Hyperparathyroidism: Symptoms and Treatment
 Hyperparathyroidism is an endocrine pathology characterized by hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands.With this disorder, an increased amount of parathyroid hormone is synthesized in them.Excess of this biologically active substance leads to hypercalcemia and pathological changes from the side of bone tissue and kidneys.
Hyperparathyroidism is an endocrine pathology characterized by hyperfunction of the parathyroid glands.With this disorder, an increased amount of parathyroid hormone is synthesized in them.Excess of this biologically active substance leads to hypercalcemia and pathological changes from the side of bone tissue and kidneys.
In women( especially the age group from 25 to 50 years), this endocrinopathy is diagnosed almost three times more often than in male patients .There may be a subclinical course of hyperparathyroidism.The main forms of pathology are visceropathic, bone and mixed.In some cases, an acute condition develops, called "hypercalcemic crisis."When the diagnosis is made, the determination of the level of parathyroid hormone, P + and Ca + in the blood is crucial.
Table of contents: Versions of hyperparathyroidism Why does this pathology arise?The mechanism of the pathological process Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism Diagnosis How to treat hyperparathyroidism?Species of hyperparathyroidism
This endocrinopathy is primary, secondary and tertiary.
In clinical practice, it is customary to distinguish 3 types of primary hyperparathyroidism:
- subclinical;
- clinical( divided into several types according to the primary lesion of organs and tissues);
- sharp.
In subclinical hyperparathyroidism, pathological changes are detected only during laboratory diagnostics.
The clinical variant includes bone( parathyroid osteodystrophy),( renal or gastrointestinal), and a mixed form.
When parathyroid osteodystrophy, the structure of bone tissue changes.For this form of hyperparathyroidism, osteoporosis and pathological fractures are characteristic, which for a very long time grow together.
Against a visceropathic renal form, urolithiasis is often diagnosed.It is severe and is accompanied by periodic episodes of renal colic.As the process progresses, kidney failure occurs.
Gastrointestinal form causes cholecystitis, pancreatitis, and peptic ulcers.
If there is a mixed form, then osteoporosis and pathology of internal organs develop in parallel.
Why does this pathology occur?
Causes of primary hyperparathyroidism:
- gland adenomas( single or multiple);
- diffuse hyperplasia;
- malignant neoplasm with hormonal activity( very rare).
Note: approximately in every tenth patient, hyperparathyroidism develops in parallel with hormonal tumors localized outside the parathyroid glands.
The primary form of endocrinopathy can be genetically determined.Hereditary hyperparathyroidism is combined with other pathologies of endocrine glands.
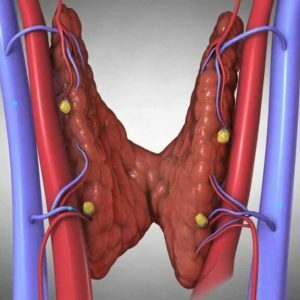
The mechanism of development of a secondary type of pathological condition is compensatory.PTH secretion increases in response to prolonged hypocalcemia and calcium-phosphorus metabolism disorders, characteristic of hypovitaminosis D, CRF, and malabsorption syndrome.
The tertiary variety is due to the formation of an independently acting parathyroid adenoma.It occurs against the background of a prolonged course of secondary hyperparathyroidism in the absence of adequate therapy.
Note: in some cases diagnoses such a pathology as pseudo-hyperparathyroidism.He appears against a background of cancerous tumors of different localization.Some malignant formations are capable of synthesizing a substance similar to parathyroid hormone.
Mechanism of pathological process
The main manifestation of parathyroid gland pathology is the excess parahormon .Under its influence, phosphorus and calcium ions are washed out of the bone tissue.Their level in the blood increases accordingly.A high level of Ca + in plasma promotes an increase in diuresis and the appearance of muscle weakness.
Active excretion of calcium salts with urine leads to the formation of stones( stones) and the deposition of these mineral elements in the parenchymal tissue of the kidneys.Thus, urolithiasis and nephrolithiasis develop.
Hypercalcemia adversely affects vascular walls, increasing their resistance to blood flow.The consequence of this process is hypertension( increased blood pressure).
Symptoms of hyperparathyroidism
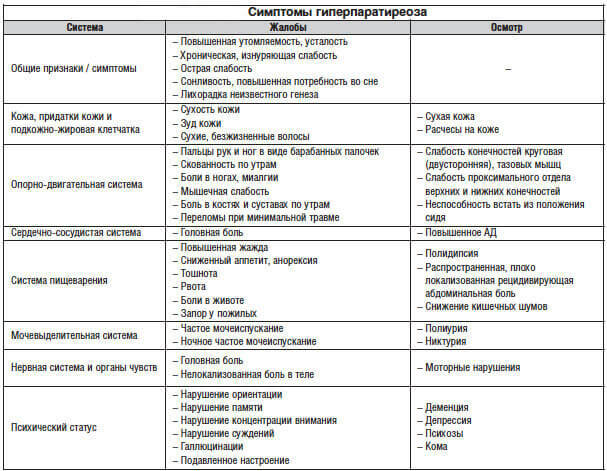
In some cases, this endocrinopathy occurs without any clinical manifestations, and is detected quite accidentally during laboratory diagnostics.
Early symptoms of hyperparathyroidism:
- muscle weakness;
- high fatigue even with low physical exertion;
- problems with walking( "climbing" gait);
- emotional instability;
- unmotivated sense of anxiety;
- depression;
- deterioration of the ability to memorize.
 Note: against the backdrop of a prolonged course of pathology, the patient's skin covers acquire an earthy-gray hue.In elderly and senile patients, development of severe mental disorders is not ruled out.
Note: against the backdrop of a prolonged course of pathology, the patient's skin covers acquire an earthy-gray hue.In elderly and senile patients, development of severe mental disorders is not ruled out.
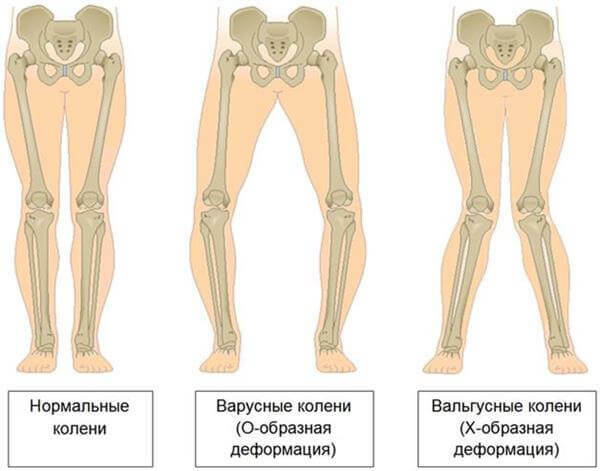
Quite often, patients develop concurrent urolithiasis and peptic ulcer, as well as osteoporosis, which is accompanied, in particular, by the bending of the tubular bones of the lower extremities .With neglected hyperparathyroidism, pathological fractures can occur with normal movements.The defeat of the jaw bone leads to abnormal mobility and the loss of healthy teeth.Patients often complain of pain in different bones and the spine.Fractures are not accompanied by an intense pain syndrome, but they fuse together for a very long time;Quite often, thus forming the so-called.False joints.Deposits-calcinates are formed in the limb joints region.In the course of the examination in the neck area, the formation of significant dimensions - the adenoma of the parathyroid gland - is usually palpable.
Note: pathology is often accompanied by various deformations of the skeleton. can be diagnosed as a flatfoot, a curvature of the spine and a decrease in growth.
Clinical manifestations of the visceropathic form are nonspecific, and gradually increase.
Frequent symptoms:
- nausea;
- gastralgia( pain in the stomach);
- decreased appetite;
- vomiting;
- increased gassing in the intestine;
- rapid and significant weight reduction.
 During the examination, patients are diagnosed with cholecystitis, pancreatitis and peptic ulcers.
During the examination, patients are diagnosed with cholecystitis, pancreatitis and peptic ulcers.
Patients complain of a constant painful thirst.Daily diuresis markedly increases, and in the course of laboratory studies, a decrease in the density of urine is detected.For the late stages of hyperparathyroidism, nephrocalcinosis and renal failure are associated with poisoning of the body with toxins( uremia).
Calcium deposits in the walls of blood vessels lead to a decrease in their elasticity and sclerosis.As a consequence, trophic tissue decreases.The defeat of the heart vessels often becomes the cause of angina attacks.
Calcium salts can be deposited in the cornea and conjunctiva.The sign of this process is the so-called."Red eye syndrome"( reddening of the sclera with the appearance of hemorrhages).
The hypercalcemic crisis is considered as one of the most serious complications of parathyroid gland pathology .He poses a serious threat to the life of the patient.
Risk factors for the development of the crisis:
- long stay on bed rest;
- uncontrolled intake of calcium preparations;
- Vitamin D hypervitaminosis.
Complications can also be caused by long-term use of thiazide diuretics, which reduce the excretion of calcium in the urine.
The hypercalcemic crisis is characterized by a sharp onset with exacerbation of all previously manifested symptoms.
Important: lethality at a crisis is more than 30%!
