Hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism
Hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism( hyperprolactinemia syndrome) is a neuroendocrine pathology due to the hypersecretion of prolactin( anterior pituitary hormone).With this condition, a number of somatic and hormonal disorders develop.
The syndrome of hyperprolactinemia is detected in 0.07% of men and 0.5% of women;It refers to the most frequently diagnosed hypothalamic-pituitary disorders.
Note: is precisely this pathology found in 70% of patients suffering from infertility.
Increasing the level of prolactin can be physiological( during childbearing and feeding the baby) and pathological.In some cases, hyperprolactinaemia is asymptomatic, and is only detected during laboratory biochemical studies.
Endocrinologists, as well as andrology and gynecologists are engaged in the treatment of the disorder.
Table of contents: Why and how does hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism occur?How does the syndrome manifest?Diagnosis Treatment methodsWhy and how does hyperprolactinaemic hypogonadism occur?
Pathology can be primary( independent) or proceed in parallel with other disorders from the hypothalamic-pituitary system.Neuroendocrine disorder is also symptomatic.
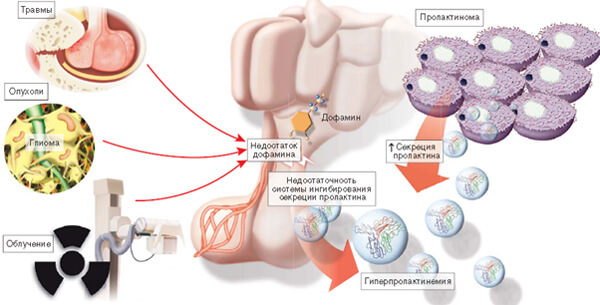
Primary hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism occurs in pituitary adenomas( prolactinomas).In some cases, an idiopathic form is diagnosed, which has nothing to do with neoplasms.The cause of its occurrence is not currently established.
Hypothalamic-pituitary dysfunctions that may be accompanied by hyperprolactinaemia:
- Itzenko-Cushing's disease;
- tumors( hormonally inactive);
- lymphocytic hypophysitis;
- acromegaly;
- syndrome of an empty Turkish saddle;
- craniopharyngioma( benign neoplasm).
Note: hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism is often combined with chronic intracranial hypertension( increased intracranial pressure).
The causes of symptomatic hyperprolactinemia include:
- chronic inflammation of the prostate;
- polycystic ovary;
- hypothyroidism( deficiency of thyroid hormones);
- renal failure;
- cirrhosis;
- long-term use of certain pharmacological agents( antidepressants, oral contraceptives, Aminazine, etc.).
Regardless of the etiology of this neuroendocrine disorder, the main factor in its development is the absence or significant decrease in the effect of dopamine.Normally, this neurotransmitter blocks the excessive secretion of prolactin.Endogenous hormones and medications are capable of breaking this process, which is observed with symptomatic hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism.
Primary form initially develops hyperplasia of cells responsible for the synthesis of prolactin, and in the course of time a benign pituitary tumor is formed.
How does the syndrome manifest?
In pathology, there is a whole complex of metabolic, reproductive, mental( personal) and sexual disorders.
Clinical signs of pathology in women:
- pathological galactorrhea( milk excretion, not associated with infant feeding);
-
 hirsutism( pathological hairiness);
hirsutism( pathological hairiness); - dysmenorrhea( impaired menstrual function);
- obesity;
- infertility;
- vaginal dryness;
- decreased libido;
- frigidity;
- anorgasmia;
- psychogenic pain in sexual intercourse;
- macromastia( abnormal increase in breast size).
Excess prolactin in women inhibits the release of gonadoliberin, luteinizing and follicle-stimulating hormones.Against this background, ovarian dysfunction develops, characterized by a lack of estrogens and an excess of androgens.
Note: Prolactin can significantly accelerate the biotransformation of carbohydrates into lipids, which contributes to obesity.
 If the syndrome develops in patients before the onset of puberty, the underdevelopment of the vulva and uterus is diagnosed.Women of fertile age are diagnosed with dysmenorrhea.The absence of ovulation leads to infertility of the neuroendocrine genesis.
If the syndrome develops in patients before the onset of puberty, the underdevelopment of the vulva and uterus is diagnosed.Women of fertile age are diagnosed with dysmenorrhea.The absence of ovulation leads to infertility of the neuroendocrine genesis.
