Stones in the bladder
The presence of stones in the bladder is a fairly widespread disease that can occur in both sexes, both in the elderly and in childhood. Stones can form either in the kidneys, and then migrate into the bladder, or in the bladder itself.
To diagnose the presence of stones in the bladder, specialized equipment is needed. However, this disease is characterized by the appearance of pain over the pubis and in the lower abdomen. Pain can be given in the inner genitals, in the perineum. Most often, the pain appears during movements, and is greatly intensified during urination.
Frequent trips to the toilet can indicate that there are concrements in the bladder. In this case, the urge to urinate in the patient can be caused even by such insignificant influences as a trip on the car, fast walking, physical activity. Another sign of the appearance of stones in the bladder is the pathology of urination of a certain type, the so-called "pawning" symptom( a symptom of jet interruption).In this case, the urine stream is often interrupted before the end of the process of urination, and the process can be completed only by changing the position of the trunk every time.
If the patient lingers with treatment, the disease can go so far that the process of urination will be possible only if the patient is lying down;So the process of treatment should begin, the earlier, the better.
The main symptoms of the appearance of stones in the bladder
In some cases, it may be that there are no external signs at all, which leads to the need for detailed diagnosis of the presence of stones, which requires the use of special equipment.
In the vast majority of cases, patients who have stones complain of frequent and violent attacks of desire to go to the toilet, which can be accompanied by pain, the presence of blood in the urine, pain in the pubic region and lower abdomen, the urge to urinate, which causePatient waking up at night.
A situation is also common where the process of urination suddenly aborts and there is pain in the lower back, genitals, abdomen, sometimes in the hips. Also, attacks of dull or acute pain in these areas are manifested when a person changes sharply the position of the body or goes in for sports.
In some cases priapism( painful erection) and urinary incontinence in children may occur.
Methods for diagnosing the presence of stones in the bladder
Key:
- Ultrasonic examination of the bladder area;
- Urinary bladder examination with a cystoscope;
- General analysis of urine.
Additional:
- X-ray panoramic image of the area of the bladder;
- Magnetic resonance imaging examination;
- Screening by computed tomography;
- Rg examination by contrast agent.
Methods of treatment
Two methods of treatment of this disease are mainly used: lithotomy( stone-cutting) and lithotripsy( stone crushing).
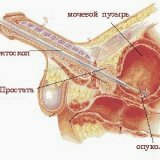
Contraindications to lithotripsy are acute cystitis, small capacity of the bladder, stricture of the urethra, prostate adenoma, paracystitis, fixed stones.
For all these cases, when there are contraindications to lithotripsy, as well as in young children, a lithotomy is performed - the suprapubic high bladder section.
Relapses of this disease are extremely rare if the cause of its occurrence has been eliminated. Prevention of stone formation is based on the removal of all factors that can disrupt the yield of urine and the therapy of inflammatory processes.
In the presence of stones in the bladder, the prognosis for recovery is most dependent on the fact that a disease that violated the urine output from the bladder caused stone formation( prostate tumor, urethral stricture, etc.).If the cause of the appearance of stones can be successfully localized and eliminated, the prognosis is usually favorable, otherwise the probability of recurrence of stone formation is very high.