Abdominal obesity: signs and consequences for male health
Fat is subcutaneous - it can be deposited on the entire surface of the body - from the face to the shins - and visceral, which is deposited around the internal organs( mainly the abdominal cavity).Abdominal obesity is the accumulation of excess fat mass in the abdomen. More precisely, a large omentum - a double fold of loose connective tissue, which protects internal organs from damage, accumulating fat as an amortization layer. Excess visceral fat is much more dangerous and can lead to a serious illness if you do not do weight reduction in time.
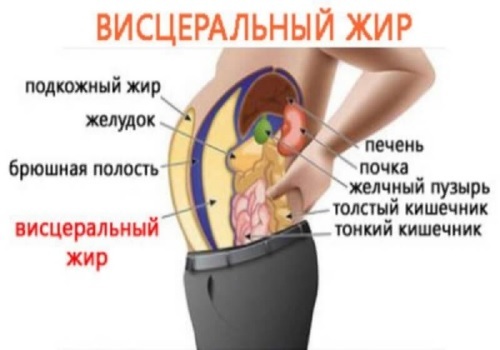
Excess visceral fat leads to abdominal obesity
Content
- 1 Criteria obesity
- 2 Complications of abdominal obesity
- 2.1 Cardiovascular
- 2.2 gastrointestinal
- 2.3 endocrine system
- 3 Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome
- 4 Prevention
- 5 Diets
disease of obesity Criteria
mass indexBody and waist circumference are the two main criteria that allow a doctor to diagnose obesity.
Waist girth is measured using a meter on the natural waist line( the middle of the distance between the top of the iliac crest and the lower lateral edge of the ribs).BMI - using the formula( weight in kilograms / square of height in meters).There are also additional parameters - the ratio of the waist circumference to the hips, the amount of fasting glucose, the amount of triglycerides and high-density lipoprotein( HDL) in the blood and blood pressure.
The table below shows the main criteria that determine the parameters of male obesity.
| Obesity level | BMI, kg / m2 | Waist circumference, cm |
|---|---|---|
| Normal weight | & lt;25 | ≤ 102 |
| Initial overweight | 25 - 29.9 | ≤ 102 |
| Obesity of 1st degree | 30 - 34.9 | ≤ 102 |
| Obesity of 2nd degree | 35 - 39.9 | ≤ 102 |
| Obesity of 3rd degree | & gt;40 | ≥ 102 |
In the western medical literature, there is also a morbid( 40-50 kg / m2) and super obesity( above 50 kg / m2).
Measurement of waist circumference helps to control excess weight
Data are given for a person with healthy metabolism( the so-called "healthy metabolic phenotype").BMI alone is not a criterion for abdominal obesity.
But if a person has an unhealthy metabolic phenotype, the waist girth even with the first degree of obesity will be greater than 102 centimeters. This means that there is a direct relationship between the waist circumference and metabolic disorders. That's why doctors separately distinguish abdominal obesity.
Under abdominal obesity is to understand the significant prevalence of visceral fat over the subcutaneous in the abdomen.
Complications of abdominal obesity
Excess visceral fat helps increase blood levels of triglycerides and low-density lipoproteins - the so-called "bad" cholesterol. In addition, it contributes to the loss of susceptibility to insulin of all tissues, which forms type 2 diabetes.
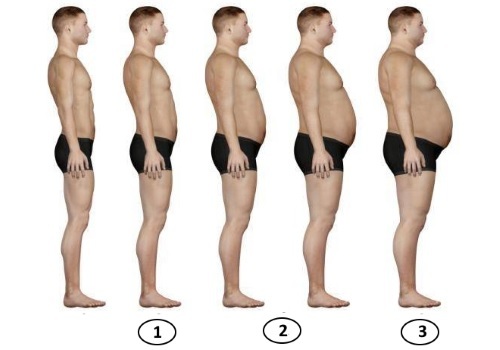
3 stages of abdominal obesity: with the first - a little excess weight, the third - a significant excess of the norm
In addition, the fatty layer in itself makes it difficult for many organs and systems.
- overweight and obesity of 1 degree - 1-5% risk of developing cardiac pathology and 7-23% risk of developing diabetes;
- obesity 2 and 3 degrees - 5% higher risk of developing heart disease and 23% or higher risk of developing diabetes.
Cardiovascular system
Abdominal obesity increases the risk of developing the following diseases:
- dyslipidemia( a violation of the ratio of fatty acids and cholesterol);
- arterial hypertension;
- atrial fibrillation;
- ischemic heart disease;
- stroke;
- varicose veins.
The digestive tract
Naturally, the digestive organs also suffer from abdominal obesity: a fat pad that fills the abdominal cavity and increases intra-abdominal pressure does not do them good.

Excess fat in the abdomen affects the internal organs of
Among the diseases that are most common in obese people are the following:
- non-alcoholic steatohepatitis - fatty liver;
- reflux esophagitis( throwing the contents of the stomach into the esophagus due to increased pressure);
- dysfunction of the gallbladder: cholecystitis, including calculous( stones).
Endocrine system
Adipose tissue is a metabolic and endocrine active organ. Excess visceral fat disrupts the sensitivity of cells to insulin, which forms type 2 diabetes. It is usually preceded by a metabolic syndrome, which will be described in more detail later.
In addition, the fat tissue produces estrogens - female sex hormones.
Also in severe forms of the disease, the adrenal glands may suffer.
Abdominal obesity and metabolic syndrome
Metabolic syndrome is a set of pathological manifestations characterized by:
- increasing the amount of visceral fat( abdominal obesity);
- -resistant cells to insulin action;
- dyslipidemia;
- by arterial hypertension.

Abdominal obesity is a precursor of the metabolic syndrome
Abdominal obesity is the main precursor of the metabolic syndrome. But there are other, not less important indicators:
- the presence of arterial hypertension( blood pressure above 140/90);
- high level of triglycerides in the blood( more than 1.7 mmol / l);
- low level of high-density lipoproteins - a fraction that takes cholesterol from peripheral tissues and carries to the liver( less than 1 mmol / L);
- impaired tissue tolerance to glucose( during the stress test, the glucose level is above normal).
Prevention of
The main factors that cause the emergence of abdominal obesity are genetic predisposition, malnutrition and inactivity. If you can not do anything with the first, you can limit the influence of the last two factors:
- Limit fatty and high-carb foods, eat more vegetables, do not overeat and eat 3-4 hours before sleep - these simple tips allow, if not reset, then, byAt least, keep the weight at one level.
- Regular moderate exercise will "burn" the extra calories that have entered the body, and also strengthen the heart.
Nevertheless, it is the healthy and balanced diet that prevents obesity and keeps the weight. Bad habits( smoking and alcohol) only exacerbate the problem with excess weight, as they disrupt the metabolism in the body. Therefore, nutritionists are advised to give up harmful habits to those who want to go on a diet and lose weight.
Diets
Diets are very popular now, but it's worth remembering that a sharp weight loss is a big stress for the body and can hurt more than obesity itself.

To choose diet for weight loss should be approached with caution
It is impossible to lose weight by 10-15% of the available body weight for several months without harm to health - usually such indicators are achieved by fasting( after which the body begins to store more fat), carbohydrate nutrition and otherExtreme diets.
To optimally lose weight and not to harm the body, it is necessary to consider the following recommendations:
- Overweight and 1 degree of obesity - it is optimal to lose weight by 3-10% of the available body weight for 6 months;
- 2 degree of obesity and the presence of pathology( hypertension, diabetes mellitus) - 10-20% for 6 months;
- 3 degree of obesity - 20-25% for 6 months.
Recommended for viewing:



