Cruson Syndrome
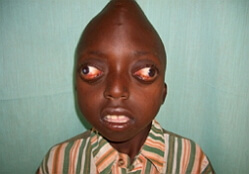 Cruson Syndrome is a rare genetic anomaly that has the second name of craniofacial dysostosis and is characterized by various deformities of the facial and brain parts of the skull. These deformations can be both congenital, and develop during the first year of life. The incidence of this syndrome is 1: 10,000 children.
Cruson Syndrome is a rare genetic anomaly that has the second name of craniofacial dysostosis and is characterized by various deformities of the facial and brain parts of the skull. These deformations can be both congenital, and develop during the first year of life. The incidence of this syndrome is 1: 10,000 children.
Cruson syndrome is characterized by hypertelorism, exophthalmia, hypoplasia of the middle part of the face with insignificant mandibular pragmatism and premature synostosis of the skull.
Cruson Syndrome
Symptoms Clinical changes are limited to the face and skull. Due to vertical hypoplasia of the middle third of the face, the nose may have an unusual shape. Often observed protruding tongue, short upper lip, lowered lower lip, relative lower mandibular pragmatism. A permanent feature of Cruson's syndrome is incomplete closure of the teeth.
Changes in the bony system .The shape of the skull deformity directly depends on which seams were involved in the pathological process. There can be observed: trigonecephaly, scaphocephaly, brachycephaly, anomaly Kleeblattschadel( rarely).When palpation, the flattened edges of the joints feel very well. Near the junction of the rifle and coronal sutures of the skull, exostoses are often observed. The onset of premature craniosynostosis usually occurs in the first year of life and most often ends at the age of three. Sometimes synostosis may not manifest until ten years.
Changes in vision from the .Exophthalmic is always secondary. Its development is due to a decrease in the depth of the orbits. Also, with Cruson syndrome, nystagmus and divergent strabismus are noted. Hypertelorism is a constant feature of this disease. The defeat of the optic nerve is observed in 80% of patients with Cruson syndrome. In some cases, there may be ectopia of the pupil, columboma of the iris, ectopia of the lens, megalocornea, spontaneous dislocation of the eyeball.
Hearing change .In 30% of patients with Cruson syndrome, deafness, usually of a conductive type, is observed. After postmortem or surgical examination in an oval window, fixation of the stapes and deformation of the auditory ossicles are detected. There is an obvious deformation of the internal auditory canal, a lack of recovery and a decrease in bone conduction. In addition, there is a conductive or mixed deafness and atresia of the external auditory canal.
No changes from the vestibular system are detected.
Diagnosis and laboratory data for Cruson syndrome
The X-ray diffraction pattern most commonly shows the lambdoid, sagittal and coronary sutures covered by premature synostosis. In addition, such radiographic findings as small paranasal sinuses, widening of the pituitary gland, basilar kyphosis, flattening of the orbit and finger impressions can be observed. Tomographic examination clearly indicates the deformation of the internal auditory canal.
A tomogram of the temporal bone reveals an external rotation of the stony section of the pyramid secondary to the dysplasia of the base of the skull. As a consequence, the auditory canals were oblique, the direction of the facial nerve was incorrect and hyperostoses were observed. And the primary changes should include the anomalies of auditory ossicles, the closure of the oval window.
Tomography of the temporal bone reveals the absence of a tympanic cavity, atresia or stenosis of the external auditory canal, narrowing and curving air spaces of the mastoid process and middle ear, deformity of the stapes, ankylosis of the malleus with the outer wall of the upper part of the tympanum. In addition, the development of the periosteal part of the labyrinth is underdeveloped.
Differential diagnosis is performed with diseases such as Sethre-Chotzen syndrome, Pfeiffer syndrome and Apera syndrome.
Cruson Syndrome Treatment
As such, treatment for Cruson Syndrome is impossible. It is only possible to carry out a functional and / or cosmetic surgical correction consisting in the partial removal of prematurely synostostic sutures, as well as preventing the dislocation of the eyeball by surgically creating blepharophimosis. The French surgeon P. Tessier described in detail a radical surgical operation, which will be able to correct the deformities of the face in Cruson syndrome as much as possible.
The forecast of Cruson syndrome is extremely disappointing. With age, there is a friendly, alternating or divergent strabismus. Binocular vision becomes impossible. Often there is an atrophy of the optic nerve, leading to an absolute loss of vision. In some cases, complete loss of one / both eyeballs is possible, which occurs due to the progressive flattening of the orbits. In the region of bregma, the formation of exostoses is observed, due to premature synostosis of the joints. With age, with normal development of the lower jaw, hypoplasia of the middle part of the face becomes more pronounced.