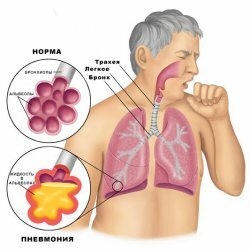
Hemotorax - intrapleural bleeding
 Hemotorax is intrapleural bleeding, due to which blood is collected in the pleural cavity, as a result of which the lung is compressed and the mediastinal organs are mixed in the opposite direction. With hemothorax there is shortness of breath, pain in the chest. There are also signs of acute blood loss, such as pallor of the skin, dizziness, cold sweat, tachycardia, fainting, hypotension.
Hemotorax is intrapleural bleeding, due to which blood is collected in the pleural cavity, as a result of which the lung is compressed and the mediastinal organs are mixed in the opposite direction. With hemothorax there is shortness of breath, pain in the chest. There are also signs of acute blood loss, such as pallor of the skin, dizziness, cold sweat, tachycardia, fainting, hypotension.
Diagnosis of hemothorax is based on physical research. For the treatment of hemothorax use antibacterial, hemostatic, symptomatic therapy, as well as aspiration of accumulated blood. If necessary, then remove the coagulated hemothorax and stop the bleeding.
Hemotorax is the second most frequent complication after traumatizing the chest. In medicine, hemothorax is considered an urgent disease, which requires emergency specialist help.
Causes of hemothorax
There are three groups of causes that most often lead to the appearance of the disease: traumatic, pathological and iatrogenic.
Traumatic causes are penetrating wounds, closed chest injuries. To traumas from which the hemothorax develops, include knife and gunshot wounds, road accidents, broken ribs and others. During such injuries, organs in the thoracic, abdominal cavity are often damaged. Damage is observed in the intercostal vessels, from which the blood is poured into the pleural cavity.
The pathological causes of hemothorax are various diseases: pulmonary tuberculosis, aortic aneurysm, lung cancer, pleural cancer, neoplasms of the chest mediastinum, lung abscess and others.
Iatrogenic factors that lead to the development of hemothorax are complications after operations on the lungs, pleura, thoracocentesis, central vein catheterization, drainage of the pleural cavity.
Pathogenesis of hemothorax
After entering the blood in the pleural cavity develops hemoplethritis - aseptic inflammation of the pleura. During hemothorax, there is swelling and small leukocyte infiltration of the pleura, sloughing and swelling of the mesothelium cells.
At the onset of the disease, the blood that enters the pleural cavity is almost similar to the composition of peripheral blood. Further in the blood there is a decrease in hemoglobin and erythrocyte-leukocyte index. Blood, when it enters the pleural cavity, first folds, but then a re-dilution of blood occurs.
Classification of hemothorax disease
Depending on the etiology, hemothorax can be traumatic, pathological and iatrogenic.
Depending on the amount of internal hemorrhage bleeding, hemothorax happens:
- Small. In this case, blood loss of up to 500 ml, blood accumulates in the sinus;
- Average. At which the volume of blood loss to 1.5 liters, the blood at the level of the lower edge of the IV rib;
- Subtotal. In which blood loss has a volume of up to 2 liters, the blood is at the level of the lower edge of the 2nd rib;
- Total. With it, blood loss of more than 2 liters, with radiographic examination, there is a total blackout of the pleural cavity.
The amount of bleeding depends on the nature of the destruction of the vessels and the location of the wound. Depending on this, small or medium hemothorax is divided, while the peripheral parts of the lung, subtotal and total hemothorax damage during injuries to the roots of the lung and damage to the main vessels with heavy bleeding are damaged.
Also distinguish limited hemothorax, with the disease is small in volume, the blood is collected between pleural spikes, in the area of the pleural cavity.
Given the localization, limited hemothorax can be interlobar, apical, paracostal, over-diaphragmatic, para-diastinal.
If intrapleural bleeding is prolonged, then hemothorax is called increasing. If the bleeding stopped - not increasing, stable hemothorax. Complicated forms of the disease include coagulated, infected hemothorax. If there was a simultaneous ingress of air and blood into the pleura, then hemopneumothorax occurs.
Symptoms of the disease
Clinical symptoms of hemothorax directly depend on the degree of bleeding, displacement of the mediastinal organs, compression of the lung tissue.
During small hemothorax, symptoms are minimal or nonexistent. Patients experience shortness of breath, chest pain, which is worse with coughing.
During the middle hemothorax or large-sized hemothorax, development of respiratory and cardiovascular disorders is observed. Patients complain of severe pain in the chest during breathing or coughing, general weakness, decreased pressure, tachypnea. At the slightest physical exertion, the symptomatology increases.
During severe hemothorax in patients, paleness of the skin, dizziness, weakness, cold sweat, tachycardia, hypotension, fainting, flashing of flies before the eyes are observed.
When hemothorax with a broken rib usually develops soft tissue hematoma, subcutaneous emphysema. If the disease occurs with a rupture of the lung parenchyma, hemoptysis may occur.
Diagnosis of hemothorax
To establish the correct diagnosis, it is necessary to clarify the details of the medical history, to conduct a laboratory, physical and instrumental examination.
During the disease, there is a lag in the diseased side of the chest during breathing, weakening of breathing, voice trembling. When X-ray examinations reveal the presence of a horizontal level of fluid, in the pleural cavity of the clots. Puncture of the pleural cavity gives precise results of hemothorax disease.
Additional diagnostic studies are ultrasound of the pleural cavity, diagnostic thoracoscopy.
Treatment of the disease
Patients with hemothorax require hospitalization in special surgical departments. There they are watched by a thoracic surgeon. For the aspiration of the blood, the pleural cavity is drained. To this end, antibiotics, antiseptics and proteolytic enzymes are introduced into the drainage. Conservative treatment of hemothorax consists of symptomatic, hemostatic, disaggregant, immunocorrective therapy, general oxygen therapy, antibiotic therapy.
Small hemothorax is usually eliminated by a conservative method. Surgical treatment of hemothorax is prescribed in cases of prolonged intrapleural bleeding;Damage to vital organs.
Prognosis and prevention of the disease
Depending on the injury or disease, blood loss, timely surgical care depends on the success of hemothorax treatment. With a small and medium hemothorax, the prognosis is usually favorable. With the folded hemothorax, there is the possibility of developing pleural empyema. A long-term intrapleural bleeding can lead to death.
Patients who underwent haemothorax during rehabilitation are recommended to practice swimming, respiratory gymnastics.