Tuberculosis of the kidneys
 Renal tuberculosis is a secondary manifestation of tuberculosis infection in the body, which is a specific infectious and inflammatory process. It is the tuberculosis of the urino-genital organs that ranks first among extrapulmonary locations of the tubercle bacillus.
Renal tuberculosis is a secondary manifestation of tuberculosis infection in the body, which is a specific infectious and inflammatory process. It is the tuberculosis of the urino-genital organs that ranks first among extrapulmonary locations of the tubercle bacillus.
Renal tuberculosis is often diagnosed today in the state of severe cavernous forms, when anti-TB drugs are ineffective and surgical interventions, often organ-carrying, are the way out.
The following categories of people fall into the risk group:
- patients with chronic nonspecific diseases of the genito-urinary organs;
- persons diagnosed with tuberculosis of a different location;
- persons who have contact with tuberculosis;
- children and adolescents who have established a turn of tuberculin samples and / or an increase in susceptibility to tuberculin.
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis
 Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis depend on the type of development of the disease and on the activity of the infectious process. Symptoms of tuberculosis are also determined by the age and individual characteristics of the patient's body. These constitutional features determine the susceptibility of the patient's body to infection, determine the types and rates of development of the infectious process.
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis depend on the type of development of the disease and on the activity of the infectious process. Symptoms of tuberculosis are also determined by the age and individual characteristics of the patient's body. These constitutional features determine the susceptibility of the patient's body to infection, determine the types and rates of development of the infectious process.
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis in adults
With kidney tuberculosis, symptoms are usually similar to manifestations of other kidney diseases. The patient may experience weakness, lethargy, fast fatigue, fever( up to 37.5 ° C), dull and vague pain in the lumbar region, in some cases - headache, progressive weight loss.
Sometimes there is a symptom of kidney tuberculosis, like blood in the urine - a microhematuria, in the urine tests protein-proteinuria, and leukocytes are detected. The reaction of urine, as a rule, is acidic. Acid urine with a significant content of pus, not decomposing even with a long standing - a characteristic symptom of tuberculosis of the kidneys. It is often difficult to find tubercle bacilli in the urine.
Patients often have pallor and puffiness of face and eyelids, legs, sometimes arms, lower back can also swell.
Fluid accumulation is possible in the pleural and abdominal cavities. Sometimes due to swelling, blood pressure may increase, the pain in the head may be intense, but short-term, possibly dizziness and nausea. Insufficient blood circulation can lead to damage to the heart muscle and liver. The contractions of the heart slow down.
In the early stage of kidney tuberculosis, due to edema, the release of daily urine decreases, then the amount of urine released per day exceeds the norm. Patients complain of frequent nighttime urination. This is due to a reflex from the kidneys to the bladder and tuberculous inflammation of the bladder, followed by a decrease in its capacity.
The spread of the inflammatory process on the urinary tract is indicated by intensifying pain in the lumbar region and painful dysuria - frequent urination.
Symptoms of kidney tuberculosis in children
Children with kidney tuberculosis rarely develop tuberculosis. The first symptoms that are observed in this disease are clouding of urine and the presence of pus in it. Subsequently, deterioration of the general condition is noted. The child can notice an unhealthy paleness, frequent urination, weight loss.
An important reason to suspect a kid's development of kidney tuberculosis is the sudden incontinence of urine. In children with tuberculosis of the kidneys, the bladder is often affected, so there are painful sensations when urinating, often of a coelike character.
If palpation of the kidney is painful, but it is not a source of pain on its own.
When analyzing the urine of a sick child, the presence of fresh red blood cells, small albuminuria, and leukocytosis are revealed. The presence of Koch bacilli in the urine is the final confirmation of the disease.
Diagnosis of kidney tuberculosis
 The diagnosis of tuberculosis of the kidneys is complex and depends more on the experience of a specialist. In most cases, the disease can be detected in an already neglected stage, when the organ practically lost its function. Let's look at the methods used by specialists in the diagnosis of kidney tuberculosis.
The diagnosis of tuberculosis of the kidneys is complex and depends more on the experience of a specialist. In most cases, the disease can be detected in an already neglected stage, when the organ practically lost its function. Let's look at the methods used by specialists in the diagnosis of kidney tuberculosis.
Initial inspection of
The diagnosis of the kidney begins with the clarification of patient complaints and anamnesis. When interviewing a patient, the doctor draws attention to the presence in the patient's anamnesis of pulmonary tuberculosis or other organs, long-term contacts with patients with tuberculosis.
When examining a patient, a specialist with palpation diagnoses the external genitalia, in men - the prostate gland and seminal vesicles. This is a very important method of diagnosing kidney tuberculosis, which allows most men suffering from this disease to identify it at an early stage.
Laboratory Diagnostics
Laboratory diagnosis of kidney tuberculosis includes bacterioscopy( detection of mycobacterium tuberculosis in microscopy), biological tests and bacteriological examination.
In women, a urine sampling is performed by a catheter. Men take two portions of urine in two different vessels. If in the first portion of urine an increased amount of white blood cells is found, then there is an inflammatory process in the urethra, if in the second portion - disease of the prostate gland, as well as seminal vesicles. But the detection of pyuria in two portions of urine indicates a pathological process in the kidneys.
Also, a general urine test reveals its acid reaction, which is characteristic of tuberculous kidney disease. In addition, if the specific gravity of urine decreases monotonically, this also indicates tuberculosis of the kidneys.
Tuberculin Diagnosis
The patient is injected subcutaneously with tuberculin, followed by an additional urine test. To increase the effectiveness of laboratory diagnostic methods, tuberculin provocative tests are performed - they cause an aggravation of the process, thereby increasing the number of bacteria in the urine.
Instrumental diagnostic methods
Instrumental diagnostic methods use renal radiography, excretory urography, angiography, radioisotope techniques, ultrasound, computer and magnetic resonance imaging.
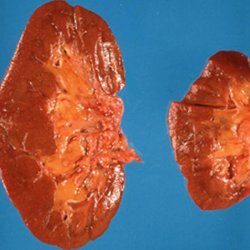
The study usually begins with an overview of the kidney X-ray. Thanks to this method of diagnosis, it is possible to identify nephrolithiasis. The nature of the kidney contours helps to assess their magnitude and the state of the pericobacterial fatty tissue.
Further excretory urography is performed, for which the normal state of kidney function is required.
Angiography and radioisotope methods are also used to detect kidney tuberculosis.
Ultrasound examination is an auxiliary diagnostic method that allows to assess the localization and extent of kidney damage.
Computer and magnetic resonance imaging of the kidneys can identify lesions and assess the state of regional lymph nodes.
Treatment of kidney tuberculosis
 The process of treating kidney tuberculosis, namely how the therapy will be performed, depends on the stage of this pathology. Conservative therapy is used at all stages, while surgical treatment is only in stages III and IV.
The process of treating kidney tuberculosis, namely how the therapy will be performed, depends on the stage of this pathology. Conservative therapy is used at all stages, while surgical treatment is only in stages III and IV.
Principles of conservative treatment:
- Simultaneous treatment with drugs of three groups: antibiotic, drugs of PASK and GINC groups.
- The duration of therapy is from 9 to 12 months.
Today, medical practice uses anti-tuberculosis drugs based on rifampicin, isoniazid, streptomycin, ethambutol, protionamide, PASC, cycloserine. Many anti-TB drugs have serious side effects, so their dosage, combination and duration of reception vary greatly from case to case, and largely depend on the patient's individual sensitivity, kidney condition, weight and age.
Under the influence of some anti-tuberculosis drugs and, in the first place, streptomycin, there is a rough scarring of the foci of tuberculosis in the walls of the calyx, pelvis, bladder, ureter. This greatly affects the condition of the kidneys. Cicatricial stenosis of the ureter causes hydronephrosis transformation. Previously, to prevent this complication, the patient was assigned biological stimulants( vitreous, aloe, etc.), adrenal hormones, and physiotherapy procedures. Recently, the internal catheter "stent" is used to prevent the appearance of scarring of the ureter, which provides an outflow of urine from the kidney.
The drug treatment of tuberculosis is always combined with other important medical conditions, for example, day and nutrition regimen, diet, climatotherapy, sanatorium treatment.
The control of the efficacy of the prescribed treatment is carried out regularly, mainly based on the results of a general urinalysis, bacteriological examination of urine, X-ray studies, for example, excretory urography. The criterion for recovering from tuberculosis and successful treatment of the urinary tract is the absence during three years of any changes in the composition of urine and disorders recognized in urograms.
As the possibilities of specific chemotherapy against tuberculosis are constantly increasing, indications and criteria for the surgical treatment of urinary tract tuberculosis and kidneys are also changing. Today, not only organ-carrying operations are possible, but also organ-preserving. Although earlier, when streptomycin was not available to doctors, it threatened the generalization of tuberculosis infection. Nephrectomy is gradually being replaced with kidney resection, cavernotomy and cavernectomy.
In order to make possible the successful conservative therapy of nephrotuberculosis, an important condition must be observed, namely, a good passage of the urine of the affected kidney. In the case where there is no possibility to restore the passage of urine through internal drainage or the volume of lesions of the urinary tract is very large, they perform a plastic reconstructive operation. Single cicatricial narrowing of the ureter involves resection of the affected area and an ureter anastomosis end to end. Multiple and extended strictures of the ureter may lead to the need to replace the sites with the tissues of the small intestine. Pelvic lesions of the ureter involve the implementation of ureterocystoanastomosis. In the case of a large distance from the bladder to the point of narrowing of the ureter, a Boari operation is performed. In some cases, transcutaneous puncture nephrostomy is performed before the plastic surgery on the ureter first stage of treatment to improve the results of chemotherapy, functional and anatomical conditions of the kidney and urinary diversion. When tuberculous microcystis( shrinkage of the bladder) often make the plastic of the bladder parts of the thick or small intestine. This operation increases the volume of the bladder, eliminates the strangulation, improves the outflow of urine from the upper urinary tract and the kidneys themselves.
If tuberculosis is detected in stage IV, a nephrectomy is performed.