Metastases in prostate cancer: approaches to diagnosis and treatment
metastases are foci of tumor cell clustering outside the primary malignant neoplasm. The spread of cellular elements occurs through the blood and lymphatic vessels. In a natural way, the activity of metastatic cells is suppressed by the primary maternal tumor, therefore at the initial stages the clinical symptoms of metastases are absent. According to studies

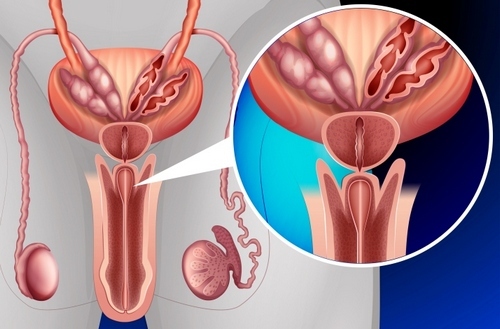
Malignant neoplasm of prostate cancer( prostate cancer)
most cases, the formation of metastases in regional occurs( the bottom of the small pelvis) and remote( outside of) the lymph nodes, bones, lung tissue, liver, and adrenals. Of the bone structures the most common lesion of the pelvis, as well as vertebrae and femur. Medical research shows that when metastasizing into bone tissue, as a rule, there is no damage to distant lymph nodes.
The peculiarities of prostate cancer is that in a number of cases it is manifested precisely by metastases, and not by symptoms caused by the activity of the tumor itself. In this case, disturbed urination, pain and discomfort in the lower abdomen, and signs depending on the localization of metastases.
Content
- 1 Clinical manifestations
- 1.1 Defeat bone structures
- 1.2 lymph node
- 1.3 defeat lung tissue
- 1.4 liver damage
- 1.5 Common symptoms of metastasis
- 2 Features
- 3 diagnostic approaches to treatment
- 3.1 Hormone therapy
- 3.1.1 The synthesized analogs of hypothalamic releasing factor
- 3.1.2 Estrogens
- 3.1.3 antiandrogens
- 3.2 Radiotherapy
- 3.3 Chemotherapy
- 3.4
- 3.1 Hormone therapy
Surgery Clinical manifestations
Defeat bone structures
most common metastatic prostate cancer affects the pelvis, sacrum and lumbar vertebrae, at least - the ribs. When lesions of bone structures are observed:
- pain in the bones of the pelvis, spine, chest;
- pathological vertebral fractures;
- complete( paralysis) or partial( paresis) loss of motor activity of the limbs( with compression of the spinal cord);
- violation of the processes of urination and bowel movement( incontinence, diarrhea and constipation).
lymph node
frequently metastatic process among distant lymph nodes affects inguinal nodes( usually on one side).
Symptoms of metastatic lesion of lymph node :
- increase in size;
- is a rounded shape;
- increased density, up to tuberosity;
- immobility, adhesion to other lymph nodes and soft tissues;
- painlessness.
Even if the lymph node keeps mobility( more often with its small size), it is always painless( unlike inflamed).When
lesion as a regional( pelvic) and remote nodes occurs compression of venous and lymphatic vessels .This leads to a violation of the outflow of fluid from the organs.
There is an increase in size, swelling:
- of the lower limbs;
- scrotum;
- of the penis.
It is also possible to squeeze the ureters, which will be manifested by constant, non-intensive pain in the lower back.
Lesion of lung tissue
When lesions of pulmonary tissue appear symptoms that indicate the development of inflammation and respiratory failure.
Main manifestations:
- cough;
- subjective feeling of lack of air;
- secretion of mucopurulent sputum;
- hemoptysis;
- persistent pain in the thorax.
Lesion of the liver
When lesions of the liver , it increases in size, becomes bumpy, the pathology is manifested by gravity in the right hypochondrium. In severe cases, jaundice is possible.
General symptoms of metastases
A common sign of metastasis( regardless of localization) is the appearance and further intensification of intoxication syndrome.
Symptoms :
- unmotivated weight loss, up to a sharp loss of body weight( cachexia);
- general weakness, loss of appetite, periodic increase in body temperature( usually not higher than 37.5 ° C);
- anemia, which is manifested by the pallor of the skin, and in the study of blood - a decrease in the level of hemoglobin and erythrocytes;
- uremia( deterioration of excretion of toxins from the body against a background of secondary impairment of the excretory function of the kidneys).
Diagnosis features
The choice of method of investigation depends on the alleged localization of metastases.
