Diffuse toxic goiter: symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
 Under diffuse toxic goiter( in German-speaking sources - Basedov's disease, in English-speaking - Graves' disease) means a thyroid disease that has an autoimmune character.It is caused by hypersecretion of thyroid hormones.Excess concentration of hormones of diffuse tissue of this endocrine organ causes poisoning, which was called thyrotoxicosis.
Under diffuse toxic goiter( in German-speaking sources - Basedov's disease, in English-speaking - Graves' disease) means a thyroid disease that has an autoimmune character.It is caused by hypersecretion of thyroid hormones.Excess concentration of hormones of diffuse tissue of this endocrine organ causes poisoning, which was called thyrotoxicosis.
Causes of diffuse toxic goiter
Note: many mistakenly believe that the concepts of "thyrotoxicosis" and "diffuse toxic goiter" are identical.In fact, this is not so.Thyrotoxicosis is a syndrome that accompanies a number of diseases, including - and Basedov's diseases. According to the current theory, diffuse toxic goiter is an autoimmune disease that is transmitted by a genetic( multifactorial) route.Thus, the probability of developing thyrotoxicosis is higher in children whose close relatives have suffered from it.Patients with this pathology have a synthesis of antibodies that damage the cells of the thyroid gland.As a result, they begin to produce a significant amount of hormonal compounds - eventually developing thyrotoxicosis.Note:
this endocrine disease affects women 8 times more often than men.In the risk group - the average age group( from 30 to 50 years).An obvious family tendency to thyrotoxicosis suggests the presence of a genetic component.Apparently, the combination of a number of genes with factors of exogenous origin plays a leading role. Among the factors predisposing to the development of pathology, are:- trauma of the cranial region;
- diseases of the nasopharyngeal organs;
- mental stress;
- diseases of infectious and inflammatory genesis.
In addition to the hereditary factor, the cause of diffuse toxic goiter may be a small alimentary( with food and water) intake of iodine.The risk group includes patients taking iodine preparations without proper medical control, as well as those who work in the mining areas of this element.The probability of getting disease is higher in people with autoimmune diseases, including diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis and scleroderma. Some exogenous factors can also trigger the development of pathology.These include:
- prolonged psychoemotional stresses,
- significant physical activity,
- hypothermia and bad habits.
Symptoms of diffuse toxic goiter
 The pathology is characterized by a "classical" stable triad of symptoms:
The pathology is characterized by a "classical" stable triad of symptoms:
- hyperthyroidism( excessive production of thyroid hormones);
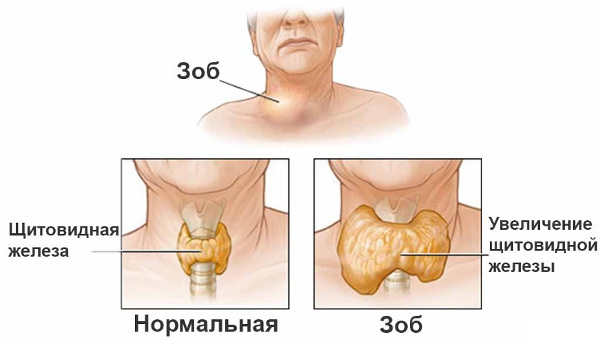
- goiter( visually noticeable increase in the neck area);
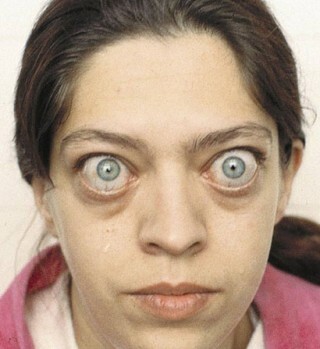
- exophthalmos( bulging eyes).
Since thyroid hormones exert a great influence on various functions of the body, their overabundance leads to a number of pronounced disorders. From the heart:
-
 arrhythmia;
arrhythmia; - tachycardia;
- extrasystole;
- arterial hypertension( increased blood pressure);
- significant difference between systolic and diastolic pressure;
- chronic heart failure and, as a consequence, dropsy( ascites) and swelling.
Characteristic for diffuse toxic goiter and the symptoms of endocrine disorders:
- weight loss( against a background of increased appetite);
- poor tolerance of elevated temperatures;
- increase in total metabolism;
- violation of menstruation in women( amenorrhea may develop);
- erectile dysfunction in men.
Skin:
- Hyperhidrosis( sweating);
- alopecia;
- of erythema;
- destruction of nail plates;
- characteristic edema on the lower limbs( pretybial myxedema).
Neurological clinical symptoms that occur with thyrotoxicosis and diffuse toxic goiter:
- headaches( including migraine);
- general weakness;
- trembling of the limbs;
- sleep disorders;
- increased tendon reflexes;
- is an unmotivated sense of anxiety;
- problem with getting up from the sitting position( myopathy).
Digestive problems:
- nausea or vomiting( rare);
- diarrhea( often).
Dental symptoms in diffuse toxic goiter:
- multiple lesions of hard tooth tissues;
- parodontosis.
Ophthalmic symptoms in thyrotoxicosis and diffuse toxic goiter:
- in the eyes;
- lacrimation;
- lifting of the upper eyelid;
- ptosis of the lower eyelid;
- incomplete closure of eyelids;
- "buckling" of the eyeball;
- overgrowth and swelling of the orbital tissues;
- pain in the eyes;
- vision impairment or complete blindness.
A severe form of pathology contributes to the development of fatty liver and even leads to cirrhosis.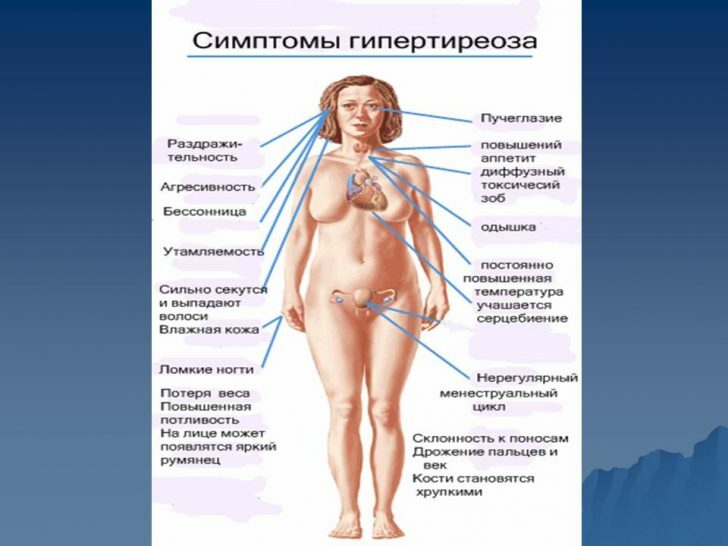 Important: thyrotoxic crisis is considered a life-threatening condition.
Important: thyrotoxic crisis is considered a life-threatening condition.
Classification of
The severity of toxicosis distinguishes 3 degrees of the disease:
-
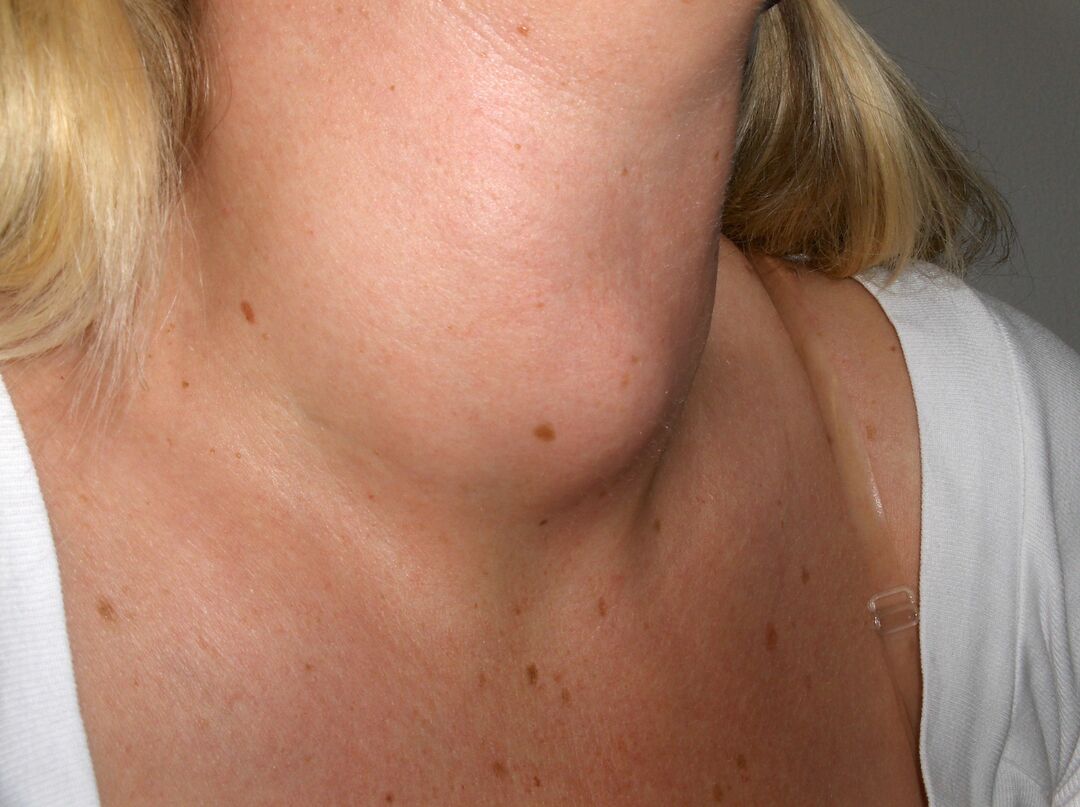 1 degree of diffuse toxic goiter is characterized by the appearance of tachycardia, decreased physical activity and weight loss within 15%.Sweating( hyperhidrosis) and skin pigmentation are noted.Thyroid gland is not enlarged.At this stage, the doctor is treated infrequently.
1 degree of diffuse toxic goiter is characterized by the appearance of tachycardia, decreased physical activity and weight loss within 15%.Sweating( hyperhidrosis) and skin pigmentation are noted.Thyroid gland is not enlarged.At this stage, the doctor is treated infrequently. - 2 degree leads to increased nervous excitability, increased symptoms of tachycardia and reduced physical activity.There may be signs of circulatory failure.The goiter is not visible, but it is determined by palpation.In the evening hours there are swelling of the lower extremities.
- 3 the degree of diffuse toxic goiter is the heaviest.Symptoms of hyperthyroidism increase, a person becomes disabled.Weight loss is clearly visible, and from the cardiovascular system there is atrial fibrillation, heart failure.For this stage, muscle weakness and liver damage are characteristic.The goiter is clearly visible even in a cursory examination.It is possible to fall and even complete loss of vision.
Diagnosis
To diagnose, there are few patient complaints and clinical picture.The syndrome is confirmed by a laboratory blood test for thyroid-stimulating hormone and thyroid hormones T3 and T4. Tables of thyroid hormone indicators
| Thyroid-stimulating hormone, TSH | ||
| mU / l | ||
| Newborns | 1,1 - 17,0 | |
| under 2 months | 0,6 - 10, 0 | |
| 2 - 14 month | 0,4 - 7,0 | |
| 14 months - 5 years | 0,4 - 6,0 | |
| 5 - 14 years | 0,4- 5.0 | |
| 14 years and older | 0,4 - 4,0 | |
| total triiodothyronine, T3 | ||
| nmol / l | Ng / dl | |
| 15 - 20 years | 1.23 - 3.23 | 80 - 210 |
| 20 - 50 years | 1,08 - 3,14 | 70 - 205 |
| Older than 50 years | 0,62 - 2.79 | 40 - 182 |
| free triiodothyronine, T3sv | ||
| pmol / l | pg / ml | |
| adults | 2,6 - 5,7 | 0,04 - 0,087 |
| total thyroxine, T4 | ||
| Age | nmol / l | ug / dl |
| children 1 to 6 years | 67 - 167 | 5,95 - 14,7 |
| children from 5 to 10 years | 68 - 139 | 5,99 - 3,8 |
| adolescents: from 10 years to 18 years | 58 - 133 | 5,91 - 13,2 |
| Adults18 years old and younger than 20 | 55 - 137 | 4,84 - 12,06 |
| Male from 20 to 39 years old | 63 - 110 | 5.57 - 9.69 |
| Women from20 to 39 years | 67 - 146 | 5,92 - 12,9 |
| Men older than 40 years | 60 - 113 | 5,32 - 10,0 |
| Women over 40 years | 56 - 138 | 4,93 - 12,2 |
| 1 Pregnancy trimester | 83 - 168 | 7,33 - 14,8 |
| 2 trimester | 90- 182 | 7,93 - 16,1 |
| 3 trimester | 79 - 178 | 6,95 - 15,7 |
| free thyroxine, T4sv | ||
| Age | pmol / l | ng / dl. |
| children aged 5 to 14 years | 8 - 17 | 0,8 - 1,7 |
| Children older than 14 years | 9 - 22 | 0,9 - 2,2 |
| Adults: | ||
| men | 8 - 21 | 0,8 - 2,1 |
| women | 2 - 21 | 0,8 - 2,1 |
| Pregnancy1 trimester | 7 - 20 | 0,7 - 2,0 |
| 2 trimester | 5 - 16 | 0,5 - 1,6 |
| 3trimester | 5 - 16 | 0,5 - 1,6 |
| Thyroglobulin, Tg | ||
| ng / ml | ||
| adults | Less 60 |
Please note: the results of the analysis in different laboratories may vary slightly, so always pay attention to the reference( normal) values indicated in the form.With diffuse goiter, the TSH level will be lowered, and the levels of T3 and T4 are increased, and - T4 is increased more noticeably.Of the instrumental techniques for the diagnosis of diffuse toxic goiter, ultrasound of the thyroid gland is most commonly used. Treatment In the treatment of thyrotoxicosis, both conservative and radical methods can be used.Well proven and radioiodotherapy. Conservative treatment of diffuse toxic goiter. In thyrotoxicosis, drugs such as Methylthiouracil and Mercazolil are used.In a day, the patient is prescribed up to 30-40 mg of Mercazolilum, and in case of complicated flow and significant goiter sizes the dose can be doubled.The maintenance dosage is about 10-15 mg.Such treatment of diffuse toxic goiter is carried out a long course - for 1.5-2 years.Gradual reduction of dosage is carried out, focusing on the patient's condition.In particular - on relief of such symptoms as tremor, tachycardia and hyperhidrosis.Once in 1.5-2 weeks, a laboratory blood test is necessary.Additional drugs are potassium preparations, glucocorticoid hormones, b-blockers and sedative drugs( Phenobarbital). Radioiodine therapy 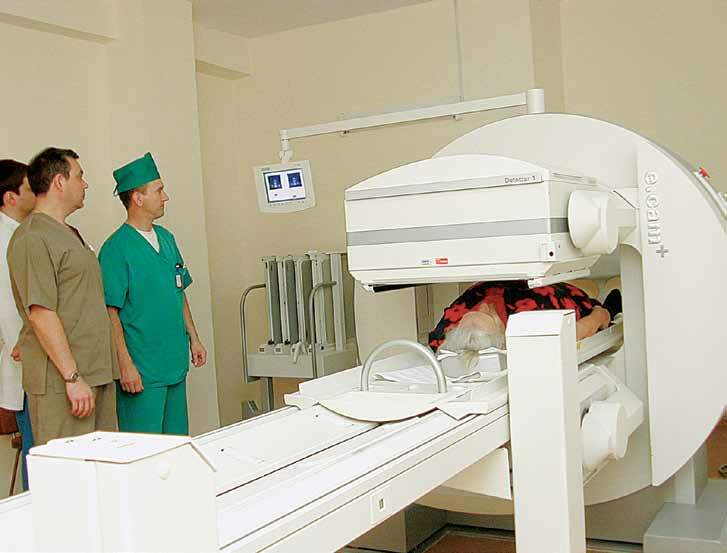 This method is one of the most innovative and unique methods for treating thyrotoxicosis in cases of diffuse toxic goiter and malignant thyroid diseases.Its essence is based on the reception of the radioactive isotope I-131, which the patient receives per os in the form of capsules or solution.Accumulating in the tissues of the thyroid, radioactive iodine acts directly on those cells that produce an excessive amount of hormones and destroy their structure.As a result of radioiodine therapy, the thyroid function is normalized in the patient or hormone deficiency is formed, compensated by the intake of the corresponding drug.Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter by radioiodine therapy is carried out in a specialized department and requires daily monitoring of the radiation dose received. Surgical treatment The indications for an operative intervention are:
This method is one of the most innovative and unique methods for treating thyrotoxicosis in cases of diffuse toxic goiter and malignant thyroid diseases.Its essence is based on the reception of the radioactive isotope I-131, which the patient receives per os in the form of capsules or solution.Accumulating in the tissues of the thyroid, radioactive iodine acts directly on those cells that produce an excessive amount of hormones and destroy their structure.As a result of radioiodine therapy, the thyroid function is normalized in the patient or hormone deficiency is formed, compensated by the intake of the corresponding drug.Treatment of diffuse toxic goiter by radioiodine therapy is carried out in a specialized department and requires daily monitoring of the radiation dose received. Surgical treatment The indications for an operative intervention are:
- allergic reactions to medications administered within the therapeutic treatment;
- persistent leukopenia;
- too large volume of growth( goiter);
- marked lesions of the cardiovascular system.
Important: to prevent the development of thyrotoxic crisis, surgery is performed only as compensation is achieved by conservative methods. Treating Based's disease in pregnant women  To prevent the negative effect of antithyroid antibodies and drugs on the unborn child, women with diffuse toxic goiter are shown to have a pregnancy warning.In the event that the conception has occurred, during the conservative treatment of thyrotoxicosis in pregnant women, preference is given to the drug Propylthiouracil.Vladimir Plisov, physician-phyto-therapeutist
To prevent the negative effect of antithyroid antibodies and drugs on the unborn child, women with diffuse toxic goiter are shown to have a pregnancy warning.In the event that the conception has occurred, during the conservative treatment of thyrotoxicosis in pregnant women, preference is given to the drug Propylthiouracil.Vladimir Plisov, physician-phyto-therapeutist