Renal failure: symptoms and their treatment
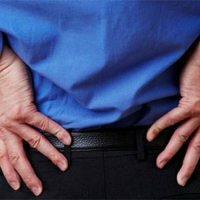
Renal failure syndrome is a disease that develops as a result of severe renal impairment. This leads to a disorder of homeostasis, which is characterized by azotemia, a violation of the acid-alkaline state of the body and water-electrolyte composition. In acute kidney failure, an acute, most commonly reversible kidney disease can occur suddenly. The development of chronic renal failure is characterized by a gradual progressive loss of functioning parenchyma.
Causes of renal failure
The causes of acute renal failure are manifold. The disease appears due to the violation of renal hemodynamics, infectious diseases, acute kidney disease, obstruction of the urinary tract and arterial conditions with trauma or removal of a single kidney.
In most cases, ARI is caused by disorders of renal hemodynamics and exogenous intoxications. The main mechanism of damage in the kidney in these two forms of the disease can be an anoxia of the renal tubules. Also, with these forms of the syndrome, necrosis of the tubular epithelium, edema and cellular infiltration in the interstitial tissue, various kinds of damage to the capillaries of the kidneys develop. In these cases, necrosis develops. These injuries can be reversible if the timely treatment courses are not started.
Symptoms of the disease and symptoms of renal failure
Hemolysis, acute poisoning are phenomena in which renal insufficiency is observed. Symptoms and their treatment are determined by the attending physician, and a course of therapy is prescribed. In the initial period of the disease, the main symptoms are the characteristic symptoms caused by pain, anaphylactic or bacterial shock; already in the first day, the process of diuresis falls, oliguria-anuria develops, homeostasis is disrupted. In the plasma layer, along with an increase in the level of creatinine, expressed residual nitrogen, urea, sulfates, phosphates, potassium, magnesium. Also noticeable decrease in the levels of sodium, calcium and chlorine.
How does renal failure manifest itself? Symptoms are detected by the growth of azotemia, hyperhydration, acidosis and electrolyte disorders, muscle twitching, blocking of consciousness, drowsiness, and dyspnea due to pulmonary edema also increase. The early stages of edema are determined radiologically. In addition, tachycardia, dull tones, widening of the heart borders, pericardial friction noise, systolic murmur at the apex are characteristic. In rare cases, there is a risk of cardiac arrest in conditions of heart block or ventricular fibrillation. Anemia persists throughout the time of the disease, leukocytosis is characteristic of oliguria-anuria. Frequent symptoms of acute uremia - increased liver, abdominal pain. In acute renal failure, death occurs from uremic coma or disorders of hypodynamia and sepsis. From the very beginning, the phenomenon of hypo-isostenuria is found.
Diagnoses are made on the basis of a sharp drop in diuresis due to one of the above reasons, typical disturbances of homeostasis or a rise in azotemia. Differentiation from exacerbations of chronic renal failure and its terminal stage is carried out by anamnesis, a decrease in the size of the kidneys in conditions of chronic glomerulonephritis and pyelonephritis. Also a chronic urological disease is detected. Acute glomerulonephritis causes the appearance of high proteinuria.
Diagnosis and treatment of of renal failure
Renal failure with the first symptoms requires the use of pathogenetic therapy. The nature of this therapy is determined by the causes that caused acute renal failure. First of all it is necessary to conduct plasmapheresis. The severity of the patient's condition and degree of intoxication are the determining factors of the volume of the applied procedure of plasmapheresis. Carry out replacement of the removed plasma with freshly frozen with the use of albumin solution. Hemodynamic disorders are characterized by anti-shock measures, replenishment of blood loss through transfusion of blood components, blood substitutes, intravenous drip of prednisolone. Continuing hypotension after the procedure for replenishment of blood loss is eliminated by intravenous drip of norepinephrine solution in isotonic sodium chloride solution. Along with anti-shock therapy for acute poisoning, measures are taken to remove the poison from the body.
After all the procedures begin the therapy of homeostasis regulation. Diets that limit the intake of potassium and protein must be high in calories due to a sufficient amount of fats and carbohydrates, if they are present in the body, acute renal failure decreases. Treatment begins with the introduction of a fluid that in quantity should exceed the diuresis and volume of water lost due to vomiting and diarrhea, not more than five hundred milliliters. The same volume includes a fifth of the glucose solution with insulin ED.With hyperkalemia, a solution of potassium gluconate is injected intravenously and a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate is added dropwise. In large quantities, a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate can be administered only after determining the degree of acidosis and under the control of blood pH.
Intramuscularly, the procedure of administering testosterone propionate 50-100 mg daily or retabolil once a week is done. The doctor prescribes the necessary antibiotics, reducing their dose 2-3 times because of the limitation of the secretions to the kidneys. Neomycin, monomycin, streptomycin in anuric conditions may have very pronounced properties of ototoxia, therefore, in acute renal failure, it is not recommended to use them. Oliguria and the increase in symptoms determine whether it is required to transfer a patient to the hemodialysis department for extracorporeal cleansing using an artificial kidney, peritoneal dialysis.
Indications for hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis are determined by the level of urea in the plasma, decompensated by metabolic acidosis and clinical picture of acute uraemia. Contraindications to dialysis are hemorrhages in the brain, intestinal and gastric bleeding, severe hemodynamic disorders.