Pituitary Tumors: Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment
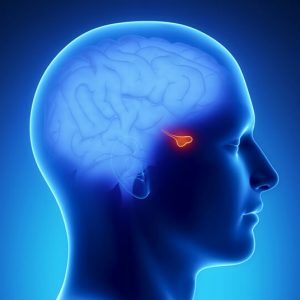
Pituitary tumors are a group of neoplasms that are concentrated in the anterior or posterior part of the gland.They account for almost 15% of all neoplasms that have intracranial localization.
Important! Typically, adenomas are classified according to the hormonal activity and size.
The mechanism of the appearance of the disease is simple.Each person has an internal secretion gland, the pituitary gland.It is a cerebral appendage of small size, which is responsible for the growth, reproduction and flow of metabolic processes in the body.On them, it affects through the production of hormones.
Table of Contents: Pituitary Functions Causes Classification Symptoms of Pituitary Tumors Diagnosis of Pituitary Tumors Treatment of Pituitary Tumors PredictionPituitary Functions
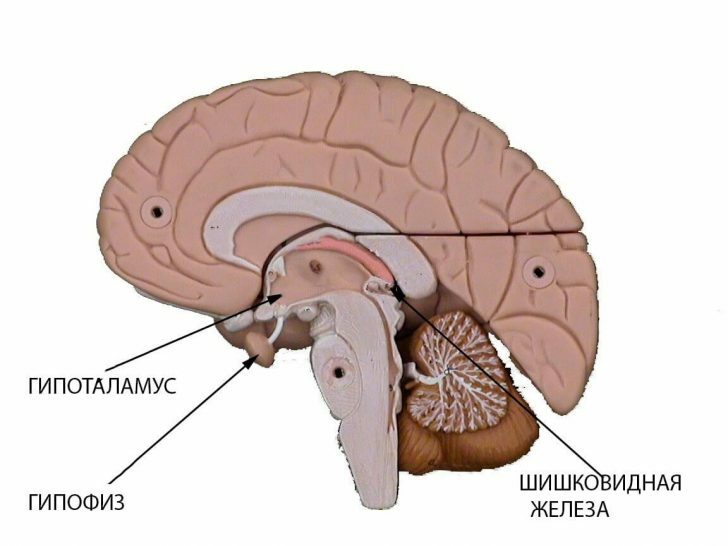
In fact, the pituitary gland is the center of the endocrine system .It is in close proximity to the sphenoid bone of the skull and, together with the hypothalamus, forms a single neuroendocrine system that ensures the permanence of homeostasis.In other words, thanks to the work of two vital structures, the body maintains the necessary temperature for life, the level of water in the cells and the level of carbon dioxide.
Features of the structure of the pituitary gland provide for the presence of anterior and posterior lobe.The first is called adenohypophysis, the second - neurohypophysis.
Adenohypophysis is responsible for the production of:
- Prolactin - supporting lactation after pregnancy;
- growth hormone - it regulates protein metabolism and provides growth of the body;
- thyroid-stimulating hormone - it affects the course of metabolic processes in the thyroid gland;
- adrenocorticotropic hormone( ACTH) - it stimulates the synthesis of protein and nucleic acids, regulates the work of the adrenal glands;
- gonadotropic hormones - they affect the work of the gonads.
Neurohypophysis is responsible for the production of oxytocin, which causes the uterus to contract, if necessary, and vasopressin, or antidiuretic hormone.He is responsible for the homeostasis in general and the preservation of the water balance - in particular.
The production of hormones is regulated mainly by the central nervous system.However, in some cases, disruption of the hormonal balance causes disruptions, and the gland cells begin to expand rapidly.So tumors are formed.
Please note! In medical practice, there have been cases when meningiomas - neoplasms of the brain envelopes or metastases of malignant tumors of other localizations - have grown into the pituitary gland.
Reasons for
At the moment, scientists are working to establish all the causes that lead to the growth of pituitary tumors.One thing is clear: heredity plays a huge role here. Increase the risk of developing neoplasms:
-
 craniocerebral trauma;
craniocerebral trauma; - Neuroinfections;
- chronic sinusitis;
- hormonal failures, including as a result of prolonged intake of hormonal drugs;
- a problem pregnancy and a negative impact on the fetus during its development.
It should be noted that the scientists put forward theories explaining the mechanism of development of pathology.According to one of them, the pituitary gland tissue grows because of the unproductive activity of the peripheral glands of the endocrine system or the increased secretion of the hormones of the hypothalamus.
Another indicates the presence of genetic disorders in one of the cells of the medullary appendage.
Classification
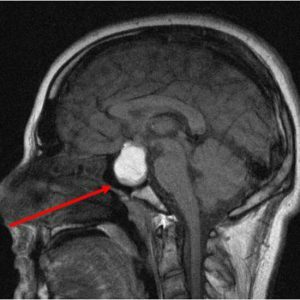 First of all, tumors are classified as benign and malignant.The former are much more frequent and practically do not affect the properties and functions of healthy cells of the gland. In addition, benign neoplasms, or adenomas, as they are also called, grow slowly, rarely penetrating into the pituitary gland.True, they tend to squeeze the surrounding tissues, so doctors recommend removing them surgically.It should be noted that cases of relapses are single.
First of all, tumors are classified as benign and malignant.The former are much more frequent and practically do not affect the properties and functions of healthy cells of the gland. In addition, benign neoplasms, or adenomas, as they are also called, grow slowly, rarely penetrating into the pituitary gland.True, they tend to squeeze the surrounding tissues, so doctors recommend removing them surgically.It should be noted that cases of relapses are single.
Malignant tumors differ from benign tumors in that their cells degenerate , while completely losing their ability to grow and differentiate, that is, the acquisition of functional differences, structural features to perform the functions assigned to them.
Such neoplasms grow very rapidly, and their metastases penetrate not only into surrounding tissues, but also into lymphatic and blood vessels.As a consequence, they are difficult to treat .The possibility of surgical removal is determined by the size of the neoplasm and the degree of penetration of metastases into the tissue.
In addition, such tumors are classified according to their size, localization, endocrine functions, staining features. Microadenoma is diagnosed if the diameter of the lesion does not exceed 10 mm, and the macroadenoma - if exceeds 10 mm.Also there are picoadenomas ( their diameter is 1 - 3 mm), giant adenomas .
Depending on the location, tumors of the neurohypophysis and adenohypophysis are distinguished.
At the location relative to the Turkish saddle( in the pit is the pituitary), the following are isolated:
- endosellar tumors - they extend beyond the saddle;
- intrasellar - do not go beyond.
In terms of its activity, tumors are divided into insidentalomas, or "mute", that is hormone-inactive neoplasms, and hormone-active ones.
The latter constitute 75% of the total number of diagnoses and in turn are divided into adenomas that produce:
- somatotropin;
- Prolactin - occur in 35% of all pituitary tumors;
- adrenocorticotropin - occur in 10 to 15% of cases;
- tyrotropin.
Please note! There are also adenomas that provoke the production of follitropin( follicle-stimulating) and lutropine( luteinizing).They stimulate the secretion of gonadotropins, which are responsible for the functioning of the sex glands.
In addition, doctors distinguish:
- chromophobic tumors are hormone-inactive;
- acidophilus - these include prolactinomas, somatotropinomas, tyrotropinomas;
- basophilic - mainly corticotropinomas.
Symptoms of a pituitary tumor
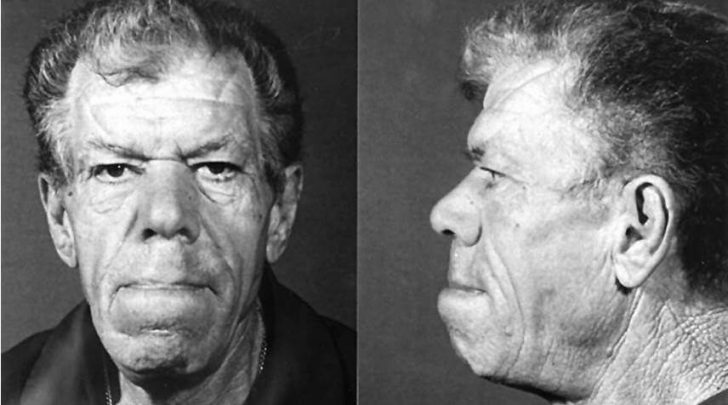
Neoplasms provoke failures in the endocrine system, inhibiting the function of the pituitary gland or, conversely, provoking hyperfunction.Moreover, they affect the neuroanatomy and neurophysiology of a person.
Symptoms are determined by the type of tumors.So:
- Somatotropinums provoke the development of acromegaly in adults( a pathology that thickens and expands the hands, feet, the front of the skull) and gigantism in children.
- Prolactinomas contribute to the development of gynecomastia( breast augmentation in men), amenorrhea, galactorrhea( this is the secretion of milk from the breast without any apparent cause).It is worth noting that such adenomas grow slowly and do not always produce full-length prolactin, as a result of which they can not be manifested.
- Adenomas producing ACTH - due to increased secretion of adrenocortical hormones, the cortex of the adrenal cortex causes the development of Isenko-Cushing's disease, which manifests itself in overweight, overdrying of the skin and the appearance of striae on them.Meanwhile, such neoplasms are not detected immediately, since they grow very slowly.
- Gonadotropic adenomas in women cause malfunctions of the menstrual cycle and uterine bleeding, while in men - impotence and gynecomastia - swelling of the mammary glands.
- Adenomas that produce thyrotropin lead to the development of thyrotoxicosis, a disease of the thyroid gland, which is manifested by a decrease in sexual desire in men, amenorrhea in women, impaired memory, attention, and weight loss.
Due to the increase in the size of the neoplasm and the pressure on adjacent tissues, there are irregularities in the work of the nervous system. When the adenoma reaches 2 cm in diameter, vision falls.Initially, the field of vision may simply narrow, but in the absence of qualified treatment, blindness often occurs.
Neoplasms more than 2 cm in diameter begin to squeeze the cranial nerves, as a result of which the patient notes:
- headache;
- ptosis, or descent of the upper eyelid;
-
 obstructed movement of eyeballs;
obstructed movement of eyeballs; - convulsions;
- Nystagmus - oculomotor pathology, expressed in the trembling of the eyeballs;
- chronic rhinitis;
- tremor;
- is a migraine;
- syncope;
- insomnia;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- acute cardiovascular failure accompanied by hemorrhages in the pituitary gland;
- dementia and personality change;
- sometimes hyperphagia( overeating as a mental disorder).
If the adenoma touches the hypothalamus, there are disorders of consciousness in which a person ceases to navigate in time, place, in the self .If the ventricles of the brain are affected, hydrocephalus( hydrocephalus) develops.Pressure on the temporal and frontal lobes of the brain provokes seizures, problems with vision.
Please note! To distinguish the headache with tumors of the pituitary gland from the pain of another origin is simple.It is dull, constant, persisting in any position of the body.It is felt in the temporal, frontal and suborbital regions and practically does not react to analgesics.It can stop, only if the brain envelope is broken due to the strong pressure of the adenoma, meanwhile this problem does not solve.From this moment, problems with vision usually begin.
It should be noted that tumors of the pituitary gland are found in children, though infrequently.Meanwhile, due to their age and susceptibility to the slightest changes, they are diagnosed much faster than adults.
Diagnosis of a tumor
In rare cases, the presence of a pituitary tumor can be suspected when the patient is first examined.The pathology is indicated by gigantism in children or acromegaly, and Itenko-Cushing's disease in adults.
To confirm the diagnosis, carry out:
- Hormonal and ophthalmological examination.In this case, the patient is assigned blood and urine tests to determine the level of hormones. Due to the examination of the organs of vision, the size and direction of adenoma growth are revealed.
- Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid for the presence of proteins that may indicate the development of pituitary tumors.
- Radiography, computed tomography, MRI( allows to detect adenomas with a diameter of less than 5 mm), angiography for imaging neoplasms.
Treatment
The endocrinologist and the neurosurgeon take a decision on the therapy of pituitary tumors based on the results of the study, indicating the type of tumor, its size, localization.
Possible methods of treatment of pituitary tumors:
- Medicated.Provides the appointment of dopamine agonists, which contribute to the wrinkling of adenomas, which produce prolactin and corticotropin.Also prescribed drugs that regulate the level of hormones in the blood.
- Radial.It is the use of radiosurgical treatment where conventional surgical intervention is impossible.Doses of irradiation are chosen taking into account the size and type of tumors, meanwhile, most often, hormone-inactive microadenomas are treated like this.The success of treatment depends on its duration( to achieve the effect should be resorted to it for 3 to 10 years).Radiation therapy is contraindicated if the tumor is closely approximated to the optic nerves.
 Please note! Modern methods of radiosurgery involve the use of a cyber knife or gamma knife.They consist of irradiating the tumor from all sides with radiation beams and do not involve invasive interference.
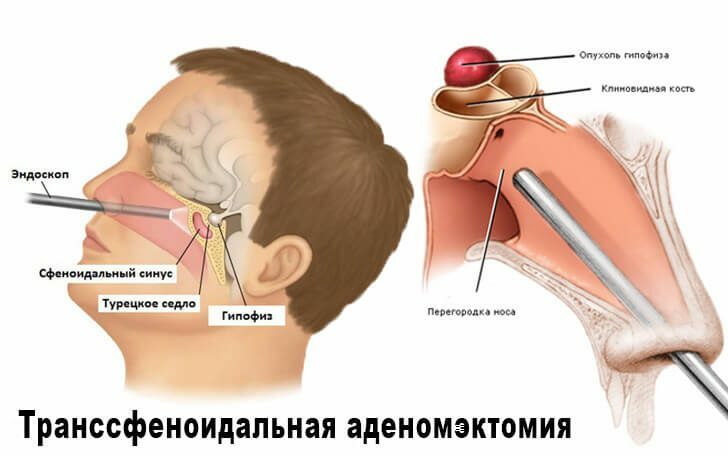
Please note! Modern methods of radiosurgery involve the use of a cyber knife or gamma knife.They consist of irradiating the tumor from all sides with radiation beams and do not involve invasive interference. - Surgical.Radical and the most effective method.Recently, it is carried out by penetrating the area of the lesion through the nasal passages.This saves the specialist from the need to make cuts, and the patient guarantees a minimal risk of complications from infection.
In some cases, the doctor may resort to the appointment of a comprehensive treatment, when all three methods are simultaneously applied.
Forecast
The prognosis of treatment directly depends on the timely diagnosis, the size and the place of development of adenomas.Almost all of them are successfully eliminated in 80% of cases, meanwhile, somatotropinomas and prolactinomas can be treated only in 25% of cases of .It is difficult to remove and macroadenomas, the diameter of which exceeds 2 cm in diameter, which is why their relapses are predicted for 5 years.
Important! If the tumor touches the optic nerves, restoration of their functions is possible only at the initial stage of development of pathologies.
Pituitary tumors are neoplasms that can be diagnosed in both sexes.The effectiveness of their treatment depends on the timeliness of the diagnosis, so when the first signs of the disease should immediately seek medical attention.
Chumachenko Olga, medical reviewer