Typhoid fever - acute intestinal infection
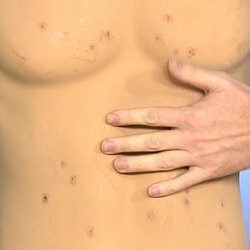
Symptoms of
In case the patient has not undergone proper treatment, the bacteria of typhoid salmonella can be released from him with feces for a year or more after infection. There are cases when symptoms in patients with typhoid fever do not appear in any way.
The duration of the incubation period of the disease is 8-14 days. The onset of the disease is characterized by a gradual increase in body temperature, joint pain, headache, constipation, sore throat, loss of appetite, abdominal pain and painful palpation. Sometimes it becomes painful to urinate, and also there is a cough and nosebleeds.
What happens to the body in the absence of treatment?
If there is no treatment for 2-3 days, the body temperature rises slowly. At the end of this period, it stabilizes at 38-39 ° C and remains on it for 10 to 14 days. By the end of the third week, the temperature begins to gradually decline, reaching a normal level already in the fourth week. Due to a prolonged rise in body temperature, the pulse slows down and severe exhaustion develops. Severe forms of typhoid fever, in addition, can cause nonsense, to whom or sopor. In 10 out of 100 patients one week after infection on the abdominal wall and chest, small spots of pink color develop, remaining for 2-5 days. Sometimes, in parallel with these symptoms, pneumonia-like symptoms or symptoms resembling urinary tract infections can occur. Quite often typhoid fever is accompanied only by an increase in body temperature.
Recovery in conditions of timely proper treatment, comes fully. However, in the absence of treatment, its incorrectness or untimely, it is possible to develop complications. Frequent cases of bleeding, sometimes very massive. Often bleeding occurs in the third week of the disease. Approximately 2% of patients develop intestinal perforation, accompanied by intense pain in the abdomen. The contents of the intestine infect the abdominal cavity, which subsequently leads to the development of peritonitis.
The risk of developing pneumonia exists in the third week of the disease. Pneumonia often occurs as a result of pneumococcal infection, but salmonella can also cause pneumonia. Cases of damage to the liver and gallbladder are common. As a result of the penetration of bacteria into the blood( bacteremia), bone tissue( osteomyelitis), the membranes of the brain( meningitis), genital organs, urinary tracts, heart valves( endocarditis), kidneys( glomerulonephritis) develop. With infection of the muscles, abscesses may occur.
In the absence of proper treatment in 10 out of 100 patients, the symptoms of infection recur after 14 days after reaching normal body temperature. The number of relapses is significantly increased from taking antibiotics at the onset of the disease. The causes of this phenomenon are not established, but if antibiotics are administered during a relapse, the body temperature normalizes faster than if administered during a primary illness, but later the next relapse occurs.
Bacteria of typhoid fever are transmitted through the feces and urine of infected people. The likelihood of infection increases with inadequate washing of hands after urination or defecation and the spread of bacteria through water and food. Also, the pathogens of typhus are directly transferred by flies from stool to food. There are cases of transmission of typhoid fever to hospital workers who do not take due precautions during the treatment of bed linen of typhoid-infected patients.
The doctor suspects typhoid fever when examining the patient, questioning and analyzing the symptoms. Confirm the diagnosis can only detect pathogens in blood, urine, feces and tissue samples of the body.
Treatment of
With timely antibiotic treatment, recovery occurs in 99% of cases of typhoid fever. Mortality is common among the elderly or patients with severe depletion of the body, as well as young children. Negative predictions for severe forms of the disease - sopre, coma, shock.
Treatment and recovery can be lengthy. To ease the severity of complications of typhoid fever, as well as reduce the duration of the disease, antibiotics are prescribed. Widely used is levomycetin( chloramphenicol), but an increase in resistance to this type of antibiotic has contributed to the wider use of other drugs. If a patient has shock, delusions, or coma, corticosteroids are prescribed to reduce signs of brain inflammation.
The high risk of gastrointestinal bleeding or other complications of the gastrointestinal tract determines the need for a sparing diet. In cases where, as a result of a gastric dysfunction, normal digestion of food is not possible, intravenous nutrition is used. Perforation of the intestine requires the appointment of an antibiotic with a wide spectrum of action, since many different bacteria enter the abdominal cavity, or surgical intervention to restore the perforated area of the intestine or to remove it.
In the treatment of relapses, the same remedies are used as in the treatment of a primary disease, but the course of taking antibiotics lasts only 5 days.
Carriers are people who excrete salmonella bacteria with feces, but the symptoms of typhoid fever are not manifested. They are registered in the health authorities at their place of residence. Such people are prohibited from working with food. Often, the use of antibiotics destroys the bacteria of pathogens in carriers already at 4-6 weeks.
Stay healthy!