The severity of galactorrhea( flow volume) varies from a few drops with mechanical stimulation of the mammary glands, to profuse spontaneous secretion secretion.
The cause of macromastia( usually bilateral) is the early fat involution of the mammary glands.
Hirsutism is manifested by the appearance of hair in atypical for women zones - along the white line of the abdomen, around the nipples and on the face.
Characteristic disorders in men:
- decreased sexual desire;
- erectile dysfunction( impotence);
- gynecomastia( enlargement of mammary glands);
- galactorrhea;
- infertility.
A high level of prolactin in the blood of men inhibits the production of the main male sex hormone - testosterone and its transformation into dihydrotestosterone.The secretory function of testicles is suppressed, which leads to a serious disruption of the process of sperm formation. Spermogram analysis shows a decrease in the amount or complete absence of viable germ cells in the ejaculate.
 If hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism has developed in the preubertal period, boys are underdeveloped with genital organs.Very characteristic delay in the appearance( or absence) of secondary sexual characteristics, and with hyperprolactinaemia in adulthood, their regression takes place.
If hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism has developed in the preubertal period, boys are underdeveloped with genital organs.Very characteristic delay in the appearance( or absence) of secondary sexual characteristics, and with hyperprolactinaemia in adulthood, their regression takes place.
If the cause of the syndrome becomes prolactinoma, the patients develop metabolic disorders and neurological symptoms of .The tumor can squeeze the intersection of the optic nerves;As a result, visual acuity decreases, and the fields of vision narrow.The growth of the adenoma can provoke swelling of the optic nerve, hydrocephalus or an increase in intracranial pressure.Compression of the posterior lobe of the pituitary gland with prolactinoma causes diabetes insipidus.Germination of the neoplasm in the sphenoid sinus is manifested by the flow of cerebrospinal fluid from the nasal passages.
Important: among the frequent complaints of patients with the pituitary prolactinoma include cephalgia( headaches of varying intensity).
The frequently occurring metabolic complications of hyperprolactinemic hypogonadism are insulin resistant diabetes mellitus and osteoporosis( a pathology characterized by a change in the structure of bone tissue).
Patients with this neuroendocrinopathy are prone to depression.They often complain of increased fatigue, sleep disturbance and impaired memory ability.
Diagnostics
One of the most important diagnostic tasks is the detection of etiological factors.
During the complex examination of the patient repeatedly determine the level of prolactin in the serum.Diagnostic criterion is considered to increase the indicator in 3 or more samples( exceeding the norm is possible by hundreds of times). Moderate hyperprolactinemia is fixed, for example, with a decrease in thyroid function.Figures less than 200 ng / ml allow to suspect an idiopathic version of a syndrome or development of a microadenoma, and more than 200 ng / ml - a macroadenoma.
The apparatus methods of examination include radiography of the skull, and MRI of the brain.The most informative tomography of the hypothalamic-pituitary region.
In parallel, the state of the organs of the reproductive system and thyroid gland is investigated( ultrasound scanning and analysis of hormonal indices).In male patients, the spermiogram parameters are necessarily evaluated.
For the detection of osteoporosis, densitometry is used - a kind of X-ray study that allows to draw conclusions about changes in the structure of bone tissue.
Methods of treatment
 The medical tactics directly depend on the identified etiologic factor.If the cause of a neuroendocrinal disorder is the taking of medications, they are canceled or at least reduced the dosage of .When hyperprolactinaemia is caused by hypothyroidism, therapy with thyroid hormone drugs is indicated.
The medical tactics directly depend on the identified etiologic factor.If the cause of a neuroendocrinal disorder is the taking of medications, they are canceled or at least reduced the dosage of .When hyperprolactinaemia is caused by hypothyroidism, therapy with thyroid hormone drugs is indicated.
Hyper secretion of prolactin is suppressed by dopamine agonists.In the treatment of men, androgens and chorionic gonadotropin are often administered in parallel.
Prolactinomas are treated medically or with the use of radiotherapy.If conservative methods are ineffective, they resort to surgical intervention.During the operation, the adenoma of the pituitary is removed by transnasal access( through the nasal passages).
Important: in women in 30-35% of cases occurs spontaneous remission after childbirth or in the menopausal period.
The prognosis for recovery is favorable. As a rule, drug treatment with dopaminomimetic treatment can eliminate manifestations of hyperprolactinemia and normalize reproductive function.
Plisov Vladimir, medical reviewer