Pneumococcal pneumonia
 Pneumococcus is a representative of the flora of the upper respiratory tract, causes pneumococcal pneumonia. The disease often occurs after the damage of the lungs by the flu, sore throat. This allows pneumococci to infect the lungs. Pneumococcal pneumonia can also enter the bloodstream, the middle ear, the lungs, and the nervous system. Healthy people can be carriers of pneumococcus. Pneumococcus most often causes inflammation of the entire lobe of the lung or most of it. Pneumococcus is the most common pathogen of pneumonia.
Pneumococcus is a representative of the flora of the upper respiratory tract, causes pneumococcal pneumonia. The disease often occurs after the damage of the lungs by the flu, sore throat. This allows pneumococci to infect the lungs. Pneumococcal pneumonia can also enter the bloodstream, the middle ear, the lungs, and the nervous system. Healthy people can be carriers of pneumococcus. Pneumococcus most often causes inflammation of the entire lobe of the lung or most of it. Pneumococcus is the most common pathogen of pneumonia.
Pneumococcal pneumonia usually manifests itself in two variants: croupous and focal pneumococcal pneumonia. Croupous pneumonia may be lobar and pleuropneumonia. Focal pneumonia is a lobular and bronchopneumonia.
Risk group
The disease usually affects small children under 5 years old and older adults from 65 years of age or older. In older people, the disease can take place in very severe forms and result in a fatal outcome.
The risk group consists of people with chronic heart, liver, lung disease, HIV and AIDS infected or people who underwent organ transplantation.
Clinical features and diseases of pneumococcal pneumonia
Croup pneumonia .This form of the disease usually begins suddenly, sharply. The temperature rises quickly, the patients feel a chill, sharp pains during breathing in the chest. At first, the cough is dry and painful. Then begins to appear brown viscous sputum with blood veins. An asymmetrical flush appears on the cheeks of the patient. The patient has a rapid breathing. This form of the disease is usually difficult. But modern drugs can reduce the duration of fever and accelerate recovery. Complications after the disease can lead to the development of purulent processes, pleurisy, abscesses. Less common complications of the disease are meningitis, hepatitis, endocarditis, nephritis, peritonitis.
Focal pneumonia .Usually appears on the background of ARI, which causes bronchitis. The clinical picture has the same syndromes as in the croupous form of pneumonia, but they are much less pronounced. The patient's body temperature is not very high, fever is short. The patient is more concerned about general weakness. Also sweating, high fatigue, dyspnea are observed. The disease is accompanied by a dry moderate cough. However, it can contain mucopurulent sputum. The skin is pale. Focal pneumonia usually occurs in mild or moderate forms. Less frequent complications of the disease than with the croupous form of pneumonia.
Diagnosis of the disease
The diagnosis of pneumococcal pneumonia is based on the detection of pneumococcus in the sputum. With this disease, diagnostic methods are conducted: laboratory tests, bacteriological culture, chest X-ray and physical examination.
The doctor interviews the patient about age, the presence of concomitant diseases that can cause the development of pneumococcal pneumonia. When the patient is examined, the frequency of breathing is determined.
Laboratory data
The disease shows changes in the general blood test. Usually there is pronounced leukocytosis. Also significantly increases the number of neutrophils. The leukocyte formula shifts to the left. During the height of the eosinophils disappear, markedly reduced the number of platelets and lymphocytes. When recovered, all indicators are normalized.
Symptoms of the disease reveals a biochemical blood test: the level of globulins, fibrin, seromucoid, haptoglobin, sialic acids increases.
Physical examination data
Typical physical manifestations of lobar pneumococcal pneumonia depend on the form of the disease.
The initial stage is the phase of accumulation of exudate. There is a blunted sound over the affected hearth. The patient's breathing is stiff, elongated, sometimes dry, wet wheezing is heard.
At the compaction stage, voice tremor sharply increases. Perhaps the appearance of bronhofonii. It is impossible to listen to vesicular breathing. Fade away crepitation. Sometimes you hear a noise from the friction of the pleura.
Permission Stage. Gradually, voice trembling normalizes, bronchophony disappears. Listening sonorous rattles. Bronchial breathing will be replaced first by a rigid, and then vesicular breathing. However, this regularity of the phases of pneumococcal pneumonia may not always be observed.
With the focal form of the disease, the physical data are less demonstrative.
X-ray studies of
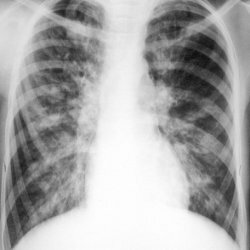
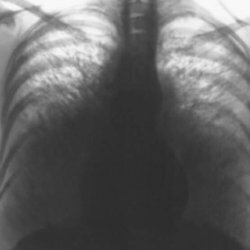
In the initial period of pneumococcal pneumonia, radiologic changes are very poorly expressed or generally absent. The most characteristic changes appear in the phase of compaction of lung tissue. With the fractional form of pneumonia, a strong darkening of the lobe of the lung can be clearly seen on the roentgenogram.
Focal form of pneumococcal pneumonia is characterized by focal shadow of local compaction.
Radiography of the lungs is carried out in two projections to detect the presence of pneumonia and severity.
Treatment of pneumococcal pneumonia
An easy form of the disease. Oral bactericidal antibiotics such as ampicillin, phenoxymethylpenicillin, 1st generation cephalosporins are used. If the patient is intolerant of the above-mentioned drugs, then erythromycin, biseptol is prescribed.
The average form of the disease. For treatment, intramuscular administration of penicillin is prescribed every 4 hours.
Complicated form of the disease. In these cases, the dose of penicillin is doubled to improve the penetration of the drug.
With mild focal pneumonia, patients can be treated at home. The district therapist constantly supervises the patient.
However, a patient with croupous or focal pneumonia, in moderate or severe forms, needs urgent hospitalization. Elderly people, patients who do not have the opportunity to be treated at home, are also subject to hospitalization.
Patients need to provide high-calorie food. Recommended: easily digestible food, rich in vitamins;Respiratory gymnastics, vitamin therapy are rehabilitation measures. It is also useful to take infusions of herbs with expectorant capabilities. An important stage for rehabilitation will be treatment in sanatoria, resorts.
Prognosis of pneumococcal pneumonia
Usually, in primary pneumonia, the prognosis of the disease is favorable. The patient usually recovers after 15-25 days. Croupous, focal pneumonia of medium or severe forms can result in death.
Methods of preventing the disease
An important tool in the prevention of the disease is the final treatment of angina and acute respiratory infections. Also for the prevention of pneumonia helps exercise, proper nutrition, rich in vitamins. It is necessary to abandon the abuse of alcohol and smoking.
Modern medicine has created a vaccine for the prevention of pneumococcal pneumonia. Vaccination protects people from at risk from pneumonia.