Types of viral hepatitis
Hepatitis is termed acute, chronic liver disease caused by various causes. Factors that cause acute hepatitis, may be pathogens of infections( viruses, leptospires), ionizing radiation. The causes of chronic hepatitis most often are tuberculosis, fungal diseases, diseases of the stomach, pancreas, intestines. The most common are viral hepatitis. There are several types of viral hepatitis, depending on the types of pathogens: A, B, C, other rare types.
Hepatitis A
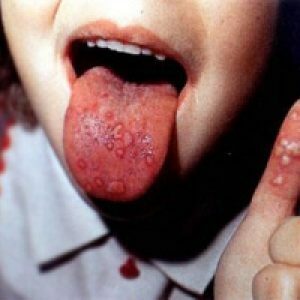
Type A belongs to the group of intestinal diseases. Another name for it is infectious hepatitis. Most often they have children. The disease can take on the nature of epidemics. The virus is determined in feces, urine, intestinal contents, in the blood of patients. Ways of transmission of infection are diverse: fecal-oral, when ingested, sexual( especially in homosexuals), airborne.
The incubation period( latent) basically lasts from 15 to 45 days( the minimum period is 7 days, the maximum period is 7 weeks).The disease begins from the pre-jaundiced period, lasting 1-2 weeks. At this time the patient is disturbed by nausea, vomiting, deterioration of appetite, in the right upper quadrant there is a certain heaviness, weakness. There may be an increase in temperature and upset of the stool, joint pain, bones and muscles, decreased performance, sleep disturbance. Perhaps the onset of the disease, which occurs under the mask of ARD: sore throat, runny nose, slightly fever. At the end of the pre-zheltushnogo period, the patient becomes hepatitis A dark urine( "color beer"), and the feces discolored( it becomes like clay).These symptoms rarely go unnoticed, and the patients most often at this stage of the disease turn to the doctor.
It should be noted that for others in the pre-zheltushnom period, the most dangerous patients: the virus stands out very intensely, and the disease is not yet recognized and often under other diagnoses.
Then the icteric period begins. At this time, the patient appears blunt hepatic pain, itching, joint pain. Skin covers, eye whites and visible mucous membranes become yellow. However, there is an icteric form when the skin color does not change. The patient at the same time, nevertheless, is the source of infection.
Prevention of hepatitis A is in the supervision of food organizations, in the destruction of flies, hygiene. When there is a risk of infection( for example, in the family - those infected with viral hepatitis), gamma-globulin prophylaxis is performed.
Hepatitis B
Type B is contained in the patient's blood, this disease is called serum hepatitis. Transmitted as with blood, and with its components( plasma, albumin, erythrocyte mass).The infection is spread by chronically ill( carriers of antigen to virus B) and those who become ill with the acute stage of hepatitis B. The hepatitis B antigen is found in saliva, semen, vaginal secretion, feces, urine. In the blood there is a virus in the acute period and a month before the clinical symptoms, and also after 2 months( sometimes years) after the disease.
Infected with transfusion of blood and its components, with injections, operative and dental interventions, sexually, when the patient's blood gets to damaged mucous membranes and skin surfaces. Hepatitis B is usually worse than hepatitis A.
The incubation period is 2-4 months( minimum 6 weeks, maximum 6 months).The disease begins gradually. At patients the appetite worsens, nausea, sometimes - vomiting is often disturbed. The chair has an unstable character( constipation, followed by diarrhea), sharply reduced working capacity, appear previously uncharacteristic apathy, lethargy or irritability. Very often( about 25% of cases) are concerned with pain in the large joints, muscles. Sometimes there are skin rashes, accompanied by itching. In patients who have been infected with blood transfusions, the temperature rises, abdominal pain appears. The pre-egg period lasts usually from 1 to 3-4 weeks. The longer this period is, the harder the course of the disease. Sometimes all these symptoms are absent, and the disease debuts with darkening of the urine or the appearance of icteric color of the eye proteins.
Jaundice increases a half to two weeks, then gradually decreases. At the beginning, the whites of the eyes turn yellow, the hard palate, then - the skin, mucous. During the period of growth and preservation of jaundice, skin itch appears, the liver is enlarged. Sometimes joint pain and fever remain.
The stage of recovery is more prolonged than with hepatitis A. From the third to fourth week the condition of the diseased becomes better, the skin and mucous membranes acquire a normal color, other symptoms of the disease also disappear. It must be remembered that here there is also an acne-free form of the disease, when the patient can be a source of infection. Therefore, if you find yourself experiencing similar symptoms, and during the last 6 months have been treated with teeth, have transfused blood, undergone surgical intervention or injected, then you should see a doctor and get tested for hepatitis.
Prevention of hepatitis B is the use of only personal or disposable syringes for injection, eradicating drug addiction, enhanced sterilization of medical instruments. Even an insignificant amount of serum or plasma of the patient or carrier of the virus is capable of infecting another person. This type of viral hepatitis is heat-resistant, so subjects require serious sterilization( autoclaving, half-hour boiling).Replace these measures with disinfectants or alcohol.
Hepatitis C
Type C has a milder flow, reminiscent of the course of hepatitis A. More often than other hepatitis, it flows in erased and jaundiced forms. Despite this, hepatitis C is prone to transition to chronic. The success of treatment and the outcome of the disease primarily depend on the timeliness of hospitalization of the ill and compliance with bed rest( during the entire time of the height of the disease).
All patients who survived viral hepatitis should be observed by a doctor after discharge from the hospital. Three months after discharge, heavy physical labor is not recommended. For 3-6 months, stop playing sports. At least three months must be followed by a diet( with the exception of fatty, fried, spicy).