Pseudomonas aeruginosa
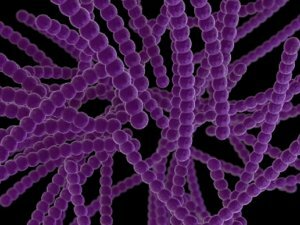
 Pseudomonas aeruginosa( Pseudomonas aeruginosa) - is a gram-negative mobile bacterium, widely distributed in the environment, which is the causative agent of a huge number of infectious diseases. This bacterium does not form a spore, has only one flagella, with the help of it and moves. This bacterium is called synergic, as it produces a special pigment that stains the nutrient medium in a bluish green color. Treatment of diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is quite complicated.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa( Pseudomonas aeruginosa) - is a gram-negative mobile bacterium, widely distributed in the environment, which is the causative agent of a huge number of infectious diseases. This bacterium does not form a spore, has only one flagella, with the help of it and moves. This bacterium is called synergic, as it produces a special pigment that stains the nutrient medium in a bluish green color. Treatment of diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa is quite complicated.
Why is Pseudomonas aeruginosa difficult to treat?
Treatment is difficult due to the following factors. The high prevalence of this bacterium facilitates infection with it.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is very resistant to disinfectants and antibacterial agents.
Nosocomial circulation of this bacterium makes it a nosocomial typical infection that affects patients and staff.
Nonspecific clinical course of diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, causes late diagnosis of the disease and identification of the pathogen.
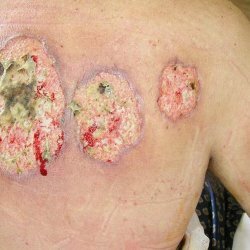 Pseudomonas aeruginosa is treated especially hard in people with weakened immunity, depleted. Infection shows its pathogenic properties in most cases when it enters organs and systems with disturbed protective mechanisms.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa is treated especially hard in people with weakened immunity, depleted. Infection shows its pathogenic properties in most cases when it enters organs and systems with disturbed protective mechanisms.
Treatment of infectious diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa
As a rule, the treatment of Pseudomonas infection is always complex and long enough. It is mandatory to conduct local and general treatment. Only a specialist can treat diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Sometimes preference is given to treatment in the hospital. Remember, self-medication of these diseases is not recommended.
The main method of treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection is considered to be antibiotic therapy. But in connection with a sufficiently high resistance of the pathogen to antibacterial drugs, their appointment is made only after sowing( mucus, blood, urine pus) with excretion of the pathogen, as well as determining its sensitivity to the drugs. Treatment is determined individually.
Antibiotic therapy in the treatment of infections of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
 If there is a Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the body, then stepwise application of antibacterial drugs of several groups is more preferable in the treatment of infection: first intravenously, then intramuscularly. As a rule, local treatment should be performed in parallel. For example, when the mucous membranes and skin are affected, ointment dressings, aerosols, lotions, rinses with antiseptics and antibiotics, to which the pseudomonas aeruginosa are sown, are especially sensitive;With the defeat of the urinary tract is applied in the form of instillations( this is the introduction of drugs into the bladder with a catheter).
If there is a Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the body, then stepwise application of antibacterial drugs of several groups is more preferable in the treatment of infection: first intravenously, then intramuscularly. As a rule, local treatment should be performed in parallel. For example, when the mucous membranes and skin are affected, ointment dressings, aerosols, lotions, rinses with antiseptics and antibiotics, to which the pseudomonas aeruginosa are sown, are especially sensitive;With the defeat of the urinary tract is applied in the form of instillations( this is the introduction of drugs into the bladder with a catheter).
The indicator of effective treatment is a reduction in the symptoms of the disease, normalization of temperature and the main one is a decrease in the titer( number) of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa, as well as the preservation of its sensitivity to this antibiotic. Re-sowing to control the quality of treatment is performed no earlier than 10 days after the end of clinically effective antibiotic therapy. If taking an antibiotic for 3-5 days does not have a positive effect, then it is replaced with another antibiotic.
In the case of soft tissue and skin lesions with Pseudomonas aeruginosa, surgical treatment of the skin, as a rule, with excision of dead tissues, acts in a par with antibiotic therapy. If bedsores are formed, skin care is mandatory, as well as the prevention of the spread of necrosis and the appearance of new foci.
Pseudomonas aeruginosa - other methods of treatment
Because the condition of infection with the infection is weakened immunity, then measures are taken to restore it. Apply for this Bacteriophage, autovaccine( prepared individually), immunocorrectors are prescribed.
Also used for the treatment of diseases caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa: homeopathic preparations;Probiotics( with dysbacteriosis mandatory long-term appointment);Phytotherapy, general restorative therapy( therapeutic rational nutrition, multivitamin-mineral complex).
If the clinic of infection with this bacterium is maintained by the underlying disease( glomerulonephritis, prostatitis, bronchiectasis, diabetes, cystic fibrosis), then it is necessary not to postpone the initiation of its treatment.