Symptoms of acute condition:
- hyperthermia( 39 -40 ° C);
- vomiting;
- intensive pain syndrome with localization in the epigastric region;
- drowsiness;
- marked weakness;
- dehydration( dehydration);
- confused consciousness;
- coma.
The most serious problems in this situation are the myopathy of the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, bleeding, thrombosis and possible pulmonary edema.Often the perforation of the existing ulcers of the stomach and duodenum develops.
Note: crisis occurs when the level of calcium in the blood increases to 3.5-5 mmol / l( the upper limit of the norm is 2.5 mmol / l).
Diagnosis
Since the primary form of hyperparathyroidism does not have specific manifestations, the diagnosis presents certain difficulties.
For the detection of endocrinopathy, urine test is required.At a pathology in it the raised level of phosphorus and calcium is revealed.Relative density is lowered, protein is often found, and in the sediment there are cylinders( hyaline and granular).
Blood is examined for calcium, phosphorus, alkaline phosphatase and parathyroid hormone levels.Ca and phosphatase are increased, and P - is lowered.An important diagnostic criterion is the serum concentration of parathyroid hormone 5-8 ng / ml( normal limits - 0.15-1 ng / ml).
Paratireodenomas with typical localization are detected during ultrasound scanning.Additionally, the patient is referred for X-ray diagnostics, computer and magnetic resonance imaging and scintigraphy.
X-ray images show osteoporosis and other pathological changes in bone tissue.
Note: is very informative hardware diagnostic method is densitometry.This is a kind of roentgenography, which is necessary to assess the mineral density of bones.
X-ray examination with contrast agent( barium salt) allows to identify ulceration of the mucous membranes of the gastrointestinal tract.
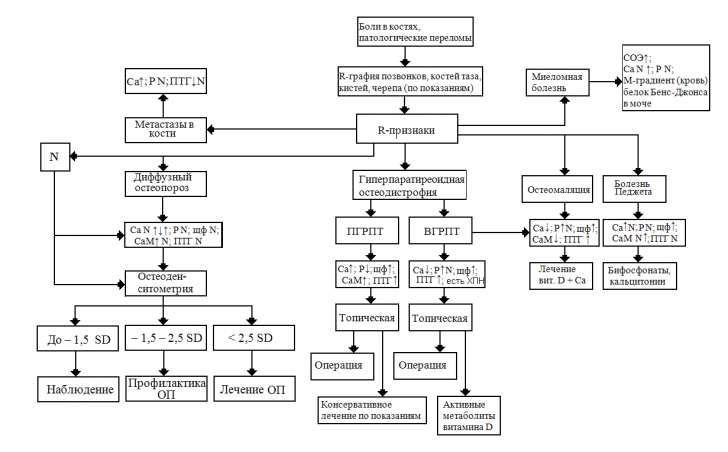
Computed tomography shows calculi in the kidney and urinary tract.
When suspected of secondary hyperparathyroidism, the main task of the diagnostician is to identify the underlying pathology.
How is hyperparathyroidism treated?
Therapy of this endocrinopathy should be comprehensive.It implies surgery and pharmacotherapy.
In the course of the operation, which is the "gold standard" of treatment, resection of the tumor is performed, and with hyperplasia - glands entirely. At present, minimally invasive techniques for the removal of pathologically altered tissues through endoscopic devices have been developed.
The hypercalcemic crisis is an unconditional indication for emergency surgical intervention. In the pre-operative period, measures are taken to reduce the level of hypercalcemia.They include IV administration of saline and a plentiful drink.If there are no signs of renal failure, diuretics( Lasix) and 5% glucose are prescribed in parallel.The administration of calcitrine( with continuous monitoring of serum calcium levels) is also indicated.In parallel, hormonal therapy is performed( a patient with crisise is given glucocorticoids).
Important: if the kidney form of endocrinopathy is not timely performed, patients die from progressive renal failure and exhaustion.
If a cancer tumor has been diagnosed, then after its removal a course of radiotherapy is performed.In parallel with irradiation, a prospective antitumor drug Plikamycin is prescribed.
Please note: because after the operation, the content of Ca in the plasma usually decreases substantially in patients, vitamin D is prescribed for its better absorption. In some situations, the introduction of calcium salts can be indicated.
With early diagnosis and timely complex therapy, the prognosis is quite favorable.How quickly the work capacity will be restored depends on the severity of osteoporosis;The normalization of bone tissue is required from 4 months to 2 years or more.In severe cases, deformations persist for life.
Prevention of hyperparathyroidism implies sufficient intake of foods rich in vitamin D( fish of fatty varieties, cheese, butter) and daily walks in the fresh air.It is also advisable to take an oral aqueous or oily vitamin D solution( for example, Aquadetrim).
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer