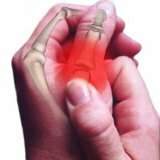
Bunion of knee joint
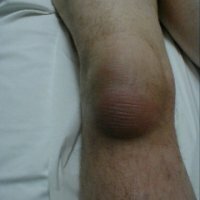
Knee bursitis is an inflammation of the synovial knee bag. A synovial bag or, as it is also called a bursa - a small bag that is filled with a small amount of fluid and is located near the joints, in places where the tendons, skin and muscles are closest to the bones. They help to facilitate the operation of the joint apparatus. Bursa is near large joints since birth, and they can develop throughout life in places of friction or pressure on the joints.
There are three bursas around the knee, and inflammation can form in either of them. Prepathel bursitis may be more common. This is the inflammation of the bursa, which is located above the calyx. This disease can begin its development, if there was some kind of knee injury, perhaps a stroke or a fall on the calyx, the cause could be the wounds that the infection got into.
There is such a bursitis as an infarapatellar or knee jumper. This disease begins when the synovial bag under the calyx is inflamed, which can occur when falling from a height or when landing on straightened legs.
Goose bursitis or Baker cysts is an inflammation on the lower inner part of the knee. Such a disease can often appear in women after forty, who are obese.
Symptoms of
- Increased knee joint, which is usually accompanied by pain. With all this, the movements remain the same.
- Skin over the joint flushed, maybe even a local increase in temperature.
- Joint pain and movement restrictions.
- If bursitis is of an infectious nature, there may be an increased body temperature, even chills and other signs of intoxication.
- If bursitis develops against a background of gout, osteoarthritis, etc., these diseases become aggravated and the symptoms increase.
How to treat bursitis of the knee joints?
Aseptic bursitis, as a rule, can be treated with conservative methods:
- Ensure peace and leg is placed higher, to ensure a decrease in blood flow in the painful knee and thereby reduce swelling.
- Make cooling compresses, but several times a day and no more than twenty minutes.
- If the inflammation is not pronounced, provide a small load on the knee. Pull the ankle back until you feel a slight pull. Do this exercise four or five times several times a day, which will increase the flow of oxygen to the tissues and accelerate regeneration.
- If the pain is severe, then prescribe pain medication, antibiotics and corticosteroid injections.
- Antibiotics are prescribed if a diagnosis of infectious bursitis is established, but only on the basis of signs confirmed by laboratory tests.
- There is also a method of aspiration of excess fluid from the bursa, this procedure is done in order to reduce the volume and tension on the shell, which greatly facilitates the movement of the joint, reduce pain and inflammation. The resulting liquid is sent to the laboratory in order to detect the presence of possible bacteria. Then, on the basis of the results of the tests, the treatment is prescribed, antibiotics are selected.
- But Baker's cysts in children can be resolved without any intervention.
- If bursitis is chronic and infectious, antibiotic treatment may be ineffective, then surgical intervention is necessary.
To heal bursitis, complete rest for the joint is necessary, as well as its protection. If you treat this disease correctly, you can overcome it in a week. But remember, if you will reap joint injuries, bursitis can develop into a chronic disease, and this form of the disease is treated much more difficultly, bursitis will complicate movements that will be accompanied by pain.
There is still purulent bursitis, and if it progresses, then the synovial bag is opened to remove pus. This entails a long process of wound healing.
There are also popular ways to cure bursitis. There are many different recipes, compresses and tinctures. If there is a suspicion of purulent or infectious bursitis, then self-medication is contraindicated! Remember that self-medication can damage your health! It is better to see a doctor right away. Watch your health!
Preventive actions to prevent recurrence of the disease
- Treating bursitis and stopping the inflammation, complete recovery of joint movement
- Strengthen leg muscles
- Do not subcool the knee joints, maintain adequate blood supply.
- Constantly use elastic knee pads, they will significantly reduce the load on the joints of
. If you do not have any signs of infectious bursitis, the disease can be cured at home. But if the symptoms increase - consult a doctor.