The most widely used:
- ultrasound examination of the abdominal cavity, as well as retroperitoneal space;
- radiography of the chest, spine, pelvic bones, femurs;
- computer and magnetic resonance imaging( CT and MRI) of the abdominal cavity;
- scintigraphy of bone structures.
Skeletal scintigraphy is based on recording the accumulation and distribution of a special drug substance in the bone structures, which is recorded with a gamma camera. Currently labeled with radioactive technetium-99 phosphate compounds. Osteoscintigraphy is especially informative in the presence of syptomatics of skeletal damage and the absence of manifestations of a primary tumor of the prostate. A similar pattern is most often observed in men over the age of 80 years.
Foci contain actively growing and multiplying cells, so they accumulate drugs and can be visualized.
Two-sided pelvic lymph node dissection is used to confirm the defeat of regional lymph nodes by metastases, which in modern clinical practice is the "gold standard" of diagnosis. The procedure involves the removal of not only pelvic lymph nodes, but also all available structures of the lymphatic system. The resulting material is examined in the laboratory, and when a metastatic cell is detected, the diagnosis is finally confirmed. Apply this technique not only for diagnosis, but also for therapeutic purposes when planning remote irradiation of tumor tissues.
Approaches to treatment
The presence of metastases indicates the impossibility of carrying out radical treatment with complete removal of tumor foci. The means are applied, not only directly affecting metastases, but also preventing them from further screening.
Basic treatment methods :
- hormone therapy;
- irradiation;
- chemotherapy;
- surgery( radiosurgery).
Hormone therapy
Hormone therapy for distant metastases is used as a palliative therapy, that is, to alleviate symptoms.
The hormonal drugs , used in the treatment of metastases, are divided into:
- synthesized analogues of the releasing factor of the hypothalamus;
- estrogens( female sex hormones);
- antiandrogens.
Synthesized analogues of the releasing factor of the hypothalamus
Artificial analogues of the releasing factor produced in the nervous structures( hypothalamus), as a result of the cascade of reactions lead to a decrease in testosterone production activity( male sex hormone) by the testicles.
The most commonly uses :
- goserelin;
- leuprorelin.
A single-dose and course dose of these drugs is selected by an oncologist, usually drugs are administered once a month, long, until their effectiveness and development of resistance to hormone therapy are reduced.
Estrogens
Estrogens directly inhibit the function of the testicles, as well as indirectly( through the hypothalamus).All this causes a decrease in the production of testosterone, and as a result - the weakening of the progression of the neoplasm.
Estrogens have a number of side effects of :
- on the cardiovascular system( increase the risk of heart attacks, strokes);
- blood system( increase the likelihood of thrombotic complications( PE, pulmonary embolism),
- gastrointestinal tract( increase bile stasis in the liver),
- weaken the immune system
Diethylstilbestrol, most often intramuscularly, is fraught with less consequencesThan taking tablets
Antiandrogens
Steroid( cyproterone) and non-steroid( flutamide) antiandrogens have a number of effects :
- block sex hormone receptorsIn the prostate
- reduce the secretion of the hypothalamus releasing factors, that is, substances that activate the secretion of the gonads
As a result, the level of testosterone and its biologically active form, dihydrotestosterone, is reduced
The antifungal drug ketoconazole also has the property of inhibiting the synthesis of sex hormones by the adrenal glands. Additionally used with insufficient effectiveness of other antiandrogenic drugs.
Radiotherapy
Main article: Radiation therapy for prostate cancer
Radiation therapy is most often performed with localization of metastases in the spine. Remote sensing of lesions with a total dose of up to 55 Gy is used.
Therapeutic effects :
- decrease( and in some cases complete elimination) of pain syndrome;
- with compression fractures allows you to prevent the screening of tumor cells during a neurosurgical operation.
If there are a lot of metastases, various parts of the body are affected, then total or half of the body is applied, resulting in a significant reduction in pain syndrome. The most modern method is intravenous administration of a radioactive element( Strontium 89), which also provides an anesthetic effect in bone metastases.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy( mitoxantrone, estramustine) with metastasis is used alone or in combination with hormone therapy. A positive effect is associated with a decrease in pain syndrome, as well as with the suspension of the spread of the metastatic process with the defeat of new tissues and organs.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is indicated only if regional lymph nodes are affected. Currently, the most feasible is the maximum possible removal of lymphatic vessels and pelvic nodes( along various parts of the iliac arteries), as well as lymph nodes located in the sacrum.
In distant metastases, in addition to radical prostatectomy, a bilateral orchiectomy( removal of the testicles) is performed, which reduces the rate of development of other metastases.
See also: Staging of prostate cancer: stages of development of oncology and survival forecast
Recommended viewing: