Normal and pathological morphology of spermatozoa( structure)
Evaluation of the morphology of spermatozoa is included in the mandatory parameters of the study of ejaculate - spermogram. Morphology or, in simple terms, the structure of spermatozoa - one of the important criteria that show the ability of the reproductive cells to fertilization. Evaluate it visually under a microscope, counting the ratio of normal and altered cells.
Contents
- 1 Morphologically normal spermatozoon
- 2 Morphology abnormalities
- 3 Reasons for
- 4 How to improve the morphology of spermatozoa
Morphologically normal sperm
Getting a normal sperm. As a basis for how morphologically normal spermatozoon should look, cells taken from cervical mucus( mucous plug in cervix) after sexual intercourse were taken. It is believed that if these cells could penetrate the cervical mucus, then they are able to go further and fertilize the egg.
This approach, on the one hand, led to the fact that even in healthy fertile men the number of morphologically normal spermatozoa does not exceed 30%.On the other hand, the lower threshold, which allows for conception, is small - 4%.A condition in which the number of normal spermatozoa is less than this value is called teratozoospermia and requires special attention.
Appearance. To study the morphology of spermatozoa, a drop of ejaculate is applied to a slide, dried and stained with two dyes. After that, the shape of the head, neck and flagellum is assessed under a microscope.
- The head is oval in shape, with smooth contours. In front of it, the acrosome is clearly visible - a membrane vial, which allows to be embedded in the egg shell. The acrosome occupies 40 to 70% of the volume of the head. In the post-macrosal region there should be no vacuoles( membrane vesicles).
- The neck is clearly defined, thin, the main axis coincides with the axis of the head, the length of the neck and head are approximately equal.
- Flagellum thinner than the cervix, about 10 times longer than the head, of the same diameter all over. Can be twisted by itself, but no more than 360 degrees.
Anomalies in the morphology of
According to the spermatozoon structures under study, abnormalities of the head, cervix, flagella can occur.
Head defects:
- resizing( large or small);
- shape change( pear-shaped, conical, round, amorphous);
- change in the size and location of vacuoles( more than 2, location in the post-acrosomal region);
- acrosome defects( too small or too large);
- two heads;
- any combination of these defects.
Cervical defects:
- asymmetrical attachment to the head;
- is excessively thin or thick;
- is excessively curved.
Flag defects are mainly related to the form:
- broken;
- twisted;
- with the wrong contour;
- and so on.
Excessive residual cytoplasm is an increased cytoplasmic drop in the neck region having a volume of> 1/3 of the head volume.
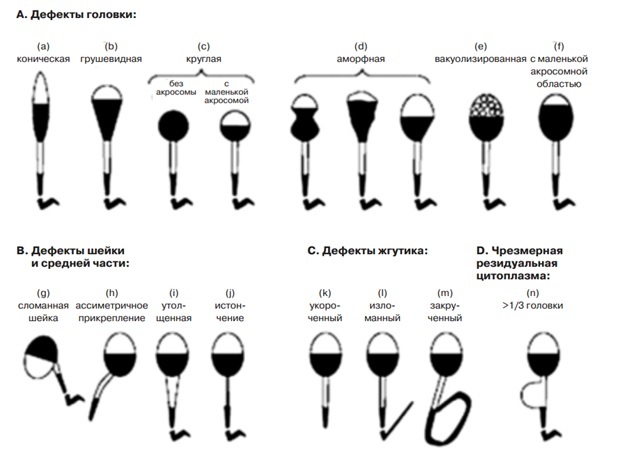
Fig.1 - Anomalies in the morphology of spermatozoa.
Separately, special structural defects are discerned - round heads, when no acrosome is formed, or complete absence of heads( acephalic spermatozoa).They are usually caused by a defect in spermatogenesis and are not capable of fertilization. Acephalic spermatozoa do not take into account the total number of sex cells, but with their obvious predominance, it is safe to talk about male infertility.
In the normal study of ejaculate, the percentage of any anomalies is not counted. This is done only for research purposes, when it is necessary to study the damaging effect of a particular pathological condition, or for diagnostic purposes( for example, to assess the possibility of IVF).
Causes of
Inflammatory processes. The most common cause of the appearance of spermatozoa with altered morphology is the inflammatory processes in the epididymis and the prostate gland. Inflammation can be asymptomatic, so PCR diagnosis of the most common sexually transmitted infections is an obligatory part of the full andrological examination.
Varicocele. Another fairly common cause of pathological changes in the morphology of spermatozoa is varicocele. This condition occurs in 20% of men in general and in 40% of men with authentically established infertility.
Hormonal disorders. Hormonal disorders also affect the development and maturation of sperm. Asymptomatic hyperprolactinemia, a drop in testosterone, an increase in the amount of luteotropic hormone - all this can cause a change in the structure of spermatozoa.
External factors. You can not discount the external factors:
- intoxication, including alcohol;
- work in hot shops( high temperature disrupts the testicles);
- deficiency in food vitamins and trace elements.
Hereditary disorders. Another common, albeit paradoxical, at first glance, situation - hereditary violations of the morphology of spermatozoa. The fact is that the normal structure of the sex cells is encoded by a multitude of genes. Since each person has a double set of chromosomes, the pathological gene inherited from one of the parents does not manifest itself if his "pair" obtained from the other parent works normally. But when two identical defective genes occur, the morphology of the sex cells changes.
How to improve the morphology of spermatozoa
Elimination of the cause. Of course, first of all, we need to identify the cause that caused the violation of the structure of the sex cells. Further work is carried out to eliminate this cause. For the treatment of inflammation, antibiotics and physiotherapy are used, hormonal factors are corrected by special drugs, which can be recommended only by a doctor. Varicocele needs to be operated on.
Increased fertility. If the cause was not found, and this is possible, vitamins, selenium and zinc preparations, and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are used to improve sperm status. When choosing an additive with Omega-3 acids, you need to pay attention to the content of docosahexaenoic acid in it. It is this substance that has a beneficial effect on fertility, both in men and in women.
Recommended for viewing: