Inflammatory diseases of the prostate gland of seminal vesicles
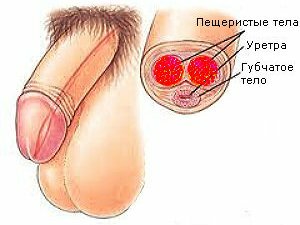
The prostate gland is located under the bladder. An organ that, like a sleeve, surrounds the upper part of the urethra tube, through which the urine flows out of the bladder. The posterior surface of this gland borders on the rectum wall. This proximity makes the prostate gland reachable for rectal palpation. The male gland has a secretory apparatus, which is responsible for the secretion. Inflammatory diseases of the prostate gland of seminal vesicles, unfortunately, in our time is common.
The most common diseases of the prostate gland.
- prostatitis;
- benign hyperplasia;
is a tumor( cancer).
What causes inflammatory diseases of the prostate gland?
In general, diseases of the prostate gland of seminal vesicles entail urinary disorders, in particular:
- difficulties in the beginning of urination;
- frequent urination;
- incontinence;
- urge to urinate at night;
is the urge to urinate, even if the bladder is not full;
-bollevye sensations;
- urine stream is weak;
- blood is found in urine;
- retention of urine;
- pain in the bones - a sharp, piercing pain in the lower back, which in most cases is the initial symptom of prostate cancer. Also described symptom is about metastases, which can appear on other organs.
- a rise in temperature and a sensation of pain in the area of the projection of the prostate gland all these symptoms are accompanied by prostatitis.
Symptoms manifest themselves depending on the stage, severity of the disease. Symptoms of acute prostatitis manifest suddenly. And the symptoms that characterize the enlargement of the prostate develop, at a time when the gland becomes bigger and starts to squeeze the urethra. Benign prostatic hyperplasia.
( DHP) The increase in the size of the prostate gland that appears in a strong half of humanity after forty or fifty years is completely normal and this phenomenon is caused by a certain hormonal restructuring of the body. At seventy years, the majority of the male population has different levels of male hyperplasia. The normal physiological state of the prostate gland is characteristic of this segment of life.
It should be noted that BPH entails narrowing of the urethra and does not damage the outflow of urine. It follows that treatment in this case is not required. For prevention, you should periodically visit a doctor who will perform a finger examination, appoint ultrasound and tests.
BPH should be treated if there are signs of an outflow of urine. The initial stage of constriction requires the use of medication. With a strong narrowing of the urethra, the male gland requires surgical intervention.
Prostate cancer.
This disease is formed from glandular cells. Malignant tumor in most cases occurs in the male population of middle and old age.
If you start a disease, the tumor goes outside the prostate and can penetrate other organs and tissues. The main and most negative feature of malignant tumors is metastasis. Prostate cancer is formed slowly and is rarely aggressive.
Consider risk factors:
I factor is the age. It is mainly found in the strong half of humanity older than 65 years;
II is a genetic factor. Genetic basis is almost 9% of those affected by this cancer;
III is a race. The highest risk of oncology is observed in black men.
IV - food. Red meat, dairy products, animal fats - all this increases the risk of disease. The formation of cancer is deterred by vegetables and fresh fruit.
V- external environment. Some types of industrial chemicals increase the risk of the disease. Also at risk are people working in the nuclear industry.
Men who experience damage to the function of the testicles, and also after they are removed before puberty, are the least at risk.
Forms of prostatitis.
- Acute prostatitis is a serious disease. It is formed after the infection in the prostate gland. It is characterized by its edema and development of pustules in the prostate tissue. Bacteria come from the urethra. The cause of the disease is also chlamydia and E. coli. The main danger of acute prostatitis is a high degree of progression. There is also a possibility of complications: paraproctitis, proctitis, cystitis, urethritis and prostatic abscess.
- Chronic prostatitis. The main reasons - promiscuous sex life, sedentary lifestyle, uncontrolled use of medicines, bacteria. This form of prostatitis proceeds imperceptibly. It is of great importance for the diagnosis to collect information about the patient's condition and rectal examination. Enlarged prostate helps to diagnose BPH.Another major symptom of prostatitis is painful sensations during palpation.
Diagnosis of prostatitis.
- blood test;
- indicators of kidney function;
- culture and microscopy of urine;
- X-ray examination of urinary tract with contrast;
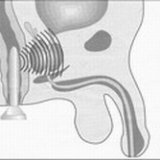
transrectal ultrasound - a small sensor is inserted into the rectum, which allows you to see the size of the prostate on the screen.
- biopsy;
- radioisotope examination of bones - helps to detect secondary foci of cancer cells.
Antibiotics fight with acute prostatitis. Chronic prostatitis is difficult to treat.
Methods of treatment of accidents.
- Medications that reduce the prostate are sometimes an alternative to surgical intervention;
- endoscope is carried up the urethra, excising surplus prostate tissue( transurethral resection of the prostate).Side effect: after a few years there is a chance of a second operation;
- radiofrequency ablation( RFA) introduces a small tube that provides urethral patency;
- cutting tissue with microwaves or a laser.
Cancer treatment depends on the stage of tumor development:
- removal of the prostate, seminal vesicles and vas deferens);
- radiotherapy.
If cancer metastasizes to other organs, progression is slowed by blocking growth stimulation.