Tuberculous salpingitis: treatment
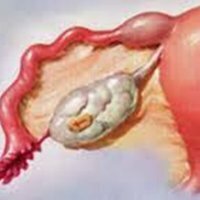
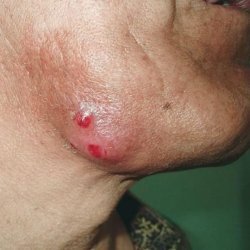
Salpingitis is an inflammation of the fallopian tubes. This is the most common disease of female internal genital organs. Disease-causing microorganisms can enter the fallopian tubes through anatomical canals, as well as by hematogenous and lymphogenous pathways. Rapid development of tuberculous salpingitis of a septic character is usually associated with severe labor or abortion, various intra-uterine manipulations. In this case, the entrance gates for infection are the damaged epithelium of the cervix and the body of the uterus.
The hospital treats acute and subacute tuberculosis salpingitis. Also, the acute exacerbation of chronic salpingitis is permanently treated. Patients with chronic salpingitis outside the period of exacerbation or exacerbation without infectious-toxic components are subject to out-patient treatment. In the hospital, a curative and protective regimen is appointed along with strict bed rest, ice is applied to the hypogastric region( two hours with breaks for 30-60 minutes for two days), a sparing diet. Doctors carefully monitor the activity of the intestine and bladder. Antibacterial detoxification, desensitizing, restorative and resorptive therapy are carried out.
Antibacterial therapy
In acute and subacute tuberculosis salpingitis, especially with its infectious-toxic variant, the role of the microbial factor is great. In this case, the most important is antibacterial therapy, which is applicable taking into account the sensitivity of the causative agent of the infection to the prescribed antibacterial agents. On the first day of the patient's stay in the hospital, when there is still no laboratory data on the nature of the causative agent and the parameters of its sensitivity, antibiotics of a wide spectrum are prescribed. Semisynthetic penicillins are used for treatment: oxacillin sodium salt, ampiox, ampicillin. Also, antibiotics of the cephalosporin group are used: cephalexin, cephaloridine, cefazolin, tetracycline drugs. Less commonly, women are prescribed antibiotics of the aminoglycoside group: kanamycin sulfate, neomycin sulfate, gentamycin sulfate, and also levomycetin.
Treatment with antibiotics continues even after the elimination of acute events for at least 10-14 days. In the case of chlamydial infection, tetracycline drugs and antibiotics-macrolides, for example erythromycin( 10-14 days to 2 grams per day) are shown. Antibiotics are better combined with derivatives of nitrofurans, which effectively affect gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria, large viruses and trichomonads( metronidazole up to 1.5 grams per day).In connection with the likelihood of developing dysbiosis and candidiasis, patients with antibiotics should be prescribed antifungal drugs: nystatin, levorin.
Detoxication and protective therapy
It is carried out at the expressed phenomena of an intoxication by intravenous introductions of a solution of glucose with various vitamins, and also reopoligljukina and gemodeza. It is prescribed dimedrol, suprastin, diprazine or tavegil. Also, pyrazolone derivatives( butadion, analgin, amidopyrine, antipyrine, rheopyrin), which have analgesic, anti-inflammatory and antipyretic effects, are used. In therapeutic doses, ascorbic acid, vitamin B1, cocarboxylase, vitamin E, rutin and glutamic acid are prescribed.
Aloe extract, placenta extract is used to stimulate protective reactions of the body, autohemotherapy is performed. With adhesive changes in the pelvic area, enzyme preparations - lidase and ronidase - are prescribed. Preparations are administered rectally in suppositories, which maximally brings them closer to the pathological focus and provides good absorption. Strengthening of immunological reactions of the organism is facilitated by the reception of bacterial polysaccharides - prodigiosan and pyrogenal.
Physiotherapy
Used to achieve a stable analgesic effect, as well as to resolve adhesions. Well-assisted ultrasound in pulsed mode of radiation, ultra-high frequency magnetic field, pulsed currents of low frequency, mud, ozocerite, paraffin and mineral waters in the form of baths and vaginal irrigation. In recent years, the treatment of tuberculosis salpingitis successfully applied acupuncture. It has an analgesic effect and promotes regression of pathological changes.