Rubella
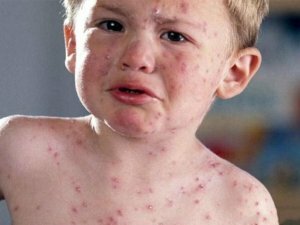 Rubella is a highly infectious acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. Most often this disease affects children two to nine years old. Especially dangerous is rubella in the first three months of pregnancy, with the development of severe congenital malformations in the child, and intrauterine fetal death is also possible. In adults, in general, rubella is more severe than in children.
Rubella is a highly infectious acute infectious disease caused by the rubella virus. Most often this disease affects children two to nine years old. Especially dangerous is rubella in the first three months of pregnancy, with the development of severe congenital malformations in the child, and intrauterine fetal death is also possible. In adults, in general, rubella is more severe than in children.
A person with an erased rubella or a clinically manifested disease can be a source of infection. Methods for the transmission of rubella are carried out by airborne droplets, or vertical - to the fetus from the mother. In addition, it is possible and a contact path of infection - with kisses, when talking with a sick child, through toys. One week before the rash appears, the patient may be contagious and continue to isolate the virus five to seven days after the rashes have appeared. With congenital rubella the child is able to excrete the pathogen for a longer time - up to a year and a half.
Symptoms of
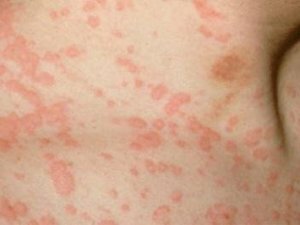 In the two-three-week incubation period, that is, from the moment of infection and until the onset of symptoms, there is no change. Then begin to develop mild headaches, malaise, pain in the muscles and joints, there is a sharp increase in temperature to 38 degrees within one to three days, redness of the throat, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and neck, rashes on the body, limbs, face and neck. With reddening of the throat, there is no pain.
In the two-three-week incubation period, that is, from the moment of infection and until the onset of symptoms, there is no change. Then begin to develop mild headaches, malaise, pain in the muscles and joints, there is a sharp increase in temperature to 38 degrees within one to three days, redness of the throat, enlarged lymph nodes in the neck and neck, rashes on the body, limbs, face and neck. With reddening of the throat, there is no pain.
Rashes are especially abundant on the buttocks, back and waist. Sometimes there is a slight itch, but usually a small patient does not disturb the rash. When rubella is a disease, children experience general reddening of the skin. In addition, pink spots appear on the upper palate. These spots gradually spread to the posterior surface of the oral cavity. The onset of the rash is observed on the first day of the disease, less often on the second-third. The rash lasts for three days, then disappears.
The development of the disease
The diagnosis is made by the doctor based on the characteristic symptoms. If the disease is mild, then the diagnosis may often be incorrect. Rubella disease is fraught with complications. Possible transitions to encephalitis( inflammation of the brain), less often - inflammation of the middle ear, otitis, arthritis. The boys may have pain in the testicles, but they pass pretty quickly. Pregnant women with rubella infection are dangerous - miscarriage, the birth of a dead child or the development of a congenital malformation is possible. In general, treatment of diseases in children should not be accompanied by complications and does not require special special treatment.
As a rule, rubella treatment should be started in a timely manner. In these conditions, the disease ends in complete recovery, forming a lifelong immunity to infections.
The incubation period lasts 11-24 days. The virus penetrates the body through the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, carries blood through the body and causes an increase in lymph nodes. In particular, those nodes that are located on the back of the neck and occiput are affected.
There is a runny nose, dry minor cough, lacrimation, feeling of perspiration in the throat. In adults, rubella causes headache, decreased appetite, muscle pain, and increased body temperature.
Diagnosis and prevention
Using a blood test for antiviral antibodies, it is confirmed whether there is rubella. Symptoms and treatment of the disease are determined by the doctor.
Usually, treatment is done at home, during the rash, bed rest is prescribed. The prognosis of the disease is favorable in most cases. Repeated infection with rubella in humans is not observed.
In order to prevent the spread of infection, the sick with rubella isolate for 5 days from the onset of the rash. There are no restrictive measures in relation to the persons who treated them, as a rule, quarantine is not imposed on groups in children's institutions. However, it is important to prevent the contact of a rubella patient with pregnant women.
The vaccination schedule includes vaccination against rubella. The most often used for children is a kind of trivaccination - measles-rubella-mumps. The vaccine is administered subcutaneously or intramuscularly. Babies are given a vaccine in 12-15 months, then they are made again at 6 years. The development of specific immunity occurs in two to three weeks and lasts for 20 years almost all vaccinated.
As a rule, there is currently no specific rubella treatment. Only patients with severe complications are hospitalized.
Treatment of rubella
 Treatment of rubella is limited to symptomatic and pathogenetic means. In acute stages, the patient is given a strict bed rest. Children with a tendency to allergic reaction and with an itchy rash are prescribed antihistamines. With symptoms of joint damage, analgesics and local heat are used. Disorders of the central nervous system require hospitalization of the patient and the use of emergency complex treatment. Appointment, depending on the level of complication of the disease, detoxification, dehydration, anticonvulsant and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Treatment of rubella is limited to symptomatic and pathogenetic means. In acute stages, the patient is given a strict bed rest. Children with a tendency to allergic reaction and with an itchy rash are prescribed antihistamines. With symptoms of joint damage, analgesics and local heat are used. Disorders of the central nervous system require hospitalization of the patient and the use of emergency complex treatment. Appointment, depending on the level of complication of the disease, detoxification, dehydration, anticonvulsant and anti-inflammatory therapy.
Etiotropic therapy is performed using recombinant interferon, viferon and candle, leukinferon, heberon, intron A, referon A and other medications. Indications for their use are the forms of postnatal rubella that occur with the CNS lesion, as well as all the main cases of congenital rubella with active infection. The dosage of recombinant interferon preparations and the duration of the course of treatment are regulated by the severity of the processes and the dynamics of restoration of functions.