Abscess of the brain
An abscess is usually limited to a purulent-inflammatory process in the brain tissues. Clinically, cerebral abscess is accompanied by an inflammatory process in combination with symptoms of volumetric brain formation. There are, albeit less often, subdural and epidural abscesses.
Pathogenesis and etiology of
The causes of abscess development are: bacterial endocarditis, lung pathology, immunodeficiency states, "blue" heart defects, open and / or penetrating head trauma. Often pathogens become: staphylococci, pneumococci, streptococci, meningococci, toxoplasma, fungi, anaerobic bacteria, E. coli. The contents of the abscess are 25% sterile. The infection spreads in the brain contact, the spread can also be hematogenous.
The clinic often encounter contact abscesses due to otitis, mastoiditis, purulent processes in the adnexal cavity of the nose, skull bones, meninges, orbit. Approximately 50% of brain abscesses are of otogennoe origin. Most often, abscesses complicate chronic purulent otitis, rather than acute inflammation in the ear. When otitis infection from the temporal bone penetrates into the middle fossa of the skull through the cavernous sinuses and the roof of the tympanum. Thus provoking an abscess of the temporal part of the brain. In addition, otogenous infection through the sigmoid sinus and labyrinth can spread into the posterior fossa of the skull, causing an abscess of the cerebellum. Rhinogenic abscesses are localized in the frontal parts of the brain.
In most cases, metastatic brain abscesses are caused by lung diseases - pleural effusion abscess, pneumonia, bronchiectasis. Metastatic abscesses usually complicate osteomyelitis, septic ulcerous endocarditis, abscesses of internal organs. In the brain, septic embolism helps to penetrate the infection.
Open trauma to the skull leads to a traumatic abscess. In case of trauma, the dura mater is damaged and the infection enters the brain tissue through the perivascular cracks. If a foreign body has entered the brain, then an infection also enters with it. The abscess develops either in the area of the foreign body or in the course of the wound.
Clinical picture
General infectious symptoms: chills, fever, increased ESR, blood leukocytosis. And also weakness, slimming, pallor are the symptoms of a chronic infectious process.
Cerebrovascular symptoms develop due to increased intracranial pressure, which is caused by an abscess. As a result of intracranial hypertension, general epileptic seizures are sometimes noted. The most frequent symptom is a severe headache, sometimes even with vomiting. At the same time on the fundus there is optic neuritis or stagnant discs. Sometimes mental disorders, bradycardia up to forty or fifty cuts per minute. The patient is at the same time sluggish, apathy and slowness of thinking are observed. Then slowly develops drowsiness, deafness.
Focal symptoms, as a rule, depend on the spread of the abscess in the temporal, frontal lobes, in the cerebellum. Abscesses, which are common in the interior of the hemispheres and are outside the motor zone, usually flow without symptoms.
The otogenic abscesses can be formed not only on the side of the otitis, but also on the opposite side, by feeding the corresponding clinic.
Together with focal symptoms, there may be symptoms that are associated with the dislocation of the brain tissue and swelling and squeezing.
Meningeal symptoms are observed if the abscess is located close to the membranes, as well as in the abscess of the cerebellum.
Diagnosis of abscess
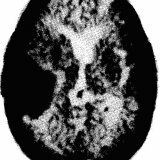
First of all, the diagnosis is based on information about the presence in the body or proximity to the brain structures of a purulent focus. Localization of the abscess can be determined by making CT or MRI of the brain. With the help of EEG and EchoEG, the paroxysms of slow waves and the displacement of the median structures are determined.
Ophthalmoscopy diagnoses stagnant discs of the optic nerves.