All about tuberculous pleurisy
 Acute chronic or relapsing tubercular inflammation of the pleura that occurs when one of the forms of tuberculosis is complicated is called tuberculous pleurisy. As a rule, tubercular pleurisy can be observed with pneumonia. In rare cases, it can be formed as a clinical form that has been formed by itself, thus, the organs can not be affected by tuberculosis and be the primary manifestation of tuberculosis infection in the human body.
Acute chronic or relapsing tubercular inflammation of the pleura that occurs when one of the forms of tuberculosis is complicated is called tuberculous pleurisy. As a rule, tubercular pleurisy can be observed with pneumonia. In rare cases, it can be formed as a clinical form that has been formed by itself, thus, the organs can not be affected by tuberculosis and be the primary manifestation of tuberculosis infection in the human body.
Causes of tuberous pleurisy
The ways of pleural tuberculosis can be very different:
- lymphogenous;
- is hematogenous;
- pin;
In its essence, tubercular pleurisy can be the only source of manifestation of the disease or it can combine its presence with other forms of tuberculosis.
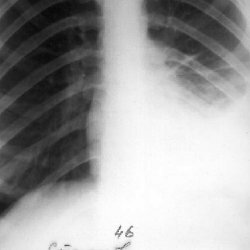
Lymphogenous or hematogenous infection on the pleura sheets occurs with the appearance of a number of rashes in the form of tubercles, and in the pleural cavity a serous-fibrinous exudate is formed. In the event that the process progresses and the tuberculosis granulomas break up, the process becomes hemorrhagic. If an involution of the process occurs, the effusion begins to resolve, the pleura becomes thicker, and the cavity is completely or partially obliterated.
Subpleural localization of an infected lung with tuberculosis implies a contact method for the development of tuberculosis and, as a rule, its spread occurs on the pleura. Most of the patients are confined to the local inflammatory reaction with inflammation of the pleura. On the pleura of the visceral species, rashes appear in the form of tubercles, fibrinous overlays, granulation tissues, and effusion may appear in the pleural cavity. If fibrins and granulations are organized, then there is a fusion between the visceral sheets and the pleura of a parietal nature.
There is one more variant of development of a contact way of pleural tuberculosis. It involves the direct entry of infection into the cavity of the pleura from the infected lung. This can happen if the decay of the caseous masses, which are located subpleurally, into the cavity of the pleura occurs. As a result, openings are formed through which the caseous masses, the composition of the cavity, and sometimes air are seeping. In the cavity of the pleura, infection with microbacteria occurs and a partial or complete decay of the lung occurs, resulting in the development of acute tuberculosis empyema. It leads to the appearance of tuberculous pleurisy in the body.
Symptoms of tuberous pleurisy
One of the main symptoms of tuberculous pleurisy are severe pains in the chest that are amplified by deep breaths, talking or coughing; in addition, dyspnea, malaise, persistent cough, weakness in the body, and fever.
If tuberculous pleurisy is dry, then in addition to the above symptoms there is a friction noise in the pleura. This noise can be determined by listening to a phonendoscope. If the disease is not complicated, then full recovery occurs within 7-10 days.
If the disease occurs with complication, the symptoms are accompanied by a rise in temperature to the maximum value, apatite decreases, skin color changes, it becomes yellowish, intoxication develops and an unpleasant odor in the oral cavity is added. With this combination of circumstances, treatment and rehabilitation can take a considerable amount of time.
Diagnosis of tuberculous pleurisy
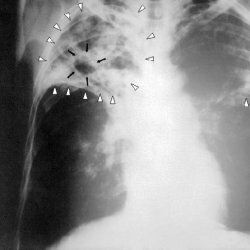
In order to determine the nature of the course of tuberculous pleurisy, one of the important factors is a complete study of pleural effusion. As a rule, the color of serous effusion in tuberculosis is usually a yellowish shade and transparent, its specific gravity is from 1015 to 1025, and the protein content is 3-6%.If the phase of exudation is acute, a small amount of eosinophils appears, as well as abundant cell saturation of mesothelium and erythrocytes.
The presence of cholesteric pleurisy, in which the color of effusions varies from green to brown and the increased amount of cholesterol is due to the presence of tuberculosis infection in the body. The formation of such effusions can be caused only by a prolonged course of serous pleurisy, the duration of the disease is about 20 years. In this case, cellular elements with a high content of cholesterol decay.
Differential diagnosis should be performed with respect to:
- pleurisy in case of nonspecific pneumonia;
- pleurisy with collagenoses;
- pleuritis of the tumor direction;
- of primary pleural cancer.
In modern medicine, the method of studying the biopsy of the parietal pleura with the help of a needle has recently been very popular, and the method itself is called pleuroskopia.
Treatment of tuberculous pleurisy
. Regardless of the form of tuberculous pleurisy, treatment should be of a complex nature. First of all, efforts should be aimed at eliminating the main process of inflammation, which served as a starting point for the manifestation of this disease. The main method of treating tuberculous pleurisy is antibacterial therapy. In acute illness, the patient must comply with the conditions of bed rest, should eat well. All food intake must contain a minimum amount of carbohydrates, they must be limited, and it must contain an increased amount of proteins, fats and vitamins, especially vitamin C.
For tubercular pleurisy, treatment is usually done in several directions:
- the introduction of pain medication;
- the actions directed on acceleration of effect of a resorption of effusion;
- need to prevent complications.
The doctor appoints the patient various analgesics, drugs that prevent inflammation, antibiotics, drugs that help fight cough and allergic reactions. Tuberculous pleurisy should be treated with specific therapy with drugs whose action is aimed at preventing the inflammatory effect. If tuberculous pleurisy occurs as a result of a lung tumor or a tumor of the lymph nodes inside the breast, the treatment should be performed under chemotherapy conditions.
If the pleural cavity is filled with a large amount of fluid, then the procedure for puncture is prescribed. Its goal is to suction unnecessary contents of the pleural cavity and to inject drugs into the cavity.
Treatment is more effective if corticosteroid hormones are used, especially in the early stages of the disease. The duration of taking these hormones should be 3-4 weeks. During the resorption of pleurisy, the doctor prescribes treatment with electrophoresis with calcium and a gymnastics for breathing. During the rehabilitation period, the physician prescribes gymnastics of the respiratory tract, treatment of physiotherapeutic nature and restorative immune therapy.