Hammen-Richie's disease( idiopathic fibrosing alveolitis)
The history of the detection of fibrosing alveolitis
For the first time about this disease, Hammen and Richie were told in 1933, describing four strange cases of unknown lung damage that ended in six months of the death of the sick.
By 1960, more and more information about such cases began to appear in the medical literature. Acute and chronic manifestations have undergone close examination by physicians. In 1964, scientist Skeding made a discovery - he found that the inflammation affects the alveolar areas of the lungs directly and suggested that this pathology be designated as fibrosing alveolitis. At present, this term unites several pathological states of non-clear origin, combined by the similarity of X-ray changes, clinical picture and the progression of pulmonary fibrosis.
It should be noted that the alveolitis - the response of the body to various agents - viruses, bacteria, fungi, allergic stimuli. Therefore this term is a stage of pathomorphological changes, and not the name of any nosology.
All alveolites are divided into two groups:
- Known etiology( toxic, allergic, etc.),
- Unknown etiology( idiopathic).
It is worth noting the tendency of the growth of cases of fibrosing alveolitis, which, firstly, is due to a true increase in cases, and secondly, to an improvement in the quality of diagnosis and a more correct diagnosis.
Why does this disease occur?
The etiological causes of fibrosing alveolitis, despite numerous studies, are not yet clear. There are several hypotheses and versions. According to one of them, this is an autoimmune response of the body, as a result of which too many hyperergic reactions occur in the interstitium of the lung tissue. There are versions that there are actually several reasons, and their combination is an etiological factor. Among these reasons it is necessary to allocate: bacterial, viral, allergic agents, immune failure of the body, exposure to various toxins, etc.
If we talk about the fibrosing alveolitis as an autoimmune process, it should be attributed to the group of collagenoses( Nasonova VA А.1978G).But the process only affects the connective tissue of the lungs.
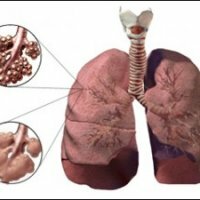
Changes in the lungs in the case of Hammen-Richie's disease
The main process that characterizes fibrosing alveolitis is a block in the alveolar-capillary system. The function of the lungs directly depends on the severity of this pathological process. The clinical picture is caused by a decrease in gas exchange function of the lungs, a decrease in the amount of oxygen in the blood and the occurrence of respiratory insufficiency. The origin of the block is due to metaplasia of the alveolar epithelium. As a result, the interalveolar septum is fibrosed and capillary contact with air ceases, as a result of which gas exchange occurs.
Specific gravity of the connective tissue that surrounds the alveoli increases threefold, and the thickness of the membrane - twice as compared with the original. The ongoing process of degeneration of normal functional tissue into collagen is irreversible, which causes a steady progression of the disease.
Two destructive processes alternately predominate in different phases of the disease:
- Desquamation;
- Fibrosis.
So, successively in the lung tissue there are several pathological stages: edema, fibrosis inflammation.
Pathomorphologically, there are 5 degrees of fibrosing alveolitis:
- I - swelling of septum between alveoli and capillaries, excessive tortuosity of capillaries and cellular infiltration;
- II - there is effusion of serous fluid in the lumen of the alveoli, which leads to their adhesion.
- III - the pathological process includes small bronchioles, where cysts are formed and the structure is broken;
- IV - Cysts gradually increase in size, which completely destroys the normal structure of lung tissue;
- V - Formation of "cellular lung".
As a result of hypoxia, a reflex narrowing of the vessels takes place directly in the lungs themselves, which leads to an increase in pressure in the small circle of the circulation and the formation of a pulmonary heart.
Clinical picture of fibrotic alveolitis
Middle-aged people are more prone to the onset of this disease. Men get sick more often than women twice.
As a rule, patients do not notice the onset of the disease. They can connect the appearance of dyspnea with ARI, physical exertion, heart problems.
Dyspnea is the earliest sign of fibrosing alveolitis, but in 15% of the disease starts with the symptoms of cough. Patients can not take a deep breath "whole chest".Very rarely, the body temperature rises( 38-39 ° C).
Cough by nature is dry, painful. Sputum mucous, poor. Sometimes there is hemoptysis.
Pain occurs during coughing or when inhaled and localized under the scapula( lower corners).Patients strongly lose weight. Complained of causeless joint pain( 10%), in muscles, severe weakness and rapid fatigue. Often there is an unreasonable low-grade fever, exhausting the patient. There may be a picture of Raynaud's syndrome.
Inspection of the patient
The first thing that catches the eye is the cyanosis of the patient, which may be different, depending on the stage of the disease. Symptoms of "drum sticks" and "watch glasses" are noted.
Auscultation
Palpitation is rapid, an accent of tone II over the pulmonary artery is possible. On inspiration, you can hear crepitus against a background of weakened vesicular breathing. What is characteristic - with forced breathing, the character of wheezing changes - they become more intense.
Percussion
When tapping, a shortening of the pulmonary sound over the affected area is detected.
Diagnosis
Blood test
- Leucoformula shift left, leukocytosis and ESR increase. Hematocrit within normal parameters.
- In biochemical analysis, there is disproteinemia, an increase in gamma globulins and sialic acids.
- A rheumatropic test will show an increase in C-reactive protein. Antinuclear antibodies can also be detected.
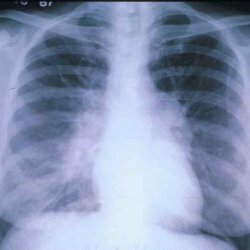
X-ray
The images show a strengthening of the pulmonary pattern due to the growth of connective tissue, which is more intense around the periphery. Cystic cavities are manifested areas of enlightenment. The motion of the diaphragm is limited.
Physiological tests allow us to detect a decrease in GEL and OEL, hypoxemia, lung resistance, an increase in the minute volume of the heart.
Treatment
Conservative methods involving the use of corticosteroids and immunosuppressants. It is widely used also kurenenil.
Symptomatic therapy consists in the appointment of veroshpiron( to reduce edema), B group vitamins, potassium and digitalis preparations( to improve cardiac activity).