Hyperaldosteronism: Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
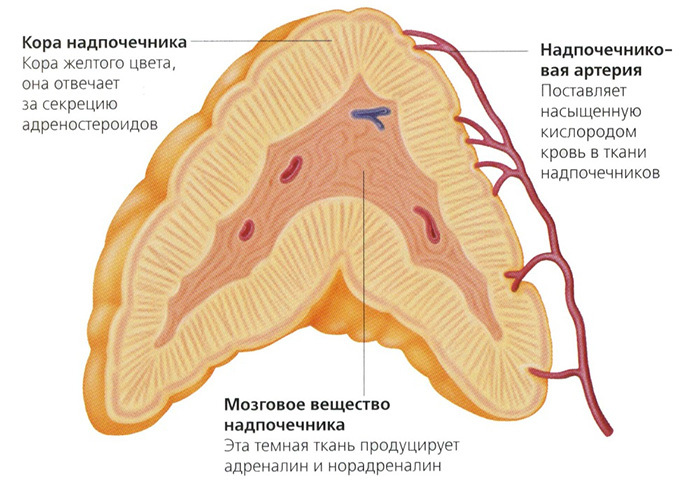
 Hyperaldosteronism is an endocrine pathology that is characterized by increased secretion of aldosterone.This mineralocorticosteroid hormone, synthesized by the adrenal cortex, is necessary for the body to maintain an optimal balance of potassium and sodium.
Hyperaldosteronism is an endocrine pathology that is characterized by increased secretion of aldosterone.This mineralocorticosteroid hormone, synthesized by the adrenal cortex, is necessary for the body to maintain an optimal balance of potassium and sodium.
This condition is primary, with hypersecretion due to changes in the adrenal cortex itself( for example, with adenoma).There is also a secondary form of hyperaldosteronism, caused by changes in other tissues and excessive production of renin( a component responsible for the stability of blood pressure).
Note: about 70% of the cases of primary hyperaldosteronism detected are women from 30 to 50 years old.
The increased amount of aldosterone negatively affects the structural and functional units of the kidneys( nephrons).In the body, sodium is retained, and the excretion of potassium, magnesium and hydrogen ions, on the contrary, is accelerated.Clinical symptoms are more pronounced in the primary form of pathology.
Table of contents: Causes of hyperaldosteronism How does the pathological process proceed?Symptoms of hyperaldosteronism Diagnosis of hyperaldosteronism How is hyperaldosteronism treated?How to prevent hyperaldosteronism?Causes of hyperaldosteronism
 The concept of "hyperaldosteronism" unites a number of syndromes, the pathogenesis of which is different, and the symptomatology is similar.
The concept of "hyperaldosteronism" unites a number of syndromes, the pathogenesis of which is different, and the symptomatology is similar.
In almost 70% of cases, the primary form of this disorder does not develop with the background of the Connes syndrome.With him, the patient develops aldosteroma - a benign tumor of the adrenal cortex that causes hypersecretion of the hormone.
An idiopathic type of pathology is a consequence of bilateral hyperplasia of the tissues of these paired endocrine glands.
Sometimes, primary hyperaldosteronism is caused by genetic disorders.In some situations, a malignant neoplasm becomes an etiological factor, which can secrete deoxycorticosterone( a secondary hormone of the gland) and aldosterone.
Secondary form is a complication of pathologies of other organs and systems.It is diagnosed in such serious diseases as cirrhosis, malignant hypertension, CRF, etc.
Other causes of increased renin production, and the appearance of secondary hyperaldosteronism include: insufficient intake or active excretion of sodium
- ;
- dehydration;
- large blood loss;
- excess alimentary intake of K +;
- abuse of diuretics and laxatives.
If the distal tubules of nephrons do not adequately react to aldosterone( at its normal plasma level), pseudohydaldosteronism is diagnosed.In this condition, a low level of K + ions is also present in the blood.
Note: is of the opinion that secondary hyperaldosteronism in women is capable of provoking the use of oral contraceptives.
How does the pathological process proceed?
For primary hyperaldosteronism, low levels of renin and potassium, hypersecretion of aldosterone and high blood pressure are characteristic.
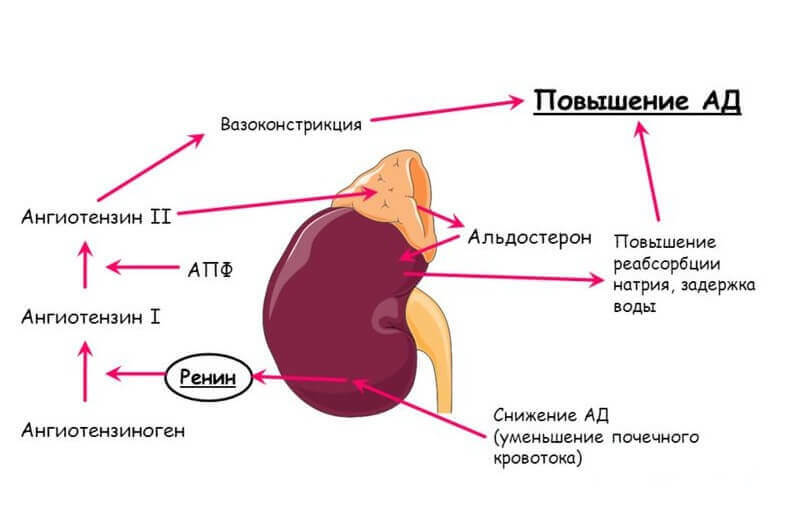
The pathogenesis is based on a change in the water-salt ratio.Accelerated excretion of K + ions and active reabsorption of Na + leads to hypervolemia, water retention in the body, and an increase in blood pH.
Note: shift of blood pH in the alkaline side has been termed metabolic alkalosis.
 In parallel, the production of renin is reduced.In the walls of the peripheral blood vessels( arterioles) Na + accumulates, as a result of which they swell and swell.As a consequence, the resistance to blood flow increases, and blood pressure rises.Long hypocalcemia causes dystrophy of the musculature and renal tubules.
In parallel, the production of renin is reduced.In the walls of the peripheral blood vessels( arterioles) Na + accumulates, as a result of which they swell and swell.As a consequence, the resistance to blood flow increases, and blood pressure rises.Long hypocalcemia causes dystrophy of the musculature and renal tubules.
With secondary hyperaldosteronism, the mechanism of development of the pathological condition is compensatory.Pathology becomes a kind of response to the reduction of renal blood flow .There is an increase in the activity of the renin-angiotensin system( which increases blood pressure) and an increase in renin production.Significant changes from the water-salt balance are not observed.
Symptoms of hyperaldosteronism
Excess sodium leads to an increase in blood pressure, an increase in the volume of circulating blood( hypervolemia), and the appearance of edema.Lack of potassium causes chronic constipation and muscle weakness.In addition, with hypokalemia, the kidneys lose the ability to concentrate urine, and electrocardiograms show characteristic changes.Perhaps the appearance of convulsive attacks( tetany).
Signs of primary hyperaldosteronism:
- arterial hypertension( manifested by increased blood pressure);
- of cephalalgia;
- cardialgia;
- drop in visual acuity;
- sensitivity disorders( paresthesia);
- convulsions( tetany).
Important: in patients with symptomatic arterial hypertension, in 1% of cases it is precisely primary hyperaldosteronism that is found.
 Against the backdrop of fluid retention and sodium ions in the body, a moderate or very significant increase in blood pressure appears in the body.The patient is concerned about pain in the region of the heart( noisy and medium intensity). During the examination, arrhythmia and tachycardia are often noted.Against the background of arterial hypertension falls visual acuity.When viewed from an ophthalmologist, retinal pathologies( retinopathy) and sclerotic changes in the vessels of the fundus are revealed.Daily diuresis( the volume of urine separated) in most cases increases.
Against the backdrop of fluid retention and sodium ions in the body, a moderate or very significant increase in blood pressure appears in the body.The patient is concerned about pain in the region of the heart( noisy and medium intensity). During the examination, arrhythmia and tachycardia are often noted.Against the background of arterial hypertension falls visual acuity.When viewed from an ophthalmologist, retinal pathologies( retinopathy) and sclerotic changes in the vessels of the fundus are revealed.Daily diuresis( the volume of urine separated) in most cases increases.
Potassium deficiency is the cause of rapid physical fatigue.In different muscle groups, periodic pseudoparalities and convulsions develop.Episodes of muscle weakness can be triggered not only by physical exertion, but also by psychoemotional stresses.
In particularly severe clinical cases, primary hyperaldosteronism leads to diabetes insipidus( renal genesis) and marked dystrophic changes in the heart muscle.
Important: If there is no heart failure, then the primary form of the condition does not cause peripheral edema.
Symptoms of the secondary form of the condition:
- Hypertension;
- chronic renal failure( CRF);
- significant peripheral edema;
- changes in the fundus.
A secondary type of pathology is characterized by a significant increase in blood pressure( "lower"> 120 mm Hg).It eventually becomes the cause of changes in the walls of blood vessels, oxygen starvation of tissues, hemorrhages in the retina of the eye and chronic renal failure .Low levels of potassium in the blood are rarely detected.Peripheral edema is one of the most typical clinical signs of secondary hyperaldosteronism.
Note: sometimes a secondary type of pathological condition is not accompanied by an increase in blood pressure.In such cases, as a rule, it is a question of pseudo-hyperaldosteronism or genetic disease - Bartter's syndrome.
Diagnosis of hyperaldosteronism
The following types of clinical and laboratory studies are used to diagnose various types of hyperaldosteronism:
-
 ultrasound scanning;
ultrasound scanning; - computed tomography( CT);
- magnetic resonance imaging( MRI);
- blood test "for biochemistry";
- urinalysis;
- scintigraphy;
- selective venography.
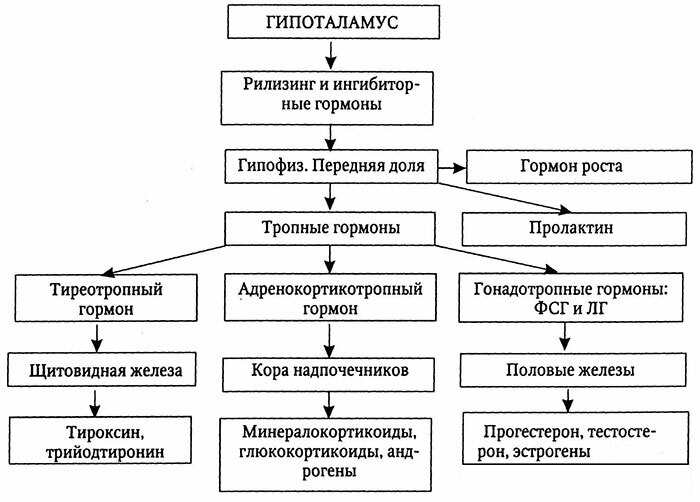
First of all, the K / Na balance, the state of the renin-angiotensin system is studied and the level of aldosterone in urine is revealed.Analyzes are performed both at rest and after special loads( "march", hypothiazide, spironolactone).
One of the important indicators at the initial stage of the survey is the level of adrenocorticotropic hormone( from ACTH depends on the production of aldosterone).
Diagnostic parameters of the primary form:
- level of aldosterone in plasma is relatively high;
- plasma renin activity( ARP) is decreased;
- potassium level is lowered;
- the sodium level is elevated;
- aldosterone / renin ratio high;
- relative density of urine is low.
Increased daily excretion in the urine of aldosterone and potassium ions.
