipid metabolism).
Causes and mechanisms
The gestosis is considered to be a polyethological disorder, that is, there is a combined effect of a number of unfavorable factors on the organism of the expectant mother.There is an opinion that a certain role is played by the family predisposition of .One of the important causes of gestosis is the immunological conflict between the fetal and pregnant tissues.According to the cortico-visceral theory, serious pathological changes on the part of the circulatory system develop reflexively against the background of disruption of connections between the cerebral cortex and subcortical structures.
Risk Factors:
- age 35 years and over;
- chronic diseases;
- family predisposition;
- Rhesus-conflict;
- is a multiple pregnancy.
 The general cause of the problems is generalized angiospasm and, as a consequence, a violation of the blood flow of .Spasm of blood vessels causes a significant increase in blood pressure and leads to a decrease in BCC( the volume of circulating blood).The rheological properties of the blood deteriorate( the probability of thrombus formation increases), and with increasing permeability of the vascular walls from the bloodstream in the tissue, the fluid swells, which is manifested by puffiness.
The general cause of the problems is generalized angiospasm and, as a consequence, a violation of the blood flow of .Spasm of blood vessels causes a significant increase in blood pressure and leads to a decrease in BCC( the volume of circulating blood).The rheological properties of the blood deteriorate( the probability of thrombus formation increases), and with increasing permeability of the vascular walls from the bloodstream in the tissue, the fluid swells, which is manifested by puffiness.
With gestosis, microcirculation in the brain suffers;Blood vessels form clots, and at the cellular level dystrophic changes often occur.Increases intracranial pressure, and hemorrhages( point or small-focal) are formed.
In case of violations of hepatic blood flow in the tissues of the body, hemorrhages and necrosis areas are formed.Dysfunction of the kidneys is manifested by proteinuria.In severe situations, the development of acute insufficiency is possible.
Poor blood supply to the placenta causes oxygen starvation of the fetus, which leads to a delay in its development.
Classification
In the clinical course, the following forms of gestosis are distinguished:
- Pre-toxicity;
- hydrocephalus;
- Nephropathy( kidney damage);
- pre-eclampsia;
- eclampsia.
The listed forms can be considered as successively developing stages of a single pathological process.
There are also clean and combined gestosis.Clean are observed in patients who do not have concomitant somatic pathologies.Combined are noted in pregnant women with various ailments in the anamnesis.
Symptoms of preeclampsia

For gestosis characterized by a triad of symptoms including:
- Swelling( dropsy)
- Hypertension
- proteinuria( protein in urine).
In the early stages of gestosis in the body against the background of a decrease in diuresis and fluid retention, there is dropsy.It is characterized by persistent edema of .Initially, they are invisible, and it is possible to suspect their appearance by significantly increasing the weight of the patient( ≥300 g weekly) and negative diuresis( the volume of the drunk liquid is much higher than the volume of urine released).As the pathological process progresses, edema is determined visually.
There are 4 stages of dropsy in late toxicosis:
- Swelling of the feet and ankles.
- Swelling of the legs and abdomen.
- Swelling of the abdomen, extremities and facial area.
- Generalized edema.
When dropsy, patients usually do not make any special complaints.With significant puffiness, a feeling of heaviness in the legs, increased fatigue and a strong thirst.Kidney dysfunction in most cases precedes swelling.
For nephropathy is characterized by hypertension( ≥ 135/85 mm Hg) and the presence of protein in the urine.Proteinuria is a sign of progressive kidney damage.On its background daily diuresis is reduced to 500-600 ml with normal drinking regimen.
In case of late toxicosis, such dangerous complications as placental abruption, bleeding and intrauterine fetal death are possible.They are due not so much to the growth of blood pressure as to its fluctuations.
In order to timely identify hypertension, indicating a violation of kidney function, you need to know the figures of blood pressure before and early pregnancy, that is, the patient's normal figures .The diagnostic criterion of arterial hypertension is an increase in the "upper" pressure by 30 mm Hg.And more, and the "lower" - from 15 mm Hg.and higher.
Important: an increase in diastolic parameters indicates a lack of placental blood flow and fetal hypoxia.
If the nephropathy develops against the background of existing hypertension, heart disease or inflammation of the kidneys( i.e., with combined gestosis), the prognosis worsens.
In pre-eclampsia, clinical manifestations of nephropathy are accompanied by nausea, vomiting, a feeling of heaviness in the occipital region, intense headaches, sleep disturbances, memory impairment, epigastric pain and right hypochondrium and psychoemotional disorders( apathy in particular).
Diagnostic criteria for pre-eclampsia:
- proteinuria ≥ 5 g per day;
- diuresis daily & lt;400 ml;
- AD ≥ 160/110;
- visual impairment;
- nausea;
- vomiting;
- thrombocytopenia;
- deterioration of blood clotting;
- liver dysfunction.
With prolonged course of nephropathy, the development of the most dangerous form of preeclampsia is possible, which can lead to the death of a child and a woman.
Symptomatic of preeclampsia becomes heavier, and convulsive seizures develop, accompanied by loss of consciousness. Seizures, lasting 1-2 minutes, can be triggered by visual and auditory stimuli, psycho-emotional stress or pain.At first, eyelids and mimic muscles twitch, and then the muscles of the whole body.The corners of the mouth drop, fingers involuntarily contract, pupils widen, and eyes roll upward.After about half a minute, pronounced tonic convulsions appear.Jaws of the patient tightly compressed, the head throws back and the backbone curves.Since the muscles of the diaphragm are involved in the process, breathing is disturbed.The skin becomes a bluish shade, and a loss of consciousness occurs against the background of hypoxia.At this stage of the seizure, a cerebral hemorrhage is possible, which in some cases ends fatal.

After another 10-20 seconds, the tonic contractions are replaced by clonic ones, in which the pregnant woman constantly involuntarily moves the limbs, that is, "beats in cramps".Then the intensity of muscular contractions is weakened.By the end of the fit, breathing becomes hoarse, and foam appears from the mouth.
After 30 seconds, breathing returns to normal, the pupils narrow, and the skin becomes a normal shade.Patients do not retain memories of a seizure;After an attack they feel weakness and weakness in the whole body and complain of an intense headache.
Complications of eclampsia include:
- retinal detachment;
- pulmonary edema;
- cerebral edema;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- premature placental abruption;
- hemorrhage in the tissues of the kidneys and( or) the liver);
- coma.
Important: some pregnant women are diagnosed with a very dangerous non-convulsant eclampsia, in which the patient falls into a coma suddenly against a background of a sharp jump in blood pressure.This form of gestosis especially often leads to strokes and death.
Diagnosis
Differential diagnosis of convulsive seizures with eclampsia is carried out with epileptic seizures.Includes anamnestic data, the presence or absence of a characteristic epileptic scream and blood pressure indicators.
To identify the degree of disturbance in late toxicosis, the following studies are needed:
- BP measurement and comparison of the indicators with normal for the patient;
- coagulogram;
- blood test( general and "biochemistry");
- urinalysis;
- assessment of the state of the vessels of the fundus;
- determination of the ratio of the volume of fluid and daily diuresis.
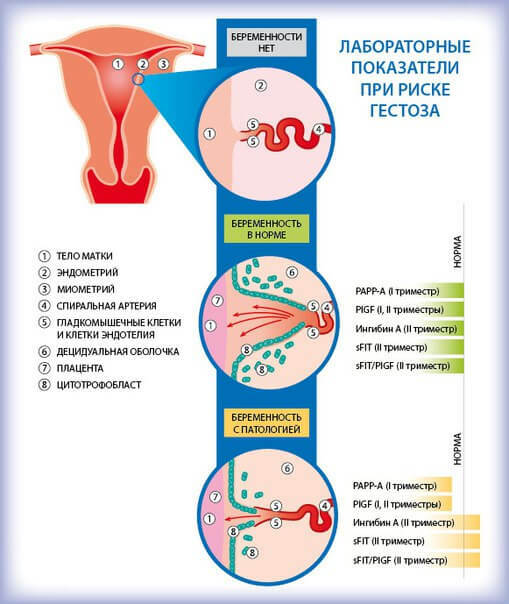
The most informative method for studying placental blood flow is Doppler.The condition of the fetus and the placenta is refined during ultrasound scanning.
Treatment for gestosis
For diagnosed late toxicosis, the pregnant woman is to be placed in a profile hospital with a resuscitation department and a block for preterm infants. Outpatient monitoring is allowed only with the easiest course of gestosis - stage I hydrocele.In severe nephropathy, preeclampsia and eclampsia, the patient is preserved until delivery.
This pathological condition requires correction of vital functions and the most careful management of labor.
The task of physicians is to correct the rheological properties and coagulability of blood, pressure, permeability of vessel walls, water-electrolyte balance, total metabolism and CNS functions of the pregnant woman.
Negative dynamics of disorders requires caesarean section, and in the most severe cases, abortion is indicated for the survival of the patient.
Prevention of gestosis

Measures to prevent gestosis should be taken from the II trimester.These include normalizing the regimen of the day( sleep and rest).A future mother needs a full meal and regular outdoor walks .Salt consumption should be limited, especially in the second half of pregnancy.
Of great importance is the early registration in the women's consultation and the management of pregnancy throughout the term.At each visit of the attending physician, pressure and weight measurements, as well as laboratory urine tests( for early detection of nephropathy) should be performed.
The need for pharmacological agents for the prevention of late toxicosis is determined individually, taking into account the presence of concomitant somatic pathologies.
Vladimir Plisov, doctor, medical reviewer