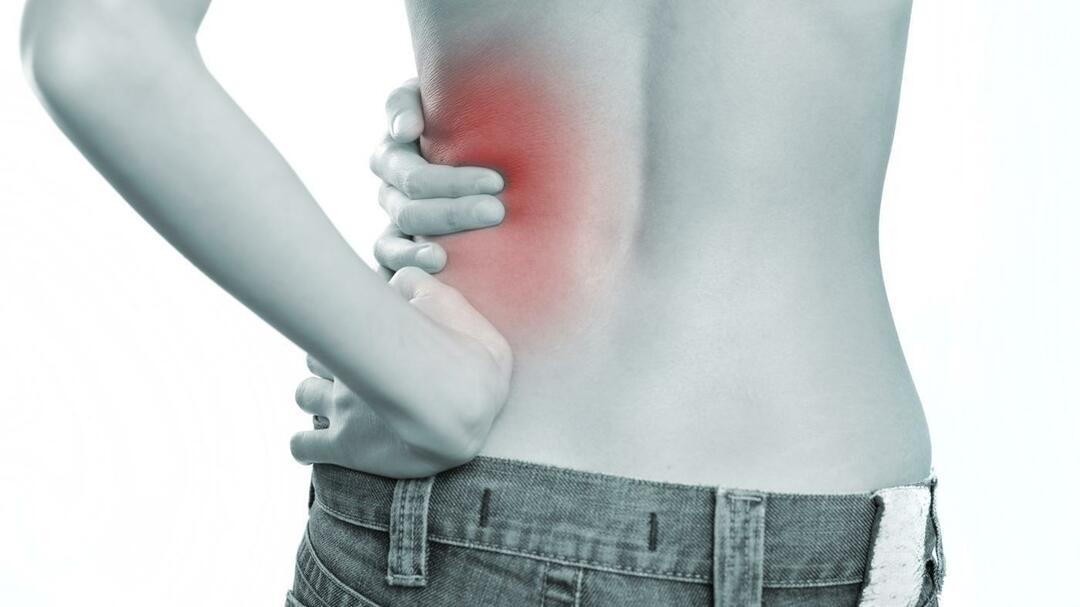
The main causes of redness of the scrotum in children and adults
Reddening( hyperemia of the skin) of the scrotum is one of the signs of the development of the pathological process. Can be observed at any age( beginning with the newborn), be a manifestation of congenital and acquired diseases. To identify the cause and diagnosis of the disease, you need to know not only the most frequent conditions for changing the color of the skin of the scrotum, but also other likely symptoms. 
Content
- 1 Causes
- 2 Features inflammation
- 2.1 Injuries
- 2.2 Secondary infection after injury
- 2.3 Fournier gangrene
- 2.4 Specific infections
- 2.5 Fungal infection
- 2.6 Malignancies
- 2.7 Allergy
- 3 reasons noninflammatory nature
- 3.1 Hematoceles
- 3.2 Elephancy
- 3.3 Torsion of the spermatic cord
- 4 Features in children
- 5 Tactics
Causess emergence
Factors leading to the development of skin redness of the scrotum is divided into inflammatory and non-inflammatory.
The main groups of causes of redness of the scrotum:
- Inflammatory nature:
- traumatic injury;
- nonspecific and specific infections;
- inflammatory processes of non-infectious nature;
- malignant neoplasms;
- allergic reactions and illness;
- Non-inflammatory origin:
- disorders of blood and lymph flow.
However, the division is partly conditional, since in the course of development the disease can move from one group to another. For example, after a hemorrhage an infection can join and a non-inflammatory process will pass into inflammation.
Features of inflammatory processes
Nonspecific infections( streptococci, staphylococci, Escherichia coli and Proteus) in most cases are spread with blood and lymph flow( primary infection).However, with traumatic injury, it is possible not only to redden the scrotum, but also to attach infection( secondary infection).In this case, pathogenic agents enter the scrotum through damaged skin.
Injuries to
There is a high probability of traumatizing the scrotum after falls, bumps, unsuccessful cycling. There is swelling of the tissues, the vessels dilate, it is possible the development of local hemorrhage( hematoma).Redness of the scrotum in these cases is accompanied by sharp pains and an increase in size. It is important here as soon as possible to see a doctor, identify the extent of damage and begin treatment, as a rule, conservative. Only with irreversible changes in tissues( squeezing, crushing) is shown an operative correction.
In case of secondary infection, a delayed reaction is possible( see below)
Secondary infection after injury
Clinically, a delayed reaction occurs( in a few days):
- pain and soreness and palpation;
- swelling and redness;
- increase in temperature( general and local, in the field of infection).
The most terrible consequences - the formation of abscesses( suppurative restricted foci).
Gangrene Fournier
The most dangerous cause of reddening of the scrotum is Fournier gangrene, in which skin, subcutaneous tissue and muscle tissue are irreversibly affected by staphylococci, streptococci and anaerobic microbes( up to complete necrosis).Treatment includes surgical removal of damaged tissues and massive antibiotic therapy( at least 2 drugs).With untimely diagnosis and treatment, the likelihood of a fatal outcome can be as high as 50%.
Specific infections
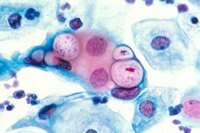
Chlamydia is the main causative agent of one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases - chlamydia
Specific infectious processes occur in sexually transmitted diseases.
Pathogens are:
- chlamydia;
- mycoplasma;
- Trichomonases;
- ureaplasma.
In this case, treatment with special antibacterial agents is necessary under the supervision of a venereologist.
Fungal infection
In addition to bacteria, fungi can be the cause of inflammatory changes. Local humidity and temperature increase the likelihood of such a process. The most common infection is epidermophyton, as well as yeast fungi Candida. Treatment is specific, both local and general, using antifungal drugs( antibiotics, fungicides).
Malignant neoplasms
Redness of the skin in the external genital area may be due to its defeat by the tumor process, and may also be a nonspecific inflammatory( protective) reaction in the spread of malignant cells. The variety of scrotum tissues causes the possibility of many malignant processes.
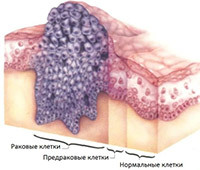
In scrotum cancer there is a rapid metastasis in the inguinal lymph nodes
The most significant:
- cancer( epithelial tumor) squamous or basal cell( according to a kind of epithelium);
- liposarcoma( from adipose tissue);
- fibrosarcoma( from connective tissue).
Clinic features:
- absence or minimal soreness / discomfort in the early stages;
- urination disorder and sexual dysfunction;
- the presence of general symptoms( weight loss, poor appetite, general weakness, periodic increase in body temperature).
Allergy
One of the important causes of redness of the scrotum is a local reaction to allergens. In most cases, synthetic fabrics, from which the laundry is made, hygiene products( shower gels, soaps).
Related signs:
- bilateral enlargement of scrotum;
- tension and smoothness of the skin;
- pronounced itching of the genitals, inguinal region;
- is a worsening condition after exposure to an allergen.
If you suspect this condition, you should exclude contact with a possible cause, refrain from consuming irritating foods and consult a doctor. Antiallergic drugs will restore health, and the use of hypoallergic hygiene products will impede the progression of the process.
Causes of non-inflammatory nature of
These conditions include disorders of blood circulation and lymphatic exchange.
The most significant:
- hematocele;
- elephant;
- torsion of the testicle or spermatic cord.
Hematoceles
With congenital or acquired hydrocele( communicating by dropsy and accumulation of fluid in the testicle shells), a complication in the form of a hematocoel can occur. This is a hemorrhage into the cavity formed by the testicle shells, which is externally manifested by the local reddening of a certain area of the scrotum. It is accompanied by discomfort or pain, and only with the attachment of infection and suppuration - an increase in body temperature and other nonspecific signs of inflammation.
Elephant
Elephancy of the external genitalia is a constant increase in size due to impaired lymph flow. Characteristic development of persistent puffiness, the violation of metabolic processes in the skin, subcutaneous tissue and connective tissue of the scrotum. It happens secondary( as a result of chronic infections) and congenital.
Clinical features:
- begins with scrotum skin( redness and swelling), spreads to the testicles, appendages and urethra;
- lasts for years with periods of exacerbations and process silencing;
- with each exacerbation increases swelling and congestion of the scrotum and penis;
- obstructs urination due to a proboscis enlargement of the prepuce;
- painful erections and gradually arising impotence.
Treatment of congenital elephantiasis is an operative, eliminating the malformation of lymphatic vessels. With the acquired pathology in the early stages of possible conservative treatment with:
- anti-edema diuretics and corticosteroid drugs;
- Novocaine blockade;
- for the purpose of resorptive therapy - injection or electrophoresis of trypsin, lidase;
- specific antiparasitic therapy( when confirming the helminth nature of the secondary process).
Surgical correction is performed with insufficient effectiveness of drug treatment and progression of the process. It consists in restoring the normal patency of the lymphatic vessels and removing the affected tissues.
torsion spermatic cord
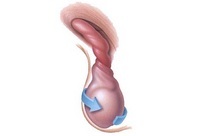
partial compression of receptacles extending in spermatic cord, lead to venous congestion and edema, total - to
infarction For injuries genital sharp voltage abdominal amid anatomical features( increased mobility, elongation cord) possible twisting of the spermatic cordWith the cessation of local circulation. If you do not diagnose and late with treatment in time, irreversible changes to the tissues develop, leading to necrosis.
Symptoms:
- abrupt state change;
- intense, acute pain in one half of the scrotum, giving into the corresponding inguinal region;
- the affected testicle is located above the usual;
- is likely to drop blood pressure due to pain;
- nausea and vomiting.
Treatment in the first hours is probably conservative, the surgeon conducts an external manual unwinding of the testicle. If this method is ineffective or in a later period( when pain increases and the blood supply to tissues worsens), surgical treatment is indicated.
Features in children
The most common cause of reddening of the scrotum skin in the first hours after birth is the intraocular trauma .This condition requires the supervision of a doctor to avoid complications( infection, circulatory disorders and loss of tissue vitality).
Concomitant signs indicating a pathology:
- general anxiety, tearfulness;
- disturbed sleep;
- refusal of feeding;
- scream and cry when changing diapers while swimming at palpation or touching the outer genitals if hygiene procedures( lubrication cream using powders).
Testicular torsion in young children is characterized not only by reddening( or bluish) scrotal skin, but also an increase in its half and the higher location of the affected testicle than normal or it was before.
Features of other symptoms:
- body temperature increase up to 38 ° C;
- frequent regurgitation until vomiting;
- expressed anxiety, crying;
- sharp soreness in the area of the external genitalia.
Torsion is an acute pathology, which carries the threat of death of the testicle and requires immediate intervention.
If the redness of the scrotum is observed during the period of an infectious disease or a few days after the stasis of its main manifestations, then the probability of complicated course and development of orchitis or epididymitis( inflammation of the testis and its appendage) is great.
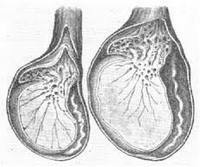
Orchitis is a complex inflammation of the structures of the testicle
. Most often this can occur:
- epidemic parotitis( mumps);
- chicken pox( chicken pox);
- infectious mononucleosis.
In this case, it is important to address not only the urologist, but also the infectious disease doctor for timely treatment in order to avoid complications, including those that violate reproductive function.
Tactics
Since redness of the scrotum is only one of the signs of the development of the pathological process, it is important to know when calling to the doctor should be urgent.
If you have the following symptoms, you should urgently consult a urologist, undergo a recommended examination and start the prescribed therapy as soon as possible:
- pain in the groin area, increasing in intensity;
- increase in body temperature( especially spasmodic), poorly treatable with antipyretics( medications that reduce body temperature);
- increased swelling of the scrotum and / or penis;
- persistent color change( from cyanotic to brown), skin structure( increased density, thinning);
- violation of urination and sexual function;
- blood in the sperm;
- itching;
- general symptoms( weakness, poor appetite, nausea and vomiting, sweating)
Recommended for viewing: