Symptoms of pancreatitis in men
Pancreatitis is an inflammatory process in the pancreas, as a result of which its tissues are digested under the influence of their own enzymes.
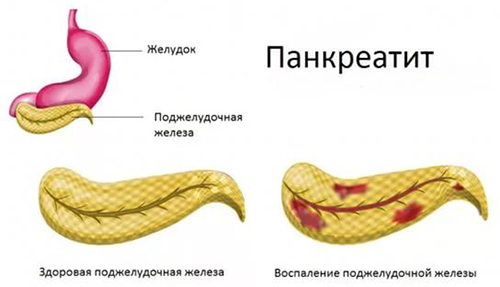
Fig.1 - Pancreatitis is an inflammation of the pancreas.
There are acute pancreatitis and chronic. Nucrose and inflammation are more common for the acute course of the disease. In the chronic form of the disease, the blood supply and nutrition of the cells is disrupted, and they are gradually replaced by a connective tissue. As a result, irreversible organ restructuring takes place: its functional activity is lost, enzymes and hormones necessary for digestion and metabolism are not allocated. In chronic pancreatitis, both exacerbations and remission conditions are observed.
Content
- 1 Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
- 2 Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
- 3 Causes
- 4 Diagnostics
- 5 treatment tactics
- 5.1 Pharmacotherapy
- 5.2 Surgery
- 5.3 Diet
- 6 Complications of the disease
- 7 forecast
Symptoms of acute pancreatitis
Acute pancreatitis in males often occurs after a heavyDrinking alcohol and a lot of fatty, spicy food. Symptoms depend on the cause, extent of pancreatic tissue damage and the general condition of the body.
Acute pancreatitis dramatically changes health. The first symptoms occur suddenly:
- there are severe pains above the navel, giving off in both hypochondria and back;
- man is sick and pulls, but vomiting does not bring relief, but only intensifies pain;
- increases heart rate and heart rate at normal arterial pressure;
- muscles in the upper abdomen tense;
- appear bloating and diarrhea.
The stool is frothy, mushy, with a sharp acidic odor and with pieces of undigested food, eaten the day before. Pain sharply increases during meals, especially acute and oily. After eating, vomiting occurs, so strong and indomitable that the patient refuses food.
The situation is further aggravated: pain and vomiting increase, body temperature rises, skin and mucous membranes are slightly colored in yellow. Because of the violation of carbohydrate metabolism and increase of sugar in the blood, dry mouth and thirst feel.
Symptoms of chronic pancreatitis
Chronic pancreatitis develops gradually, together with a worsening of the pancreas. The following early signs are observed in patients:
- bloating;
- discomfort, a feeling of heaviness after eating in the upper abdomen, sometimes tingling;
- constipation.
If earlier any food and alcohol were well tolerated, then the discomfort after eating is gradually developing - initially slightly expressed and often left without proper attention. In the future there are pains above the navel, in the region of one or both of the sub-shores. Then the pain spreads round and becomes shrouded.
Characterized by the appearance of severe diarrhea within 15-20 minutes after the start of eating. The chair is light, liquid, foamy, and plentiful. The patient feels a sharp rumbling in the abdomen. After evacuation of the intestine, the condition improves somewhat, the pain subsides, but does not disappear.
Subsequently, the normal pancreatic tissue is replaced by a fibrous tissue that is unable to secrete enzymes and hormones. For this stage of the disease is characterized by:
- gradual reduction of abdominal pain;
- chronic diarrhea several times a day with whitish drops of fat, which are poorly washed away by water from the surface of the toilet bowl;
- weight loss;
- dryness of the tongue, increased bleeding of tissues( for example, when brushing teeth, cuts), decreased vision in the dark, bone pain;
- development of secondary diabetes mellitus.

Fig.2 - Possible symptoms of pancreatitis.
In the presence of such symptoms, medical supervision and research are necessary, excluding malignant processes in the body.
Causes of
The most common cause of pancreatitis in men is the regular intake of a large amount of alcohol. In addition, the causes of pancreatitis may be:
- violations of bile outflow in inflammatory diseases of the biliary tract and cholelithiasis;
- the predominance of fatty foods in the diet, as well as its combination with alcohol;
- deepening of the duodenal ulcer and spreading it to a nearby pancreas;
- gastritis and duodenal ulcer with high acidity;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - disorders of the sphincter tone, developmental anomalies, gastritis, duodenitis, diverticula;
- viral hepatitis, especially B, "mumps", infectious mononucleosis, Coxsackie viruses and ECHO, parasites;
- disorders in the endocrine sphere - the hyperproduction of hormones with parathyroid glands, which leads to the deposition of calcium in the tissues of the pancreas;
- large doses of hormonal drugs, chemotherapy in the treatment of oncology, an overdose of diuretics and other drugs - tetracycline, sulfonamides;
- methyl alcohol poisoning;
- closed and penetrating abdominal injuries;
- vascular disease.
If the bile contained in the ducts of the pancreas is infected with bacteria, the situation is sharply aggravated. Bile components cause pancreatic tissue necrosis, activate its own enzyme systems. As a result, the process of self-digestion begins.
Fig.3 - Possible causes of pancreatitis.
Hereditary( family) forms of pancreatitis are associated with genetic disturbances in the metabolism of certain amino acids and their accumulation in pancreatic tissue( aminoaciduria).
Development of pancreatitis in men is promoted by smoking, which causes a prolonged spasm of pancreatic vessels. This leads to a deterioration of metabolism in the organ and contributes to the chronic disease.
Acute pancreatitis can occur as a result of a number of diagnostic and therapeutic procedures:
- after endoscopic retrograde pancreatocholangiography( ERPHG) for the diagnosis of bile duct obstruction( stones, tumors, adhesions), in which contrast can enter the pancreatic duct;
- after operations on the stomach and biliary tract and bile flow;
- after kidney transplantation on the background of treatment with azathioprine, corticosteroids.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of pancreatitis is performed by a therapist or gastroenterologist. To confirm the diagnosis, a number of laboratory and instrumental examinations are carried out:
- a general and biochemical blood test. It allows to identify inflammatory changes, increase in enzyme activity and glucose level, which indicate the destruction of the gland tissue;
- urine analysis for diastase;
- ultrasound examination, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and endoscopic retrograde pancreatocholangiography.
Instrumental studies allow to reveal structural changes: an increase in the organ, fistula formation, cysts, calcification, involvement in the peritoneum process.
To confirm chronic pancreatitis, it is necessary to investigate the functional changes in the enzymatic activity of the pancreas. The most modern are the respiratory test of the diagnosis of Lipase activity, as well as the determination of the activity of pancreatic Elastase 1 in feces. Also, study feces( coprogram) allows you to identify the amount of undigested food, fat, the amount of fiber, which determines the severity of chronic pancreatitis.
If suspected of a specific infectious or other process that led to the development of pancreatitis, conduct additional profile studies: identify infections, diagnose diseases of the digestive system, exclude oncological processes.
Tactics of treatment
Treatment of pancreatitis depends on the form and severity of the disease. In chronic pancreatitis, much attention is paid to the patient's diet, but medicines are not excluded. Acute pancreatitis is treated necessarily in the hospital and apply both medication, and surgical treatment, and diet.
Medical treatment
To begin treatment of acute pancreatitis it is necessary with the exception of taking any food( complete hunger) for a period of up to 3 days.
Drug treatment is prescribed:
- for pain relief - preparations of spasmolytic and analgesic action( No-shpa, Papaverin, Analgin);
- to reduce the activity of enzymes and digestion in general - antisecretants( Sandostatin, Omeprazole, Famotidine);
- for maintenance of a metabolism - intravenous infusions of salt and protein solutions;
- for preventing the development of infectious complications - broad-spectrum antibiotics( cephalosporins, penicillins);
- to reduce bloating recommend courses of sorbents and defoamers: Activated charcoal, Atoxil, Espumizan;
For chronic pancreatitis, pain is prescribed by antispasmodics Duspatalin, Meteopazmil. Enzyme preparations containing pancreatin, lipase, amylase are required to replace impaired pancreatic function. Outside the exacerbation, alkaline mineral, or weak mineralization of water of Borjomi type, Essentuki, has a positive effect.
Surgical treatment
Surgical intervention is necessary in the development of acute complications:
- abscesses;
- of large areas of necrosis;
- significant cysts;
- in the presence of stones in the bile or duct of the pancreas;
- with a large amount of inflammatory fluid in the organ and surrounding tissues.
Treatment of chronic pancreatitis is aimed not only at easing pain and preventing complications, but also to prevent a decrease in the level of enzymes and hormones in the pancreas.
Diet
Without strict adherence to diet, the treatment of chronic pancreatitis is ineffective. Basic principles of dietary nutrition:
- frequent receptions in small portions( not more than 300 g);
- a small amount of fat, better than vegetable;
- abstinence from sweet, if the carbohydrate metabolism is disturbed.
Completely excluded:
- fatty meat and fish broth;
- carbonated beverages;
- alcohol;
- rye bread;
- coffee and strong tea( see "Personal experience of giving up coffee and tea");
- solid cheeses;
- sour juices( grape, apple, grapefruit);
- spices( pepper, mustard);
- cocoa;
- chocolate.
It is compulsory to monitor the attending physician, which determines the dosage and timing of medication.
Complications of the disease
Complications of pancreatitis are dangerous and can lead to death. Early complications of acute and recurrent chronic pancreatitis:
- shock - the patient falls sharply blood pressure, and denied vital organs;
- acute renal and hepatic insufficiency( cessation of the liver, as well as filtration of urine, which leads to poisoning of the body with toxic products of metabolism);
- ulceration of the mucosa of the digestive tract, gastrointestinal bleeding due to intoxication;
- thrombosis of the vessels of internal organs, which leads to the necrosis of their sites;
- psychosis due to intoxication. In patients who consume alcohol, hallucinations and motor excitement are observed.
Late complications are usually associated with infection and develop no earlier than 2 weeks of the disease. The most common:
- purulent processes - abscesses, phlegmon, melting fatty tissue surrounding the pancreas, peritonitis;
- sepsis;
- cyst;
- fistula;
- lesions of the lungs and surrounding pleural sheets.
With an increase in the size of the pancreatic head, mechanical jaundice occurs.
Prognosis for
Pancreatitis prognosis depends on the cause, timeliness and adequacy of treatment interventions, as well as the presence of complications. Death can occur only with large volumes of necrotic lesions of the pancreatic tissues. With a mild course of acute pancreatitis, complete recovery is possible.
Two-thirds of patients with alcoholic pancreatitis live more than 10 years if they stop taking alcohol. Otherwise, death occurs much earlier.
Recommended for viewing: