Cavernous and fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis of the lungs
 and fibrocavernous tuberculosis - two insidious forms that have the highest percentage of deaths and are characterized by having a specific cavity.
and fibrocavernous tuberculosis - two insidious forms that have the highest percentage of deaths and are characterized by having a specific cavity.
The cavity - cavity which has formed in tuberculous lung lesions and distinguished from normal lung dense wall.
After the formation of a cavern, the course of tuberculosis changes its manifestations and acquires new features. What is important is that the process is reversible and limited( the adjacent tissue has neither infiltration nor focal changes).In the absence of adequate treatment, there is always a significant risk of transformation into fibro-cavernous tuberculosis, since the decay cavity has a constant source of infection.
Fibrous-cavernous tuberculosis is characterized by the fact that there is a specific rough fibrosis in the surrounding tissues in addition to the collapse of the cavity. In this regard, the possibility of the effect of drugs on the process is sharply reduced, and the disease acquires a chronic progressive course.
Epidemiology
The disease affects mainly adults. Children caverns are extremely rare. Among patients who died of tuberculosis, the largest number of patients are with a fibrous-cavernous process.
Pathogenesis of
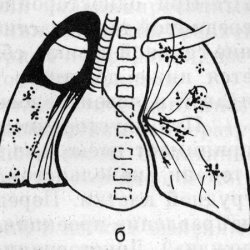
Cavern can form with the progression of any form of tuberculosis. The reason for this can be both drug resistance, and a decrease in immune defense. If immunity is compromised, the number of bacteria inevitably increases, which leads to increased exudation, microcirculation disturbance and damage to the surfactant. From the destroyed cells, the caseous masses are formed, which fill the alveoli. When the masses are rejected by the drainage bronchus, a cavity of decay is formed. Also, the cavity of decay can form when penetrating the pathogen into the bronchiectasis. The cavity of decay is surrounded by caseous-necrotic masses, tubercular granulations are located outside. Over time, the collagen fibers form in the granulation layer, forming a thin fibrous layer. Thus, a three-layer shell around the decay cavity is formed. This process takes several months. After the formation of the cavity inflammation spreads to the mucous draining bronchus lumen bronchial narrowing and cavern "inflated", which further increases the inflammation and toxicity. The treatment cavity can heal with scar formation, because it can form a center or focus.
With the progression of the process,caseous-necrotic inflammation extends beyond the walls of the cavity, affects the previously intact sections. The wall becomes thicker and denser in the adjacent tissue fibrosis develops. eventually cavern "olderm ": walls become thick and continuous, in the cavity appears mucopurulent contents with crumbs caseosa, the inner surface becomes uneven. Its formation indicates the transition of the process to fibro-cavernous. The walls have a cartilaginous density. Usually aging takes from 1.5 to 3 years. The development of this form can occur with the progression of any other tuberculosis process. The dimensions of the fibrous cavity increase, the partitions between the closely located cavities are destroyed, multi-chambered giant caverns are formed. When the septa are destroyed, pulmonary hemorrhage may occur. Since the conditions for the destruction of the wall are always there, the danger of developing such a complication never decreases. About the wave-like flow of the process, new caverns and foci are formed, the bacterial release becomes permanent. Over time, the formation of new cavities, and in the tissues of the lung and pleura form rough irreversible changes produced bronchiectasis with purulent contents. With this form, the pleura( in the form of empyema) and other organs are often affected. The development of caseous pneumonia often leads to death. With adequate treatment, the process stabilizes and is delimited, the foci dissolve.
Clinical picture
Cavernous cavities are usually formed with unsuccessful treatment, which can be caused by many factors. Specific complaints with this form do not exist, they are often due to previous large drug loading and intoxication: cough with mucous expectoration, increased fatigue and sweating, low mood, slight increase in body temperature, weakness. When examining the patient over the area of the cavern, the percussion sound is shortened, which is explained by the consolidation of the pleura and the surrounding pulmonary tissue. But most of the caverns are "dumb", that is, they can not be detected by physical methods. "
In medicine, there is such a thing as a symptomatic complex of the decay phase, the main features of which are: blood and sputum coughing, bacterial excretion, wet wheezing in the lungs during auscultation. The fibrous-cavernous process develops, then intoxication grows, and when coughing sputum with a blood impurity can appear. The chest cell can visually be deformed, the mediastinum organs are biased toward the fibrous lesionComplaints directly depend on the phase of the process: the state of remission is satisfactory, and when exacerbation is characterized by an abundance of various complaints. With the progress of the disease, patients lose weight significantly and develop cachexia. As the volume of the pulmonary tissue contracts, there is a lung failure, the patient suffers from dyspnea and there are characteristicFor this chronic pathology of the change. It is characterized by the isolation of mycobacterium tuberculosis from the mucus.
X-ray picture of
More often caverns can be detected in the upper parts of the lungs. The most informative in this situation is the method of computed tomography.
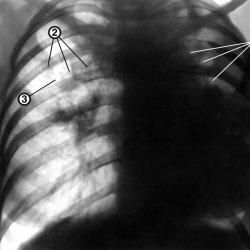
Signs of cavernous tuberculosis: a single cavern up to 4 cm in diameter, a rounded shape, a wall thickness of about 3 mm, the outer contour is blurred, and the inner one is smooth and even. If the cavern passes through the process of scarring, then its features will be an irregular shape with strands to the root of the lung.
Signs of the fibrous-cavernous process are very diverse and depend on many factors. Detect annular shadows of irregular shape of various diameters( it can reach the lobe of the lung), in the lumen it is possible to reveal the level of liquid or sequestrum, while the internal outlines are sharp, the outer ones are more blurred. You can identify a fibrous decrease in the affected area or the shadow of seeding. The root of the lung is pulled upward toward the fibrous changes. Intercostal spaces narrowed. If the process is bilateral, the symmetrical changes in the upper parts of the lung are characteristic.
Treatment of
In fibro-cavernous form, patients constantly excrete bacteria and therefore belong to the group of epidemic patients with open tuberculosis. Conservative treatment is complex, based on chemotherapy, according to the generally accepted scheme, this is usually the fourth treatment. If necessary, hormonal preparations( glucocorticoids), immunotherapy are prescribed. The duration of therapy, as a rule, is not less than 1.5 years.
The need for surgical treatment is prescribed by a physician. Indications for surgery for these forms can be: bleeding, constant hemoptysis, a decrease in the thickness of the cavity wall, resolution of infiltrative and focal changes, the presence of open caverns if the treatment is not successful within 6 months, pleural empyema, lung collapse, fibrous bronchus.