Drugs for endocrine diseases

Endocrine diseases are a class of diseases that arise from disorders in the functioning of one or more glands of the endocrine system. In more detail, they arise as a result of hypofunction, hyperfunction or dysfunction of these glands.
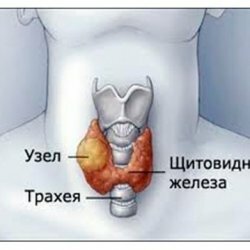
The most common of this class of diseases are those that are associated with thyroid disorders, such as hyperthyroidism, and impaired pancreatic function( diabetes mellitus).As in the case of any other diseases, medicines are used to treat disorders of the endocrine system. In fact, there are simply a huge number of them, so we will only talk about the most popular.
Drugs for the treatment of endocrine diseases
For the treatment of hyperglycemia, two types of hypoglycemic oral agents are generally prescribed: biguanides and sulfonylureas.
The hypoglycemic effect of sulfanilamides can be explained by an increase in the volume of insulin production by beta cells contained in the pancreas and by how sensitive the peripheral tissues are to it. Physicians believe that they can bind to receptors located on cell membranes and inhibit potassium ATP-sensitive channels, thereby leading to depolarization of the envelope, which opens calcium channels, stimulates insulin production and accumulates calcium inside cells.
Biguanides reduce the level of absorption of carbohydrates and increase their absorption by peripheral tissues, and also increase insulin sensitivity of b-cells, glucose absorption rate of the muscles, anaerobic glycolysis, inhibit neoglucogenesis, absorption of glucose, bile acids and amino acids in the small intestine. When using biguanides by a healthy person, they, unlike sulpho-urea preparations, do not lead to hypoglycemia.
Antidiuretic hormone( vasopressin).The main purpose of this drug is to maintain plasma osmolarity. The drop in the level of production of this hormone can be observed with a disease such as diabetes insipidus.
At the moment, there are many drugs of this hormone - pitessin, desmopressin, disipidine, lypressin, sintopressin. In some cases, they are used for the therapy of certain non-endocrine diseases.
Parathyroid hormone, produced, as can easily be understood, parathyroid glands. It serves to regulate the exchange of phosphorus and calcium, accelerating their resorption from the bones, increasing the level of calcium absorption from the gastrointestinal tract and enhancing the reabsorption of calcium in the renal tubules and the excretion of phosphate. All these effects lead to an increase in the concentration of calcium in the plasma. In such a case, vitamin D preparations, such as alfacalcidol, are used to restore the normal level of calcium.
Vitamin D preparations are represented by a fairly wide range of products. For example, the drug Kaltsiferol used in the form of injections, contains in its composition about 600000 ME in only 2 ml and, if necessary, can be used in large doses. Calcitriol and Alfacalcidol are also often used.
When violations in the work of the adrenal cortex - Addison's disease or primary hypokorticism requires replacement treatment with adrenal cortex preparations - mineralocorticosteroids and glucocorticosteroids.
Mineralocorticosteroids include: florinef, Dox.
Glucocorticosteroids: cortisone, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, prednisolone.
With excessive adrenal cortex function, production blockers such as aminoglutamide, chloridant are prescribed. Most often, these drugs are used in the disease of Itenko-Cushing.
Nowadays, more attention is paid to drugs that affect the transmission of serotonin, formed in the nerve endings of tryptophan. With the introduction of drugs that release serotonin, as well as the precursors of serotonin, there is a decrease in appetite, and, accordingly, food intake. One of the drugs in this group is fenfluramine, which is a mixture of two isomers.
Fluoxetine, which reduces body weight in obese patients, also refers to agents that affect serotonin re-uptake.