Meningitis in adults: symptoms, causes, diagnosis and treatment

Meningitis in medicine is an inflammatory process that takes place in the brain envelope, which is located between the skull and directly the brain.It differs transience and can lead a patient to death in a few hours.Moreover, the incubation period of meningitis can last from 4 to 7 days, so everyone should know the first signs of this dangerous disease.
Table of contents: Classification of the disease Causes of development Symptoms of meningitis in adults Methods of diagnosis of meningitis Principles of treatment of meningitis Complications and consequences of meningitis Recommended reading:Classification of the disease
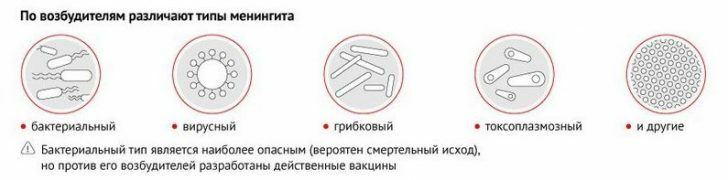
Meningitis is well understood and accurately classified.There are several types of this disease:
- By the nature of the inflammatory process:
- purulent meningitis - the disease is caused by pathogenic bacteria( meningococcus), pus is formed, differs very heavy course;
- Serous meningitis is caused by viruses( for example, enteroviruses, polio viruses, mumps epidemic and others), is characterized by the absence of purulent contents in the inflammation zone and less severe current than in the previous form.
- By the origin of the inflammatory process:
- primary meningitis - is diagnosed as an independent disease, when examining the focus of infection in the body of the patient is not detected;
- secondary meningitis - in the body there is a focus of infection, against which the current inflammatory disease develops.
- Due to the development of meningitis:
- bacterial meningitis - pathogens are E. coli, meningococci, staphylococci, streptococci, Klebsiella;
- fungal meningitis - meningitis is caused by candidias or cryptococci;
- Viral meningitis - the possible pathogens of the inflammatory process include the virus of mumps, herpes;
- the simplest - provoked the development of an inflammatory disease of amoeba or toxoplasma;
- mixed type of meningitis - there are several types of pathogen at once.
- Depending on how fast the development of inflammation goes:
- fulminant meningitis - develops very rapidly, almost immediately passes all stages of progression, the patient's death occurs in the first day of the disease;
- acute meningitis - development is not rapid, but rapid - maximum 3 days to reach the peak of the disease and death of the patient;
- chronic - proceeds for a long time, the symptoms develop "on an increasing", doctors can not determine when meningitis has developed.
- On the localization of the inflammatory process:
- basal - the pathological process develops in the lower part of the brain;
- convective - localization of the inflammatory process occurs on the anterior( convex) part of the brain;
- spinal - pathology affects the spinal cord.
Causes of development of
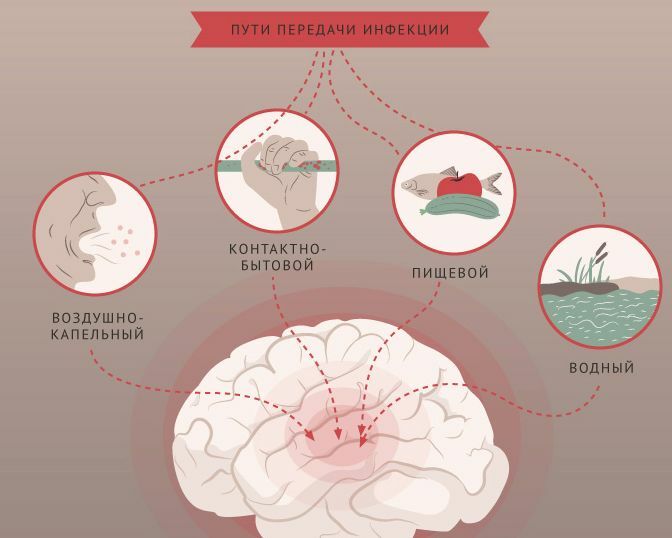
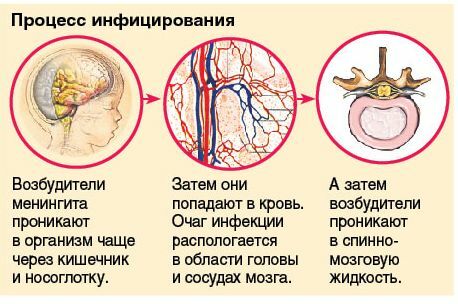
The only cause of the development of the inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain is the penetration of infection in them. This can happen in different ways:
- airborne;
- oral-fecal - it is about the use of unwashed vegetables, fruits, berries;
- is hematogenous - through the blood;
- is lymphatic - through the lymph.
A causative agent of meningitis can be:
- pathogenic bacteria - tuberculosis and E. coli, staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus, Klebsiella;
- viruses of various origins - herpes, the virus of mumps;
- fungi - candida;
- protozoa are amoebas and / or toxoplasm.
The factors that can trigger the development of the inflammatory process under consideration are:
- decreased immunity due to chronic diseases or forced long-term use of medications;
- chronic malnutrition;
- chronic fatigue syndrome;
- diabetes mellitus;
- peptic ulcer of the duodenum and stomach;
- human immunodeficiency virus.
Symptoms of meningitis in adults
Meningitis is characterized by severe symptoms, but the fact is that many of the signs go unnoticed or are removed by taking simple medicines.And this not only "lubricates" the symptomatology, but also makes it impossible to seek medical help in a timely manner. Symptoms of meningitis that should be a signal for immediate seeking professional help:
- Headache.This is generally considered the main sign of meningitis, but this pain syndrome will have distinctive features:
- headache constant;
- has a feeling of bursting the skull from the inside;
- the intensity of the pain syndrome increases when the head is tilted forward and backward, as well as when turning left-right;
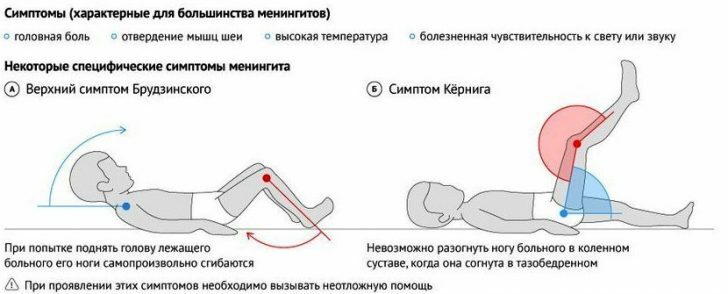
- The headache with meningitis becomes stronger with loud sounds and too bright color.Strain of the back of the neck muscles.
- .It's not about a convulsive syndrome, just a person can not lie on his back in the usual position, he will necessarily turn his head back, otherwise he experiences a strong pain syndrome.
- Indigestion.This means that one of the signs of the inflammatory process in the brain envelopes is nausea and vomiting.Note: vomiting will be repeated, even if the patient completely refuses food.
- Hyperthermia.The increase in body temperature with meningitis is always accompanied by chills, general weakness and increased sweating.
- Photophobia.A patient with a developing inflammatory process in the brain envelope is not able to look at the bright light - this immediately causes an acute headache.
- Impaired consciousness.It's about lowering the level of consciousness - the patient becomes listless, answers questions slowly, and at a certain point and completely ceases to respond to the speech addressed to him.
- Mental disorder.A person may have hallucinations, aggression, apathy.
- Convulsive syndrome.The patient may experience convulsions of the lower and upper extremities, in rare cases, against the background of convulsions appear arbitrary urination and act of defecation.
- Strabismus.If the progression of the inflammatory process affects the eye nerves, the patient begins to have a pronounced strabismus.
- Muscle aches.
Diagnosis of meningitis
Diagnosis of meningitis is a complex and time-consuming process.After all, it is important not only to establish a diagnosis, but also to determine the degree of development, the type of meningitis, its location and pathogen, which caused the onset of the inflammatory process in the brain envelopes of .The methods for diagnosing meningitis include:
- Patient Complaint Analysis:
- how long ago the symptoms of meningitis appeared;
- , did the mites bite in the recent past-some species of this insect are the bearers of the causative agent of meningitis?
- , was there a patient's stay in countries in which mosquitoes of the meningococcal infection( for example, the countries of Central Asia) are present.
- Inspection of the patient for a neurological condition:
- whether the patient is conscious and at what level it is - reacts to the speech addressed to him, and if there is no reaction to hail, then the reaction to pain irritation is checked;
- are there signs of irritation of the meninges - these include the tension of the occipital muscles and headache with a feeling of bursting and photophobia;
- whether there are focal neurological symptoms - it is about the symptoms of the lesions of specific areas of the brain: seizures with a biting language, weakness in the limbs, speech is broken, there is asymmetry of the face.Note: similar signs indicate the spread of the inflammatory process from the meninges directly to the brain( encephalitis).
- A laboratory study of the patient's blood - the analysis reveals signs of an inflammatory focus in the body: for example, the erythrocyte sedimentation rate will necessarily increase.
- Lumbar puncture.The procedure is performed only by a specialist and using a special long needle - it punctures the back skin at the lumbar level( subarachnoid space) and takes a little liquor( max. 2 ml) for analysis.It may contain pus or protein, which is a sign of the inflammatory process in the meninges.
Liquor is a liquid that provides the metabolism and nutrition in the brain and spinal cord.
- Computerized tomography or magnetic resonance imaging of the head - the doctor can layer-by-layer examine the meninges and identify signs of their inflammation, which include the expansion of the ventricles of the brain and the narrowing of the subarachnoid fissures.
- Polymerase chain reaction.This is an analysis during which the blood or blood is examined, which enables specialists to identify the pathogen and select a truly effective treatment.
Principles of treatment of meningitis
Important: treatment of the considered inflammatory process in the meninges should be carried out only in the hospital - the disease is rapidly developing and can lead to death in a few hours.No folk methods will help to cope with meningitis.
The doctor immediately prescribes medicines, namely antibacterial drugs( antibiotics) of a wide spectrum of action - for example, macrolides, cephalosporins, penicillins.This choice is due to the fact that it is possible to establish the causative agent of the disease in question only when sampling and researching the cerebrospinal fluid - this process is quite long, and the patient needs to be urgently given help.Antibiotics are administered intravenously, and in the case of severe patient health and directly into the cerebrospinal fluid.The duration of the use of antibacterial drugs is determined only individually, but even if the main signs of meningitis have disappeared and the body temperature of the patient has stabilized, the doctor will continue to inject antibiotics for several more days.
The next direction in the therapy of the considered inflammatory process in the meninges is the appointment of steroids.Hormonal therapy in this case will help the body to cope with the infection faster and normalizes the pituitary gland.
Diuretics are also considered mandatory in the treatment of meningitis - they will relieve swelling, but doctors must take into account that all diuretics contribute to the rapid washout of calcium from the body.
Patients undergo spinal puncture.This procedure facilitates the patient's condition because the cerebrospinal fluid exerts much less pressure on the brain.
Treatment of meningitis always takes place against a background of vitamin therapy:
- first, it is necessary to support the body and help it resist infection;
- Secondly, vitamins are needed to replenish the necessary macro / microelements, which do not enter the body due to eating disorders.
Complications and consequences of meningitis
Meningitis is generally considered a life-threatening disease. Complications of this inflammatory process in the meninges are:
- Cerebral edema.Most often this type of complications develops on the second day of the disease.The patient suddenly loses consciousness( this occurs against the background of the standard symptoms of meningitis), it sharply decreases, and after a while the pressure suddenly increases, the slow heartbeat is replaced by the rapid heart rate( bradycardia passes into a tachycardia), there is intense shortness of breath, all signs of pulmonary edema are clearly traced.
Note : if medical care is not available, then the meningitis symptoms disappear completely after a short time, the patient has involuntary urination and act of defecation and death due to respiratory paralysis.
- Infectious-toxic shock.This complication develops as a consequence of the decay and absorption in the cells and tissues of the body of a large number of decay products of pathogens of pathogenic microorganisms.The patient suddenly has a fever, the reaction to light and sounds( even not loud) becomes very sharp and negative, there is excitement and shortness of breath.
Note: infectious-toxic shock often occurs against the background of cerebral edema.The death of the patient occurs within a few hours.
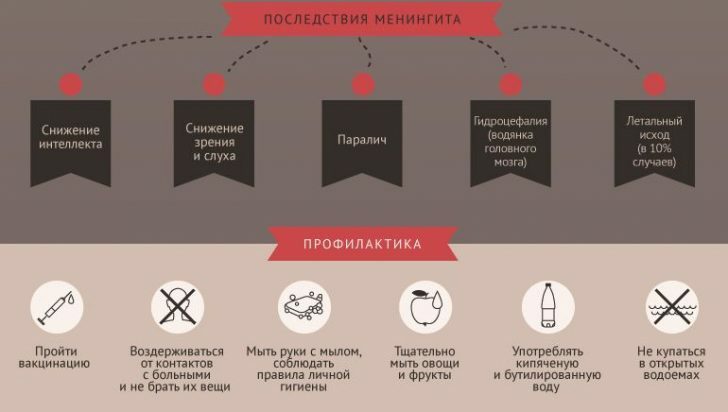
Consequences of meningitis can be epilepsy, deafness, paralysis, paresis, hormonal dysfunction and hydrocephalus.In general, any body organs and systems can be affected by meningococcal infection, so the recovery after an inflammation of the meninges lasts very long, and in some cases, all life.Only an immediate request for help to doctors will help reduce the risk of complications and the consequences of meningitis.
To remember all signs of meningitis and, if necessary, be able to help the patient with this dangerous disease in a timely manner, review this video review:
Tsygankova Yana Aleksandrovna, medical reviewer, therapeutist of the highest qualification category.