Hyperthyroidism: Symptoms and Treatment
 Hyperthyroidism is a chronic disease characterized by an increase in the hormonal activity of the thyroid gland and excessive production of hormones of thyroxine( T4) and triiodothyronine( T3).Due to an overabundance in the blood of these hormonal substances, metabolism in the patient's body is greatly accelerated.Hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland is also called thyrotoxicosis.
Hyperthyroidism is a chronic disease characterized by an increase in the hormonal activity of the thyroid gland and excessive production of hormones of thyroxine( T4) and triiodothyronine( T3).Due to an overabundance in the blood of these hormonal substances, metabolism in the patient's body is greatly accelerated.Hyperthyroidism of the thyroid gland is also called thyrotoxicosis.
Anatomy and functions of the thyroid
The thyroid gland is the largest gland in the human body,Located in the front lower region of the larynx.The endocrine organ is responsible for the synthesis of thyroid hormones containing iodine atoms.Iodine is extremely necessary for the body of every person, since this substance takes a direct part in the regulation of metabolic processes, thermoregulation, affect the nervous system and psyche.
Synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones occurs in the follicles of the organ in several stages.First, along with food, iodine enters the body, which enters the blood in an inorganic form.Thyroid cells capture it and convert it to organic iodine.After oxidation, iodine molecules are attached to a substitute amino acid tyrosine, compounds such as monoiodothyrosine and diiodotyrosine are formed.Then there is condensation and the formation of hormones T3 and T4, which are released into the bloodstream.The blood, which is over-saturated with hormones, carries these substances to all tissues of the body, which leads to an acceleration of metabolic processes in virtually all organs of man.
To all, hyperthyroidism develops hormonal changes caused by the transformation of androgens( male sex hormones) into estrogens( female sex hormones) and the accumulation of the latter in the blood.The sensitivity of the tissues to the sympathetic nervous system
significantly increases. The hypothalamus and the pituitary gland take the main part in the regulation of thyroid function.
According to statistics, hyperthyroidism in women occurs eight times more often than in males.With thyroid dysfunction, the reproductive function suffers, which can lead to infertility.
Causes of hyperthyroidism
 Development of the disease is the result of some pathological processes occurring directly in the gland, or a violation of the process of regulation of its function.
Development of the disease is the result of some pathological processes occurring directly in the gland, or a violation of the process of regulation of its function.
There are a number of pathologies in which hyperthyroidism usually occurs:
- Basedova disease( diffuse toxic goiter) - manifests a uniform increase in the gland in the excess synthesis of thyroid hormones;
- Plummer's disease( nodal toxic goiter) - is detected mainly in adulthood and is characterized by the presence of nodal seals in the organ;
- subacute thyroiditis form - inflammation arising due to viral infections.Pathology provokes destruction of follicular cells of the gland and excessive secretion of thyroid hormones;
- tumor diseases of the pituitary gland;
In addition, the cause of hyperthyroidism may be:
- Systematic administration of thyroid hormones;
- reception of a large number of iodine preparations;
- ovarian teratomas;
Hyperthyroidism can also be congenital.In this case, it develops as a result of the disease transferred by a pregnant woman or is caused by a genetic factor.
Varieties hyperthyroidism
Modern classification distinguishes three types of the disease:
- primary hyperthyroidism - is the main reason leading to the development of the disease - disease of the thyroid gland
- secondary - caused by the failure of the functioning of the pituitary gland
- Tertiary - the reason for this variety of hyperthyroidism arepathological processes in the hypothalamus
Primary hyperthyroidism in its development takes several successive steps:
- subclinical - usually has no significant symptoms, with a decrease in the level of TSH( thyroid stimulating hormone, thyrotropin) at a normal T4 level;
- manifest form( explicit) - characterized by a vivid clinical picture;In the blood there is an increase in the level of T4 and a more pronounced decrease in the level of TSH;
- complicated form - manifested by the presence of psychoses, weight loss, heart and adrenal insufficiency, dystrophy organs rich in parenchymal tissue, arrhythmias, and other complications hyperthyroidism from various organs and systems.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism
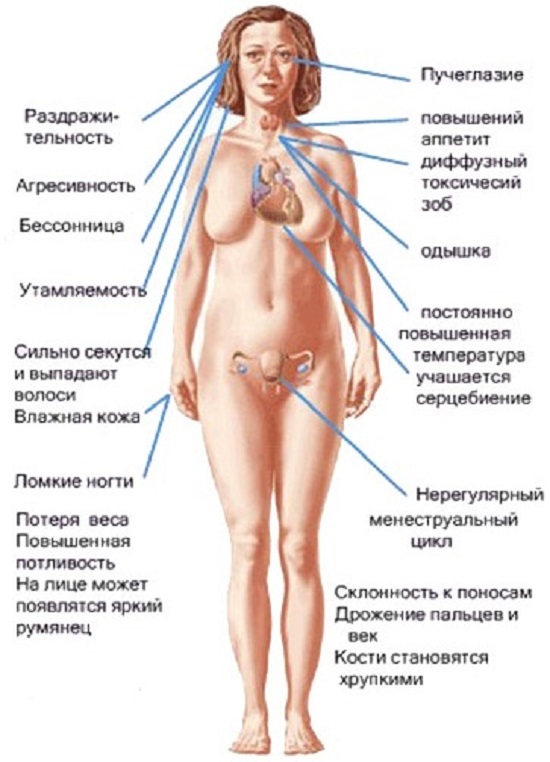
pathological symptoms, depending on the severity of the disease can affect many systems and organs of the human body.The main external sign is an increase in the thyroid gland.
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism CNS
the part of the central nervous system of an overabundance of hormones T3 and T4 is :
- sleep disorders,
- tremor,
- mood swings,
- irritability,
- excessive excitability,
- memory disorders and concentration of attention.
symptoms of pathologies of the cardiovascular system, indicating hyperthyroidism
Many patients with hyperthyroidism observed symptom of cardiac arrhythmias: persistent sinus tachycardia, atrial flutter.There is also an increase in systolic with a simultaneous decrease in diastolic pressure.There are signs of heart failure.
Clinical signs of the disease on the part of the genital area
Hyperthyroidism in women is manifested by menstrual irregularities up to amenorrhea, painfulness of mammary glands arises.Due to the violation of the production of sex hormones, the reproductive sphere suffers, which can lead to infertility.
In men, there is a decrease in potency and sexual desire, often develops gynecomastia - swelling of the mammary glands.
Violations of
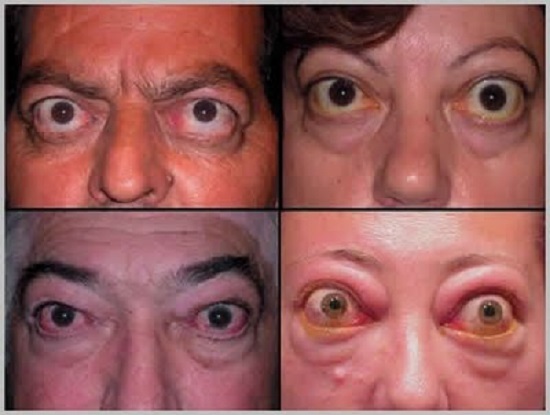 organs In such a disease, hyperthyroidism, signs of pathological processes in the thyroid gland and spread to the eyes.One of the external symptoms of pathology is the protrusion of the eyeballs, the limitation of their mobility.There is also an enlargement of the ocular gap, dryness and burning in the eyes, increased tearing.
organs In such a disease, hyperthyroidism, signs of pathological processes in the thyroid gland and spread to the eyes.One of the external symptoms of pathology is the protrusion of the eyeballs, the limitation of their mobility.There is also an enlargement of the ocular gap, dryness and burning in the eyes, increased tearing.
Typical symptoms of hyperthyroidism on the part of other organs and systems
Other typical clinical signs of hyperthyroidism include:
- weight loss due to accelerated metabolism;The appetite can be raised or lowered;
- digestive disorders;
- increased urination;
- increased sweating and severe thirst;
- muscle wasting;
- trembling in the limbs;
- shortness of breath;
- adrenal insufficiency;
- a violation of liver function, in severe cases, the development of hepatitis;
- nail and hair deterioration
- skin thinning
Please note! In the elderly, the symptoms of the disease may not appear - this is the so-called hidden hyperthyroidism.In elderly people, a typical reaction to an overabundance of thyroid hormones is drowsiness, a tendency to depression, and retardation.
What is the hyperthyroid crisis
 In severe illness and lack of adequate therapy, complications may occur - hyperthyroid crisis.Provoke it can and stress.In this condition, the clinical symptoms of pathology reach their maximum peak.
In severe illness and lack of adequate therapy, complications may occur - hyperthyroid crisis.Provoke it can and stress.In this condition, the clinical symptoms of pathology reach their maximum peak.
Hyperthyroid crisis is characterized by a sharp impetuous beginning.In patients, a mental agitation is observed, which can be accompanied by delirium, hallucinations.Strong tremor spreads throughout the body, pressure drops sharply, strong weakness appears, indomitable vomiting, body temperature rises.The heart rate can reach up to 200 beats per minute.
Important! Lack of timely medical care for hyperthyroid crisis can lead to a coma and the death of a patient.
Diagnosis of the disease
Hyperthyroidism is diagnosed by the presence of the patient's clinical symptoms and data from the research:
-
 blood test for the determination of thyroid stimulating hormone( TSH) and thyroid hormone levels - hyperthyroidism increases the concentration of thyroid hormones and decreasesThe level of TSH;
blood test for the determination of thyroid stimulating hormone( TSH) and thyroid hormone levels - hyperthyroidism increases the concentration of thyroid hormones and decreasesThe level of TSH; - ultrasound and computed tomography of the thyroid for evaluation of its size and structure, as well as blood flow studies;
- scintigraphy - radioisotope method is used to assess the activity of various parts of the body;
- if necessary, biopsy of nodal seals;
- ECG to detect abnormalities in the cardiovascular system.
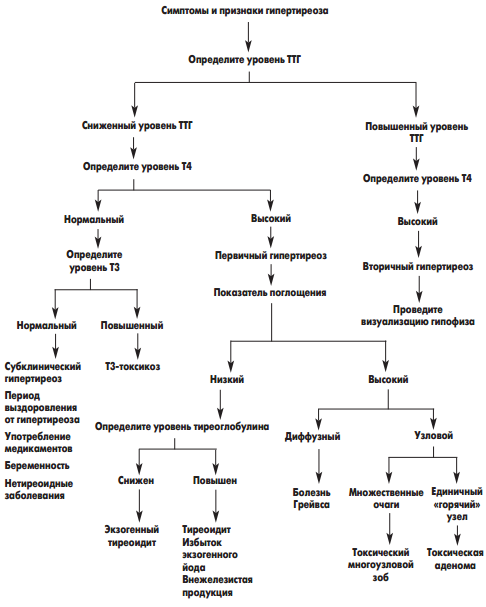
An important point in the presence of symptoms of hyperthyroidism is its differentiation from other thyroid diseases.This scheme will be of great help:
Hyperthyroidism: treatment of
Treatment of hyperthyroidism, depending on the degree of lesions, can be carried out by conservative and surgical methods.The therapeutic tactics are developed by the endocrinologist, he can recommend the existing methods of treatment in combination or separately.
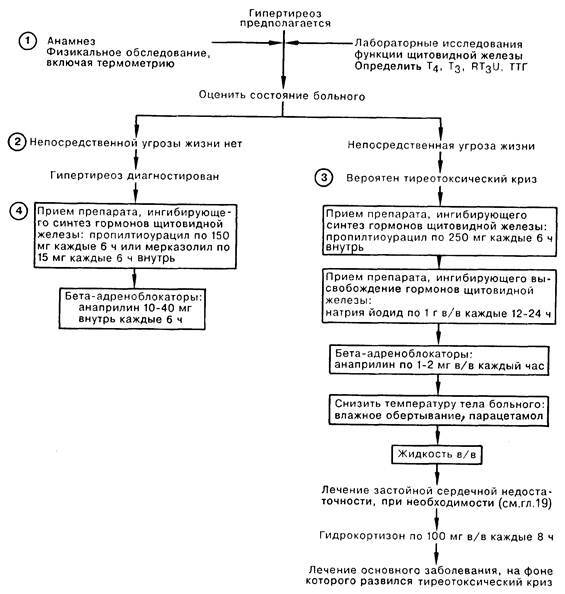
Medication correction for the disease in question has as its goal the suppression of the secretory activity of the organ.To this end, patients are prescribed thyreostatic drugs.In conservative treatment, hydrotherapy and diet therapy are of great importance.Patients should include in their diet products rich in proteins, carbohydrates and fats, limit the consumption of foods that have an irritant effect on the central nervous system.
Another method used in the treatment of the described pathology is radioiodine therapy.The patient takes inside a radioactive iodine, which destroys the malfunctioning cells of the gland.As a rule, such therapy is carried out in conjunction with a medical correction.
Surgical treatment of hyperthyroidism consists in surgical excision of the site of the gland.The rest of the organ will function normally, but if a large area is excised, the development of the opposite hyperthyroid state - hypothyroidism - is possible.In this case, the patient is shown lifelong replacement therapy.
Basic indications for surgical intervention:
- presence of large goiter;
- individual intolerance of medications necessary for effective drug treatment;
- relapse after the course of drug therapy.
Please note! During the treatment and during the recovery period, an important role is played by diet compliance.Twice a year, patients with hyperthyroidism are recommended to undergo a course of treatment aimed at eliminating cardiovascular disorders.
Hyperthyroidism: folk remedies
With such a disease as hyperthyroidism, folk treatment can produce good results, but it should be addressed only with the permission of the attending physician.
Alcoholic tinctures of medicinal plants are considered effective in the fight against the disease:
-
 Persimmon tincture - freshly squeezed persimmon juice should be mixed with alcohol in a proportion of 5: 1, insist a few days in a darkened place.Take a drug is recommended three times a day, one tablespoon before meals.
Persimmon tincture - freshly squeezed persimmon juice should be mixed with alcohol in a proportion of 5: 1, insist a few days in a darkened place.Take a drug is recommended three times a day, one tablespoon before meals. - Tincture of hawthorn - two tablespoons of dried flowers are poured in 500 g of 20% alcohol, insisted for one and a half months.Take medication four times a day for 25-30 drops.
- Tincture of bilberry leaves - 10 grams of raw material is mixed with crushed laurel leaves, 20 grams of chicory rootlets and string beans.Now the mixture needs to be filled with half a liter of vodka and insist for several days.The filtered drug is taken for ten days on a tablespoon three times a day, washed down with water.After a five-day break, the course of treatment should be repeated.
- Tincture of cranberries and blueberries - 20 grams of berries are mashed into a slurry and poured into 0.5 liters of vodka.Six days the drug should be infused in a dark place.A strained medication is taken after eating on a tablespoon according to the following scheme: 30 days of intake, two weeks of a break for six months.
- Balm from the leaves of dandelion and blueberry - for this drug you need 20 grams of blueberries and dogrose, 10 grams of dandelion leaves.Raw materials should be filled with a glass of vodka, tightly closed and put in a dark place for a week.At the end of this period, you can start taking the balm on a teaspoon three times a day, diluting it in a glass of water.After a week of treatment, he takes a break for seven days, then the course is repeated.

In addition to infusions on alcohol, traditional medicine as an effective treatment for hyperthyroidism offers healing infusions.So you can make an infusion of valerian, if you pour a spoonful of raw material with a glass of boiling water and insist for a couple of hours.The drug is drunk in small portions throughout the day.
In early spring, it's time to prepare the infusion from the buds and cherry twigs.To do this, cut 100 grams of branches with swollen buds, pour half a liter of water and boil for half an hour.The drug should be taken on a tablespoon before meals three times a day.
All the favorite citrus lemon and orange also help with hyperthyroidism.Any of these fruits must be rubbed together with zest, add a little sugar.Get a very tasty and useful remedy, which should be taken one spoon three times a day.
You can also resort to treatment with natural clay, which will help normalize the functioning of the thyroid gland.Clay should be diluted with water to a gruel-like condition and make a lotion for an hour on the front of the neck.
Thyroid hyperthyroidism even after successful treatment can recur, so patients are required to visit a regular endocrinologist on a regular basis.As a preventive measure, all people are encouraged to monitor their diet, use iodine-containing foods, and consult a specialist promptly at the first signs of thyroid disorders.
Chumachenko Olga, medical reviewer