Details of appendicitis in men: causes, signs and treatment
Appendicitis is an inflammation of the appendix( appendix) of the cecum, from which the large intestine begins. Localized these organs in the lower right abdomen. The appendix is up to 10 cm long and can be adjacent to the anterior, posterior, lateral, upper, or lower surface of the cecum. Therefore, with its inflammation, the symptoms sometimes resemble other diseases, which can make diagnosis more difficult.

Appendicitis occurs when the appendix wall is infected with the microbial flora
The frequency of appendicitis development depends on age. In the group of patients up to the age of 20, morbidity is higher in males, while older males suffer significantly less than women.
content
- 1 Causes of
- 2 Classification
- 2.1 Acute appendicitis
- 2.2 appendicism
- 3 Symptoms
- 3.1 main clinical manifestations
- 3.2 Further development of symptoms
- 3.3 Age clinical manifestations
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 Properties treatment and recovery period
- 6 Postoperative complications
- 7 Prevention of
Causes of development of
Appendicitis occurs when infection of the wall with wormlikeTh process microbial flora( Escherichia coli, enterococcus, streptococcus, staphylococcus).Microorganisms fall into the appendix directly from the lumen of the intestine, and also through the lymphatic or blood vessels.
A number of factors of that facilitate appendicitis damage:
-
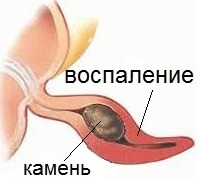
One of the most common causes of appendicitis is clogging of the appendix with a calyx stone or other foreign body
, congenital changes leading to unevenness and narrowing of its lumen;
- occlusion of the appendix with a calcified stone, foreign body, tumor;
- blood supply disorder due to a blood clot entering the blood vessel feeding the appendix, or its persistent spasm with subsequent irreversible necrotic changes in its tissues;
- impairment of normal peristalsis( motor activity) of the intestine in disorders in nervous regulation, which leads to the accumulation of mucus, dilatation of the lumen of the cecum and stagnation in the process.
Based on the results of medical research, the development of appendicitis in men is promoted by :
- , the presence of chronic foci of infection in the organs of the genitourinary system;
- diseases of the digestive system, manifested by chronic constipation( a rare evacuation of the intestine and the formation of very dense feces), primarily - chronic colitis;
- deterioration of the immune protection( with chronic diseases of the respiratory system, digestion, as well as with neoplasms and the consequences of their treatment);
- permanent and prolonged contact with allergens( domestic, industrial);
- irrational food, consumption of large amounts of fried, smoked food, excessive doses of alcohol and smoking.
Classification of
The modern nomenclature of diseases includes acute and chronic appendicitis. If the acute develops for several hours, less often - days, the chronic is characterized by a languid, multi-monthly or perennial course.
Acute appendicitis
According to , the extent of lesions is divided by acute appendicitis into:
- is superficial, in which the inflammation is limited only by the mucosa;
- destructive, involving all layers of the appendix wall formation of purulent inflammation( abscess) or sharp violation of its blood supply( gangrene).
Acute appendicitis can complicated development:
- appendicular infiltrate when the pathological process involved surrounding tissue outgrowth;
- perforation( rupture of the appendix wall, in which the purulent contents enter the abdominal cavity);
- peritonitis( inflammation of the peritoneum surrounding the process, with possible spread to other parts of it);
- limited purulent foci( abscesses) of the abdominal cavity, liver;
- pileflebitis( inflammation of the portal vein of the liver);
- sepsis( spreading of purulent process throughout the body).
Chronic appendicitis
Chronic appendicitis can occur as a consequence of an acute, in that case, when the background analgesic and antibiotic therapy was subsidence of the inflammatory process, and was not carried out surgery to remove it. Such appendicitis is most often characterized by a recurring course with exacerbations and remissions. If cyclicity is absent and only residual changes of the transferred disease are observed, doctors diagnose residual chronic appendicitis .Its peculiarity is the absence of any other manifestations, except pain syndrome.
It is also possible primary chronic course of appendicitis , when pathological changes gradually occur without a preliminary acute phase of the disease.
Boys usually develop acute appendicitis, a destructive form, which requires immediate surgical intervention. Without a timely operation, there is an extremely high probability of complications such as perforation( more often - 24 hours after the onset of the disease).Postoperative complications in childhood are rare.
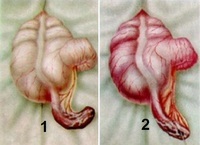
1 - gangrenous appendicitis( scrotal wall necrosis);
2 - perforated appendix( the edge of the gap presented necrotic tissue)
Older men often develop appendicitis such forms as gangrenous and perforated .
This is promoted by :
- thinning of the mucosa;
- decrease in the number of lymphoid cells performing a protective function;
- decrease in the tone of the muscular layers of the appendix wall.
As a result, occlusion of appendicitis lumen and development of phlegmonous process is less common than at a young age. In chronic appendicitis
prolonged inflammatory changes lead to a decrease in the number of viable cells( atrophy) and proliferation of connective tissue with the development of sclerotic lesions, adhesions and scarring. As a result, there is a change in the shape of the appendix, deformation, a decrease in the lumen, and also the fusion of it and closely located organs.
Symptoms of
The clinical picture of appendicitis in men depends on the localization of the appendix, the volume of the affected tissue, the development of complications, and age.
The main clinical manifestations of
- are severe pains in the abdominal region, sharply aggravated by coughing, sneezing, laughing, hiccough;
- nausea, vomiting is possible( single or 2-3 times within an hour, it does not improve the condition);
- dry mouth and white coating on the tongue;
- chills, fever, elevated temperature( above 38 ° C), which, with the development of purulent complications, can reach 40 ° C;
- lethargy, pale skin, poor overall health.
The pain either immediately appears in the lower abdomen on the right, or has a migrating character. In this case, at the onset of pain sensations occur in the epigastric region( in the middle of the abdomen below the sternum and), and a few hours or descend down the center of the abdomen, either in the lower right side section.
appendix at various positions relative to the cecum and its considerable size pain may have another localization , often:
- right hypochondrium - at the position above process cecum;
- lumbar region and right side - when localized posterior to the intestine;
- in the lower abdomen, in the pubic area( can give into the scrotum) - with the pelvic location of the appendix. Additionally
may occur urination disorder( inflammation in the transition process to the bladder wall), and disorders such as constipation chair( reflex) and relaxation( with involvement of the large intestine).
The specific for men are the following symptoms of :
- moving slightly up the scrotum of the right testicle;
- pulling of the right testicle during palpation of the affected area( lower abdomen on the right);
- the appearance of pain in the right testicle while pulling the skin of the scrotum down.
further development of symptoms Symptom
Shchetkina-Blumberg( appearance of pain when pressure is applied to the affected area of the abdomen and a sharp strengthening of its withdrawal at the hands)
With the development of complications or progression of the process can be observed:
- lowering blood pressure;
- the increase in the number of cardiac contractions per minute;
- cold sticky sweat and a sharp weakness.
with involvement of the peritoneum of tension right abdomen muscles lag affected area with respiratory movements and positive symptom Shchetkina-Blumberg ( appearance of pain when pressure is applied to the affected area of the abdomen and a sharp strengthening of its withdrawal at the hands).
Age features of the clinical manifestations of
In childhood, manifestations are more vivid, but more often there is a localization of pain in the center of the abdomen. If such pains for a boy last several hours without moving, then against the background of changes in the work of the intestine and stomach( vomiting, nausea, diarrhea) and fever, it is important not only to suspect acute appendicitis, but also to exclude intestinal infection.
In the elderly, acute appendicitis can develop against a background of well-being of the man, the pain is more often diffuse and does not have a pronounced intensity, the body temperature rises slightly. Given this uncertainty in the clinical picture, careful monitoring of the patient and consultation of the surgeon are important, even with minor changes in the condition. Untimely treatment of a doctor can cause complications, including life-threatening complications.
For chronic appendicitis during an exacerbation, clinical manifestations similar to acute appendicitis are characteristic. In the phase of remission, there is no violation of the general condition and specific symptoms. In the primary chronic course of the disease, prolonged pain sensations, insignificant fluctuations in body temperature are characteristic, which necessarily requires the use of instrumental diagnostics.
Diagnostics
described the presence of clinical manifestations to confirm the diagnosis of appendicitis is necessary to detect the presence of a man of the inflammatory process in the body and install a local cause, ie the defeat of the appendix.
Laboratory changes:
- in the general blood test - an increase in the level of neutrophils and leukocytes in general, as well as the acceleration of the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation( ESR);
- in the biochemical analysis of blood - an increase in the content of C-reactive protein, fibrinogen and individual fractions of globulins( alpha1 and alpha2);
- in the analysis of urine is likely the appearance of the protein as a reaction to severe intoxication.
Ultrasonography( ultrasound ) of the abdominal cavity and magnetic resonance imaging( MRI ) can accurately determine the size of the appendix, the structural changes it and the surrounding tissues. Computed tomography( CT ) reveals other diseases with a similar pattern, confirms, or excludes the presence of stool as the cause of appendicitis.
In case of difficulties in diagnosis, use laparoscopy - visual examination of the abdominal cavity with the help of endoscopic equipment. This technique allows you to see the state of the appendix, other parts of the intestine and peritoneum, to reveal the extent of the lesion and determine surgical tactics.
Features of treatment and recovery period
In acute appendicitis, doctors perform a surgical procedure.
Types of operations depending on access and technical features:
- open appendectomy, in which the surgeon cuts the skin in the lower right side of the abdomen, about 10 cm long, removes the appendix, inspects the surrounding tissues and corrects the pathology;
- is a laparoscopic operation in which the doctor performs several punctures of the skin and uses endoscopic equipment and special instruments to reduce the volume of cicatricial changes.
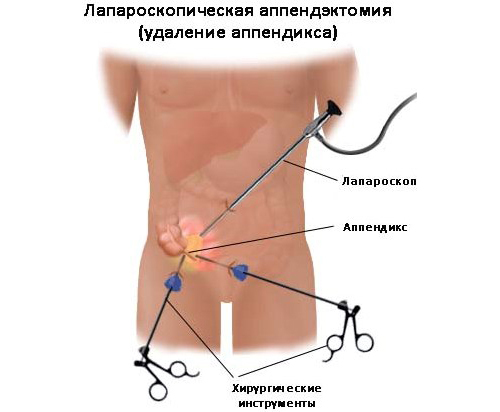
Laparoscopy is a less invasive method of appendicitis removal( small seams are practically invisible afterwards) and, as a consequence, the safest
. Since the operation, in most cases, is performed urgently immediately after diagnosis, it is necessary to quickly carry out tests( blood tests, urine tests, Ultrasound) and prepare the patient. A male doctor is examined by a physician-therapist to determine the concomitant diseases, the boy is a pediatrician. Obligatory consultation of an anesthesiologist is necessary in order to identify the risk of surgical intervention and selection of the method of anesthesia( local, epidural( in the space of spinal cord membranes in the spine) or general).Immediately before the operation, enemas cleanse the intestines.
Given that the operation affects the intestines directly, the restoration of his work is the main goal of rehabilitation. During the first day, the patient should not drink water and eat. All the necessary fluids he receives intravenously. In a day it is recommended to start drinking: water in small portions and natural juices( carrot, apple), diluted with water. Further, in the diet gradually rubbed vegetable soups, cereals, boiled meat without spices and spices. After the first self-emptying of the intestine, the number and variety of dishes is increased.
Doctors recommend to climb from the bed after appendectomy after 8 hours. Respiratory gymnastics is also shown to prevent complications associated with congestion in the lungs and bronchi.
Sutures are removed on the 7-12 day, after which the patient can be discharged from the hospital home. The full period of rehabilitation lasts, as a rule, about 1 month( less often - up to 2 months).
In this period it is better to to abstain from from:
- of sexual activity;
- physical overvoltage, slopes, squats, lifting weights;
- reception of fatty, spicy, spicy food, products promoting gas generation( beans, carbonated sweet drinks), alcohol.
Postoperative complications of
With appendicitis, both the complications of the disease itself and the undesirable consequences of surgical intervention are possible.
To the local postoperative complications include:
- hemorrhage( hematoma);
- infection with postoperative infection and pus formation;
- Inflammatory tissue seals( infiltrates);
- postoperative hernia.
If the process extends beyond the appendix and extends through the abdominal cavity, then intra-abdominal complications of occur.
Most often this leads to development:
- intestinal obstruction( resulting from the toxic effects of substances formed during inflammation, and also in engagement intestine);
- peritonitis( limited and diffuse);
- bleeding;
- intestinal fistula, with destruction of the intestinal wall, previously affected by a purulent process;
- peliflebit;
- abscesses( under the diaphragm, pelvic, between the bowel loops in the retroperitoneal space.
Also, in very rare cases( severe disease in middle and old age) are possible pneumonia and thromboembolic processes, when, due to stagnation in the veinslower limbs off the clot and clog the lung vessels.
Prevention
to prevent appendicitis development in men it is important to maintain the health of the digestive system and the body as a whole, as a specific prevention of this disease does not exist
Basic Principles :
- abstinence from smoking and taking high doses of alcohol;
- full and rational.food, providing regular bowel habits( enough fiber, ie fruits and vegetables, no over-irritating foods( spices, smoked));
- timely diagnosis and prevention of parasitic infestations;
- treatment of chronic foci of infection and diseases of the gastrointestinal tract;
- normalization of intestinal flora.
Recommended for viewing:



