Iodine deficiency in the body - symptoms, consequences
A person needs daily intake of iodine molecules with food and water. If the diet does not have enough of this trace element, then characteristic disorders in the thyroid gland and other organs are gradually formed.
In Russia, most of the territory belongs to iodine-deficient regions. Residents of all these areas need regular preventive examination. Correction of micronutrient deficiency is one of the tasks of public health. In our country, the prevention of endemic diseases is carried out at the individual, group and mass levels.
Iodine deficiency disorders are observed in men of all ages. The most vivid picture of diseases is typical for children and adolescents. Endemic are all regions where the incidence of juveniles is more than 5%. In such areas, goiter usually affects up to 30% of the adult population. In men, the prevalence of this pathology is slightly lower than that of women. This trend is explained by the lower need for iodine in the stronger sex. Also plays a role and the general stability of the hormonal background in men.
Contents of
- 1 Why do I need iodine?
- 2 daily requirement for iodine men
- 3 signs of iodine deficiency
- 4 consequences of iodine deficiency
- 4.1 Iodine deficiency disorders
- 4.2 consequences of long-term iodine deficiency
- 5 Endemic goiter in men
- 6 How to make up for deficiency of iodine?
- 6.1 Food
- 6.2 Nutritional supplements and medicines
Why do we need iodine?
In the human body, only thyroid cells are able to capture and accumulate iodine. The microelement comes with a diet in the form of organic compounds. Thyreocytes store iodine in the follicles. A special biological gel is used for storage - a colloid.
Iodine uptake is increased by the action of thyroid-stimulating hormone( TSH).The same factor stimulates the synthesis of thyroid hormones. Iodine-containing biologically active compounds include thyroxine and triiodothyronine.
Each molecule of thyroxine has 4 iodine atoms. Triiodothyronine is a stronger form of the hormone, in its composition there are 3 iodine atoms. If
Daily need for iodine in men
For the normal functioning of the thyroid, regular daily intake of a microelement is required. Own reserves of iodine in the body are always small - about 15-20 mg. In regions endemic in the goiter, this indicator is even smaller.
The daily requirement for a microelement depends on age and sex. On average, a person needs 2-4 μg per kilogram of body weight.
In infants of the first year of life, the daily requirement is estimated at 25-50 μg. For a boy 1-5 years old, consumption of 90 μg of a microelement per day is considered the norm. Primary school children should receive about 120 micrograms of iodine per day. Young men aged 12-17 years need slightly higher - 150 mcg.
In most of the Russian regions, this requirement for a microelement is not met 100%.Many men get only 40-60 micrograms of iodine with food and water. So much trace element is contained in the usual diet, which includes products of local production.
Prolonged iodine deficiency triggers pathological processes in the thyroid tissue. Far from all men form focal formations and diffuse goiter. But the propensity to these diseases in endemic regions is high.
Symptoms of iodine deficiency
To find out if you have a deficiency of iodine in the body, you can by characteristic symptoms. In addition, you need to take into account the region of residence, features of nutrition and lifestyle.
You are at higher risk of iodine deficiency if:
- you live in a remote area from the sea;
- you do not like seafood;
- you do not use iodized salt;
- you drink more than 25-30 g of pure alcohol daily;
- you smoke.
Indirectly, the lack of a trace element is indicated by complaints of weakness, fatigue, memory impairment, hair loss, dry skin, brittle nails.
It is a mistake to think that the lack of a trace element helps to reveal a home test with alcohol tincture of iodine. If this solution is applied to the skin, then the rate of its disappearance is affected by a number of random factors( the sebaceous glands, the thickness of the stratum corneum of the epidermis, the temperature in the room, etc.). But the iodine deficiency itself does not actually accelerate this index.
A micronutrient deficiency can be more accurately diagnosed in a laboratory. Physicians appoint for this purpose an analysis of urine for iodine. Usually in a day from the body is deduced 100-150 micrograms of a microelement. In endemic areas of goiter, this indicator is 2-3 times less.
Consequences of iodine deficiency
iodine deficiency states
For regions of iodine deficiency, subclinical hypothyroidism( a deficiency of thyroid hormones) is especially characteristic and a wide spread of cognitive dysfunction. In adult men, chronic iodine deficiency can lead to changes in the intellectual and psychological sphere.
Patients report:
- memory impairment;
- decreased vitality;
- drowsiness;
- apathy;
- deterioration of logical thinking;
- decreased attention;
- loss of interest in surrounding people.
In children, these conditions manifest themselves:
- mental retardation;
- by stunting;
- susceptibility to viral and bacterial infections;
- is a violation of puberty.
Consequences of prolonged iodine deficiency
According to the World Health Organization, up to 30% of adults and children in all countries face iodine deficiency.
Main consequences of micronutrient deficiency:
- nodular, diffuse or mixed goiter;
- hypothyroidism;
- iodine-induced thyrotoxicosis;
- violations in the intellectual sphere.
In children, a micronutrient deficiency at the stage of intrauterine development can cause cretinism and congenital malformations. In boys and boys, iodine deficiency provokes a backlog in the mental and physical spheres.
In addition, the lack of a microelement may be an unfavorable factor in getting into a nuclear accident zone. Men from iodine-deficient regions are more vulnerable in such situations.
Endemic goiter in men
Goiter with lack of iodine is formed due to the constant stimulation of thyroid tissue with thyroid-stimulating hormone( Figure 1).
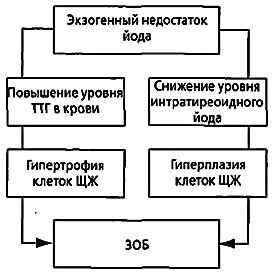
Fig.1 - Formation of goiter with a lack of iodine in the body.
This exposure results in:
- increasing the number of thyroid cells;
- increase in the size of each endocrine cell;
- increase in the total mass of the thyroid gland;
- occurrence of focal formations.
Hyperplasia and hypertrophy of the thyroid gland on the background of iodine deficiency is a protective mechanism that allows the fullest use of all scarce resources. But with a prolonged lack of a trace element in the diet, an increase in the volume of thyroid tissue becomes pathological. In this case, endemic goiter develops( Figure 2).
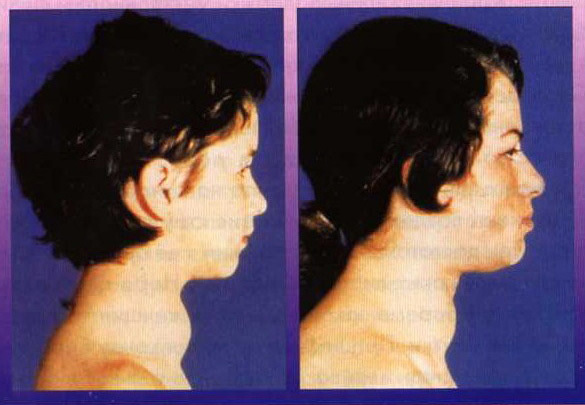
Fig.2 - Patients with endemic goiter.
The goiter is classified as:
- diffuse;
- nodal;
- mixed.
Diffuse goiter is diagnosed if all glandular tissue is uniformly hypertrophied. If focal formations are found in the thyroid gland, then put the nodal goiter. In a number of cases, an increase in the total volume and the appearance of nodes are observed in the same patient. In this situation, they talk about mixed goiter.
Normally, the volume of the thyroid gland in an adult male is up to 25 cm3.In children, the size of the organ depends on the body surface area and age. Standards for boys and adolescents are standardized and consolidated into special tables for specialists.
The volume of the thyroid gland is evaluated when examining the neck and palpation. The doctor takes into account the physique of a man, his weight and anatomical features. Usually the thyroid gland is not visible by a simple examination. Sometimes the contours of it become noticeable if the patient tilts his head back.
Palpation( feeling) of the neck allows you to roughly determine the size of the gland. If each of the shares is smaller in size than the phalanx of the patient's thumb, there is no obvious goiter.
Table 1 - Degrees of goiter according to the results of the examination.
| DEGREE | CHARACTERISTICS |
|---|---|
| 0 | Thyroid not visible and almost not palpable |
| 1 | Iron not visible, but palpated with enlarged |
| 2 | Thyroid is noticeable when examining the neck |
To 1 degree of goiter, the nodular forms are also included when tissue volume remains normal, but focal formation in lobes orIsthmus.
More accurate information on the volume of thyroid tissue can be obtained by ultrasound.
Normal ultrasound picture of the thyroid gland for a man:
- contours of the gland are clear;
- fabric structure is uniform;
- echogenicity is average;
- no nodules;
- the dimensions of each of the shares - vertical up to 8 cm, transverse to 6 cm, thickness up to 2 cm;Isthmus is less than 0.6 cm;
- the total volume of up to 25 cm3.
Even in endemic regions, a man needs a follow-up to accurately establish the nature of the process and the hormonal function.
Usually prescribed:
- assays for hormones TSH and thyroid( T4, T3);
- analysis for calcitonin( if there are nodes);
- puncture biopsy( if there are nodes);
- study of antibody titer.
Goiter in most cases is non-toxic, that is, the functional activity of the tissue is normal or below average. Calcitonin is elevated in case of oncology( medullary cancer).The results of puncture with endemic goiter show a benign process. In the material are found follicles, colloid, blood cells. According to the results, a histological diagnosis is made( colloid goiter with varying degrees of proliferation).Iodine deficiency can contribute to the development of autoimmune inflammation. But usually in men with endemic goiter the antibody titer remains normal.
Treatment of nodular goiter:
- elimination of iodine deficiency;
- correction of hypothyroidism( if detected);
- surgical treatment( with large size of the gland or large nodes).
In the 1st stage, a patient with diffuse goiter at normal TTG is given potassium iodide at a therapeutic dosage( 200 μg / day).Further, after 6 months, the dynamics of the disease are assessed by ultrasound. If the goiter continues to grow, then a synthetic analogue of thyroxine is added to the treatment. In the event that this is not sufficient, the patient is recommended an operation. If the patient has a hypothyrosis after additional examination, then immediately he is prescribed both potassium iodide and synthetic thyroxine.
In elderly men, the nodal and mixed goiter is a dangerous diagnosis in terms of the occurrence of thyrotoxicosis. Often focal formations become autonomous from the influence of TSH and begin to produce an excessive amount of hormones. This state is first corrected by thyreostatics. The patient is then referred for surgery.
Indications for surgical treatment:
- compression of surrounding tissues( goiter prevents eating, breathing, talking);
- nodes more than 4 cm in diameter;
- toxic( autonomous) sites;
- cosmetic defect( goiter deforms the neck, and this worries the patient).
After surgical treatment, many men need lifelong hormone replacement therapy with thyroxine. Such treatment is carried out by the endocrinologist under the control of analyzes on TTG.
How to make up for iodine deficiency?
In the regions of iodine deficiency, doctors recommend constant prevention of endemic diseases. Replenishment of a micronutrient deficiency is especially important in childhood and adolescence, and also for adults up to 35-40 years. In these population groups the lack of iodine provokes diffuse forms of goiter and mild hypothyroidism.
People in the age of 40-50 years in the thyroid gland already often have focal formations. Such nodes can react to the receipt of high doses of iodine by the hyperproduction of hormones. Therefore, before starting the prevention of endemic goiter, it is necessary to do a follow-up. Doctors prescribe ultrasound, and if necessary - puncture biopsy and scintigraphy.
Food
For the prevention of goiter in the diet include:
- marine and river fish;
- sea kale;
- oysters and other seafood.
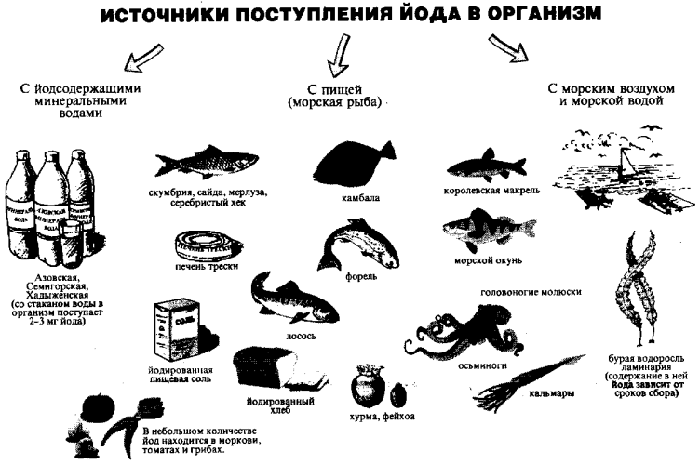
Fig.3 - Sources of intake of iodine in the body.
In addition, iodized salt helps to enrich the food with a trace element. It is used at home and for industrial production of products. In the salt for each kilogram is 25-55 mg of potassium iodate.
Nutritional supplements and medicines
From medicines for the prevention of goiter are used:
- Sea-cabbage and marine layers;
- Food supplements with organic iodine compounds( "Iodine-Active");
- complex products with vitamins and trace elements;
- preparations of potassium iodide( "Iodomarin", "Iodobalance").
All products with natural ingredients( for example, with sea cabbage) are characterized by a large heterogeneity of raw materials in the concentration of biologically active substances. Vitamins and one-component agents with potassium iodide are much more stable. They allow to maintain a uniform supply of microelements to the body.
Prophylactic doses of potassium iodide for men:
- , boys under 12 years of age - 50 to 100 μg;
- adolescents and young people under 35 years of age - from 100 to 200 mcg;
- men older than 35 years - 100 mcg.
Before the beginning of prophylaxis with preparations it is desirable to pass an ultrasound of the thyroid gland, donate blood to hormones and visit an endocrinologist.
Doctor-endocrinologist Tsvetkova IG
Recommended for viewing: