Tuberculosis of the lymph nodes
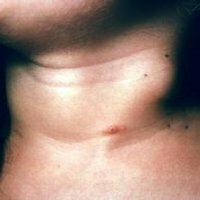
The form of extrapulmonary tuberculosis, which occurs quite often, is tuberculosis of the lymph nodes. In most cases, through the mucous membrane of the nose and mouth( through the lymph nodes) gets into the lymph nodes infection, less often it comes from the foci of tuberculosis hematogenous way. In 90% of cases, cervical lymph nodes are affected. Tuberculous lymphadenitis can occur independently, and may accompany pulmonary tuberculosis. Most often, lymph node involvement is multiple, but single sites are often affected. In general, jugular( in most cases upper and middle) are affected, pre-horticultural and submandibular lymph nodes.
Clinical picture of tuberculosis of lymph nodes
In many ways, the patient's condition( absence or presence of pulmonary tuberculosis) determines the clinical picture of tuberculosis of these nodes, and it is determined by the nature of the process( predominance of productive, hyperplastic or destructive component of inflammation).In the hyperplastic form of this disease, granular tissue proliferate at the nodes. They become denser, less painful and more mobile. If destructive specific inflammations predominate, the nodes that consist predominantly of tubercles rapidly undergo caseous necrosis and become soft. Because of the periadenitis, they merge with each other. These corners are painful and soft. When combined with an infection, the pyogenic process of breakthrough, the opening of the nodes is accelerated, and the fistulas are not closed for a long time. Between these morphological forms there are many transitional forms.
Eventually, in the hyperplastic process, the nodes undergo caseous necrosis, which usually begin at the center of the node. Around the foci of destruction due to the large number of fibrous tissue, the node is rarely opened rarely. In these nodes fibroticization can develop, sometimes with the deposition of salts. But scarring does not indicate a recovery, since virulent microbes are in scar tissue.
How is tuberculosis of the
nodes? The course of the disease depends on the immune and general reactivity of the body. Sometimes the disease has little or no effect on the patient's condition. If the reactivity is lowered, then lymphadenitis can become a source of generalization of the infection. At any current of a tuberculosis of lymphonoduses treatment should be carried out persistently and systematically.
The diagnosis of the disease is quite difficult. It is based on the results of X-ray, immunological, clinical and histomorphological research methods. Often diagnosed only after a histological examination.
Treatment of this disease
Treatment of tuberculosis of the nodes is determined largely from the stage of the disease. There are a large number of medications that can reduce or completely stop the reproduction of mycobacterium tuberculosis. The most active drug is streptomycin and isoniazid. It is very important to observe continuity of treatment. It is necessary to know that the treatment is long enough, with the use of several drugs. Otherwise, there may be an addiction to the drugs and treatment of lymph nodes will be more difficult.
In the initial stage of tuberculosis of lymph nodes the treatment is applied conservatively, with the help of anti-tuberculosis and antibacterial drugs.
In the second stage, the disease takes a chronic form, the structure of the node itself is violated and it is becoming increasingly difficult to penetrate to the outbreaks of infection with medical preparations. At this stage of the disease, surgical care is needed, namely, in the removal of the lymph node and long-term treatment of the patient with antituberculous drugs.
In the third stage of tuberculosis, the lymph node becomes a bag of pus. In this case, the content is sucked off, and the medicinal solution is injected inside.
Special attention should be given to the fourth stage of the disease fistula formed after opening the lymph node. They must be treated with special medications and apply bandages.