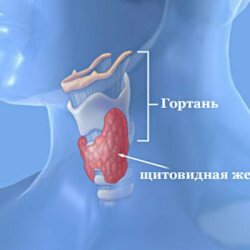
Brief characteristics of the main diseases of the thyroid gland
 The term "autoimmune diseases" means "attacking oneself".What does it mean? To fight against bacteria and viruses penetrating from the outside into our body, the latter created its own army consisting of lymphocytes that recognize and destroy the antigen by themselves or with the help of specific( produced by lymphocytes) antibodies. Similarly, protection is also provided against own cells that have changed their normal genetic characteristics( eg, tumor cells).
The term "autoimmune diseases" means "attacking oneself".What does it mean? To fight against bacteria and viruses penetrating from the outside into our body, the latter created its own army consisting of lymphocytes that recognize and destroy the antigen by themselves or with the help of specific( produced by lymphocytes) antibodies. Similarly, protection is also provided against own cells that have changed their normal genetic characteristics( eg, tumor cells).
At occurrence of autoimmune disturbances the organism for not clear reasons ceases to distinguish own normal fabrics from alien. He begins to produce antibodies that attack his own organs. These antibodies are called autoantibodies. This is the reason for the occurrence of two, widespread, thyroid diseases:
- diffuse toxic goiter( synonyms - Graves disease, Basedov, Parry, Flejani).Many synonyms are explained by the fact that the British and Germans, French and Italians believe that it was their scientist who was the first to describe this disease;
- autoimmune thyroiditis( Hashi-moto disease - here the priority is unconditionally belongs to the Japanese).
Diffuse toxic goiter affects about 1% of the US population. And women get sick 15-20 times more often than men. Disease in certain families is much more common than in others, however, to assert that there is direct inheritance, there is currently no reason, since a specific gene responsible for this disease is not identified.
In case of diffuse toxic goiter, pathological antibodies are produced that are similar in structure to the thyroid-stimulating hormone of the pituitary gland, which cause uncontrolled stimulation of the thyroid cells, causing them to produce a significant amount of thyroid hormones, resulting in thyrotoxicosis.
Another common autoimmune thyroid disease is autoimmune thyroiditis. As well as diffuse toxic goiter, this disease has a predominant distribution in certain families. It is caused by autoaggression of its own lymphocytes and antibodies produced by them, which, unlike diffuse toxic goiter, do not stimulate, but destroy the cells of the thyroid gland, which gradually leads to hypothyroidism.
It should be noted that in some people, these two diseases can exist simultaneously, with alternating manifestations of hypo- and hyperthyroidism.
There is a point of view that these are not two separate diseases, but variants of one called immunotireoidism, and the clinical picture depends on the type of antibodies that are predominantly formed in this patient-stimulating or damaging the gland.
Inflammatory diseases( thyroiditis)
There are several types of inflammatory diseases of the thyroid gland.
Subacute thyroiditis( De Carven's disease)
It is believed that the cause of it is a viral infection. At first, the course of the disease resembles the flu: weakness, pain in the muscles, headache, fever. As the disease progresses, the thyroid gland increases and becomes painful, there is a difficulty in swallowing, symptoms of hyperthyroidism may appear.
The duration of the disease is usually about six weeks, although there are cases when it lasts up to six months.
In the usual course of the disease, aspirin is used to stop the inflammatory process. In severe hyperthyroidism, treatment is supplemented with a beta-blocker, such as propranolol - to normalize the heart rhythm. In severe cases, steroid hormones are used.
Sometimes the process causes a significant destruction of thyroid cells and the appearance of hyperthyroidism, which makes it necessary to conduct short-term hormone replacement therapy.
Postpartum thyroiditis
This name refers to the thyroiditis developing in the mother after the birth of her child, which can lead either to the development of symptoms of mild hyperthyroidism, or mild hypothyroidism.
More recently, these symptoms have been considered as a postpartum depression caused by significant hormonal changes. But studies have shown that approximately 10% of the women have impaired thyroid function. In most of them, the production of hormones is reduced, but insignificantly, and few require replacement therapy.
If symptoms of hyperthyroidism are expressed, antithyroid drugs may be prescribed.
Acute suppurative thyroiditis
A sharp disease commonly found in children. The development of purulent inflammation is caused by a bacterial infection.
The thyroid becomes inflamed, sharply painful, there is a high fever and chills. Sometimes an abscess is formed inside the gland.
Treatment consists in prescribing antibiotics, and in the formation of an abscess - its dissection and drainage.
Fibrous thyroiditis( Riedel)
Extremely rare form of thyroiditis. The reason is unknown.
Normal thyroid tissue is replaced by fibroids, and it becomes extremely dense( therefore, thyroiditis is sometimes called "iron goiter").Fused glands with surrounding tissues and skin, resulting in patients feel constant compression of the throat, although serious breathing disorders are extremely rare.
The physician's tactic is to perform a biopsy( to exclude cancer) and according to the indications - an operation consisting in removing the thyroid gland located in front of the trachea to reduce its compression.
Diffuse goiter
Benign enlargement of the thyroid gland, sometimes evenly enlarged all the thyroid gland. The cause is usually iodine deficiency in the soils of the locality where the patient lives. It can be endemic if more than 5% of children in the area between the ages of 6 and 17 have an increase in the thyroid gland, and sporadic. May be accompanied by the appearance of both hyper- and hypothyroidism.
Prevention of iodine deficiency is necessary to prevent the appearance of goiter.
Nodular goiter
A "knot" of the thyroid gland is a common name for any formation that differs from surrounding gland tissue by density or other characteristics. However, 80% of them are randomly growing, normal cells of the thyroid gland.
Benign thyroid tumors
Benign( adenomas) arise from the epithelium of the thyroid gland and produce thyroid hormones. Grow, pushing out surrounding tissues, and can cause disturbances of function of a thyroid gland.
Stay healthy!