Meningitis
 Meningitis is an infection that causes inflammatory processes in the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. The causes that cause this disease, in the most frequent cases are all kinds of viruses. For example, one of such viruses is parotitis, when parotid inflammation occurs. Viruses provoke the easiest form of the disease. However, it should be remembered that regardless of the severity of the disease, a person needs isolation and hospitalization.
Meningitis is an infection that causes inflammatory processes in the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. The causes that cause this disease, in the most frequent cases are all kinds of viruses. For example, one of such viruses is parotitis, when parotid inflammation occurs. Viruses provoke the easiest form of the disease. However, it should be remembered that regardless of the severity of the disease, a person needs isolation and hospitalization.
There is also a more severe form of meningitis, the causative agents of which are bacteria, respectively, and the form has the name bacterial. Such pathogens are all known pneumococcus, meningococcus, etc. The consequences of this particular form of meningitis are very sad. It can lead to very serious complications or even death of the patient.
 To avoid this, it is necessary to identify the symptoms in time and start the correct therapy. So - meningitis, symptoms, treatment, consequences - we read more about them in more detail.
To avoid this, it is necessary to identify the symptoms in time and start the correct therapy. So - meningitis, symptoms, treatment, consequences - we read more about them in more detail.
Symptomatic of meningitis
A pathogenic microbe, which most often causes meningitis, lives in our throat. A very large number of people live with this microbe and are its carriers, but they do not suffer from it. The disease that is usually caused by this microorganism is pharyngitis. The disease is absolutely not life-threatening and easy to treat, but there is one thing. .. but with the weakening of the immune system, meningococcal infection through the blood penetrates the CNS( central nervous system) and then through the nerve endings to the brain where it is localized and causes the most severe inflammation. The bacterium itself is transmitted through saliva.
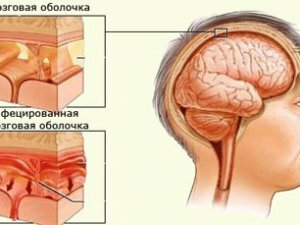 Depending on the pathogen of infection, the symptoms of the disease also differ.
Depending on the pathogen of infection, the symptoms of the disease also differ.
The very first signs for all kinds of meningitis do not differ at all from the common cold. Therefore at an early stage to diagnose the disease is difficult. However, every day, instead of improving, as with colds, we are seeing deterioration.
Meningitis caused by meningococcal
After a while, other symptoms appear.
Meningitis is characterized by:
- severe headache;
- sudden attacks of vomiting;
- high temperature.
These three symptoms are called meningeal syndrome.
Later such as:
- drowsiness,
- convulsions( especially in infants),
- delirium,
- loss of consciousness,
- pinpoint hemorrhages in the form of small purplish-red spots.
Fatal outcome with such meningitis is 50% of cases. With timely therapy, it is reduced to 5%.
Meningitis pneumococcal
For this type of infection in half the cases characterized by a previous disease, sinusitis, otitis or pneumonia. In the second half of cases, the disease comes as primary. It differs in that, even with early hospitalization, it very quickly progresses. Day 3 shows meningeal syndrome.
Almost simultaneously with this:
- Seizures;
- Consciousness disorder;
- Hemiparesis;
- Cerebral Nerve Cuts.
Even when therapy is started on time and hospitalization is made at an early stage, the lethal outcome is up to 25%.
Hemophilus meningitis
This type of meningitis usually affects children under the age of one year. Characteristic of both acute and smooth development. Manifestation of meningeal syndrome usually occurs from the second to the fifth day of the disease.
The main symptoms of the disease for infants under one year:
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Vomiting;
- The rodnichok swells and stops pulsating;
- A shrill scream for no apparent reason;
Viral meningitis
Characteristic of two current waves:
- The first exhibits the usual viral symptoms
- The second wave is a weakly expressed meningeal syndrome. And it can appear as on the second - the third day, so on the seventh and later.
The danger is that the course of the disease is mild and not noticeable. Symptoms of meningitis are not pronounced.
Tuberculous meningitis
It used to be 100% incurable. It occurs frequently, and in most cases as a disease that precedes tuberculosis.
It begins with a fever. On the third-tenth day there is a meningeal syndrome. Nerve cuts and brain disorders occur towards the end of the second week. With a good treatment, a strong complex of antibiotics of lethal outcome can be avoided in the vast majority of cases. In the absence of treatment, the patient dies within a month, because by that time all the brain functions have been completely out of order.
Mutes all symptoms - antibiotic treatment, which can be carried out to get rid of the previous meningitis disease. In this case, the deterioration is sharp and strong, brain atrophy comes just as suddenly.
In case you observe such symptoms, you must call an "ambulance".
How to treat meningitis
 Regardless of the age of the patient, he is treated in a hospital. Treatment of meningitis requires necessarily complex, conservative. The basis of treatment are antibiotics and antiviral drugs, selected individually. In cases where the patient's condition is particularly severe, resuscitation is permitted. With the timely and correct treatment of the disease, it is cured completely, leaving no traces behind. Treatment in general terms can not be recommended, since there is a huge variety of antibiotics, tolerance of which in all people is different.
Regardless of the age of the patient, he is treated in a hospital. Treatment of meningitis requires necessarily complex, conservative. The basis of treatment are antibiotics and antiviral drugs, selected individually. In cases where the patient's condition is particularly severe, resuscitation is permitted. With the timely and correct treatment of the disease, it is cured completely, leaving no traces behind. Treatment in general terms can not be recommended, since there is a huge variety of antibiotics, tolerance of which in all people is different.
In viral meningitis, a lumbar function is used, evacuating the cerebral fluid in a volume of 4 to 6 ml. This procedure brings considerable relief to the patient.
It is important to emphasize the following:
- Non-targeted treatment with rifampicin, aminoglycosides and other antimicrobial medications only gives temporary relief and at the same time greatly complicates the diagnosis of the disease.
What consequences of meningitis can occur
Meningitis does not have consequences, after complete cure, a person becomes the same. But there are always exceptions to the rule. The statistics recorded that only 0.2% of those who had recovered had consequences in the form of deafness, blindness, mental retardation, coma and death.
The disease does not usually recur.