Secondary hyperaldosteronism is indicated by an increase in ARP.
Note: if the condition can be corrected by the administration of glucocorticoid hormones, is practiced so-called.Trial treatment with prednisolone.With its help, BP stabilizes and other clinical manifestations are eliminated.
In parallel, the study of the state of the kidneys, liver and heart using ultrasound, echocardiography, etc. .It often helps to identify the true cause of the development of a secondary type of pathology.
How is hyperaldosteronism treated?
Medical tactics are determined by the form of the condition and the etiological factors that led to its development.
The patient undergoes a comprehensive examination and treatment with an endocrinologist.A nephrologist, an ophthalmologist and a cardiologist are also required.
If excessive hormone production is caused by a tumor process( reninoma, aldosteroma, adrenal cancer), then surgery( adrenalectomy) is indicated. During the operation, the affected adrenal gland is removed.Hyperaldosteronism of other etiology shows pharmacotherapy.
 A good effect is achieved by low-salt diet and consumption of potassium-rich products .In parallel, potassium preparations are prescribed.Drug treatment involves prescribing a patient with potassium-sparing diuretics to fight hypokalemia.It is also practiced during the preparation for surgery for general improvement of the condition.With bilateral organ hyperplasia, Amyloride, Spironolactone, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are shown in particular.
A good effect is achieved by low-salt diet and consumption of potassium-rich products .In parallel, potassium preparations are prescribed.Drug treatment involves prescribing a patient with potassium-sparing diuretics to fight hypokalemia.It is also practiced during the preparation for surgery for general improvement of the condition.With bilateral organ hyperplasia, Amyloride, Spironolactone, and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors are shown in particular.
Hormone therapy( with forms corrected by glucocorticoids) requires the patient to receive Dexamethasone or Hydrocortisone.
Treatment of secondary hyperaldosteronism necessarily includes therapy of the underlying disease.During course therapy, the serum potassium content is regularly monitored and an electrocardiogram is taken.
If the cause of the pathology is stenosis of the renal arteries, reconstructive procedures and stenting of the affected vessel are practiced.
Important: In malignant tumors, the prognosis is usually disappointing.In other cases, early diagnosis and adequate complex therapy give a good chance of recovery.
How to prevent hyperaldosteronism?
Regular prophylaxis of people with identified liver and kidney diseases, as well as hypertension, is important to prevent the development and progression of pathology.They must strictly observe the prescriptions of the attending physician and adhere to the low-salt diet.It is also advisable to consume foods rich in potassium.
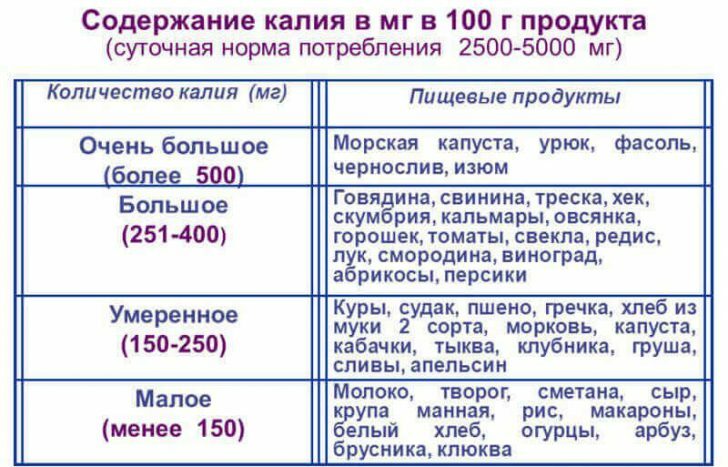
List of products containing high potassium content:
- dried apricots;
- raisins;
- prunes;Beans and other leguminous crops;
- ;
- potatoes;
- sea kale;
- pine nuts;
- peanuts;
- hazelnut( hazel);
- walnuts;
- mustard.
Vladimir Plisov, medical reviewer