Mastopathy - causes, signs, treatment
Pathology of mammary glands in the form of fibrocystic transformation is called mastopathy .This disease is attributed to female, although in men there are similar conditions. In representatives of the stronger sex, the breast glands are more often affected in adolescence. But sometimes painful densities occur at another age( including in childhood and senile).

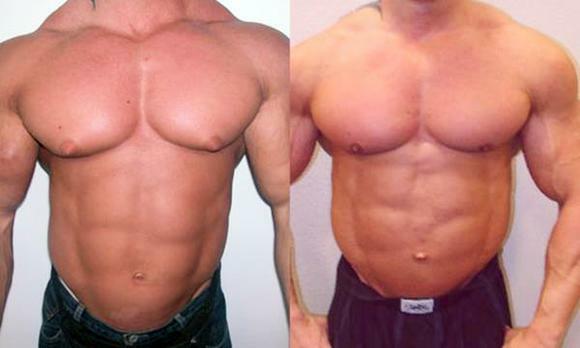
Fig.1 - Hypertrophy of mammary glands in men - gynecomastia( before and after surgery).
Contents of
- 1 Normal structure of mammary glands in men
- 2 What is gynecomastia?
- 3 Pathologic causes of gynecomastia
- 4 Symptoms Pathology male breasts
- 5 survey in mastopathy in men
- 6 mastitis treatment in men
normal structure of the breast in men
Dairy( breast) gland lays in utero and in boys and girls. Until puberty( puberty), there is practically no difference in the anatomical structure of this area. Then in adolescent girls there is a proliferation of glandular tissue under the influence of estrogens, gestagens, prolactin. The volume, shape, structure of the organ changes. In young men, the mammary glands practically do not develop. In adulthood, men have areoles of relatively small diameter and a nipple of 2-4 mm in height. Thoracic glands are localized between the fourth and fifth ribs to the left and right of the median line. The tissue of the organ( in the study of the macro preparation) is whitish in color. Slices and strokes are weak and short. The thickness of the mammary gland in a man is normal - up to 5 mm, and the width - up to 15 mm.
In the histological structure, 2 departments are distinguished:
- secretory( composed of epithelial ducts);
- is interstitial( composed of connective tissue).
A number of hormones affect the glandular tissue in men. The main role belongs to androgens, prolactin, estrogens, gonadotropins, somatotropin. In this case, sex steroids affect the epithelial ducts( parenchyma) more, and prolactin - on interstitial tissues.
What is gynecomastia?
Hypertrophy of the mammary glands in men is called gynecomastia. The increase can be due to different tissues. If the volume grows because of subcutaneous fat, then gynecomastia is false. The increase in size due to glandular tissue is called the true form of this condition. Quite often gynecomastia is considered mixed( the tissue contains both glandular and fatty components( see Figure 1)).
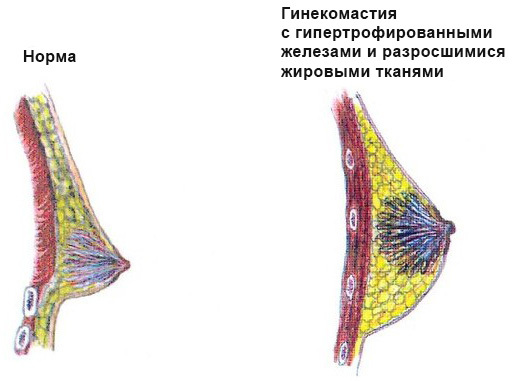
Fig.2 - gynecomastia induced proliferation of glandular tissue and subcutaneous fat( mixed gynecomastia).
False Gynecomastia usually occurs with obesity, and true, and there are mixed manifestation of hormone imbalance or a serious illness.
Stages of development of gynecomastia:
- proliferation of thoracic ducts;
- proliferation of glandular component;
- fibrotic proliferation( proliferation of connective tissue).
version of the rules is considered gynecomastia:
- in infants( defined at 50% of boys);
- in adolescents( detected in 40-60% of young men);
- in the elderly( occurs in 25-30% of men over 50).
The increase in mammary glands in newborns is associated with the effects of the mother's estrogens. Usually gynecomastia occurs in the first month after the birth of the child.
Hypertrophy of glandular tissue in boys in pubertal is associated with hormonal changes in the body. The enlargement of the mammary glands passes independently for 6-24 months.
In older men, gynecomastia occurs due to a drop in testosterone levels and the occurrence of relative hyperestrogenism.
In adult young men without excess weight, gynecomastia is relatively rare( in 10-20%).
Table 1 - Degrees of mammary hypertrophy.
| DEGREE | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| 1 degree | A small nodule under the areola( nodularity subareolar) |
| 2 degree | Iron occupies almost the entire site under the areola |
| 3rd degree | The entire areola area is occupied by the glandular tissue |
| 4 degree | The knot exceeds the size of the areola and beyondlimits( up to 10 cm in diameter) |
These degrees are used to evaluate true and mixed gynecomastia.
Pathological causes of gynecomastia
Hypertrophy of mammary glands in men may occur due to physiological or pathological causes. The first group includes all natural etiological factors( aging, puberty, etc.).
For pathological reasons include:
- genetic diseases( Klinefelter's syndrome);
- tumors with hormonal activity;
- thyrotoxicosis;
- hyperprolactinaemia;
- metabolic syndrome;
- hypogonadism;
- kidney failure;
- hepatic impairment;
- taking certain medicines;
- fasting.
One in 500 newborn boys has an extra chromosome in the cells( 47, XXY versus 46, XY).Such children subsequently form all the symptoms of Klinefelter's syndrome. They include a characteristic appearance, hypogonadism, infertility, erectile dysfunction. Also from adolescence, gynecomastia is observed in patients.
The most pronounced change in the hormonal background and the appearance of gynecomastia provoke neoplasm of the testicle, adrenal cortex, pituitary gland. Such tumors can be a source of gonadotropins, estrogens, gestagens, androgens. Relatively frequent and prolactinoma of the pituitary gland. In this case, a benign neoplasm releases an excessive level of prolactin into the blood.
Thyrotoxicosis is accompanied by gynecomastia in 20-40% of men. Excess hormones of the thyroid gland leads to activation of the reticular zone of the adrenal cortex. Endocrine cells in this region produce androgens. But these sex steroids because of thyrotoxicosis quickly undergo transformation into estrogens. As a result, the relative predominance of female steroids is formed in the body.
Excessive aromatization of testosterone in peripheral tissues provokes and metabolic syndrome( see Figure 3).At the heart of the pathology is the inadequate sensitivity of the tissues to the insulin of the pancreas. This condition is also often accompanied by hypogonadism. Testosterone is not secreted enough, as testicles can be damaged by hyperglycemia and hypercholesterolemia, characteristic of the metabolic syndrome.

Fig.3 - The effect of increased activity of aromatase on the level of androgens in men.
Kidney disease leads to chronic intoxication of the body. The products of metabolism accumulate in the blood. Toxic substances inhibit the production of testosterone. This leads to the appearance of hypogonadism and relative hyperestrogenism.
The pathology of the liver has even more vivid manifestations. To the failure of the body can lead chronic hepatitis, fatty hepatosis, cirrhosis, cancer. In the hepatic tissue, due to these diseases, aromatase is activated, which turns androgens into estrogens( see Figure 3).The process of transformation is very fast. Because of this, men acquire feminine traits and develop gynecomastia. In severe cases, Silvestrini-Corda syndrome develops, including testicular hypotrophy, mammary hypertrophy, liver cirrhosis, and low testosterone levels in the blood.
Fasting, stress, severe somatic diseases sometimes disrupt the hormonal balance of the male body. If estrogens become relatively large, then gynecomastia naturally appears.
From drugs and drugs, hypertrophy of the mammary glands provokes:
- antiandrogens( flutamide, veroshpiron, finasteride);
- androgens;
- anabolic steroids;
- antiretroviral drugs( efavirenz, etc.);
- sedative( diazepam);
- antidepressants;
- antibiotics;
- chemotherapeutic agents;
- cardiac glycosides( digoxin);
- antihypertensive( calcium channel blockers);
- alcoholic beverages;
- drugs( opiates, marijuana, amphetamines, etc.).
Fig.4 - An increase in the mammary glands, provoked by the intake of anabolic steroids.
Symptoms of breast pathology in men
Signs of gynecomastia may be weak or rather severe.
The main complaints in men related to this disease:
- swelling in the nipples;
- pain in the nipple;
- discomfort and feeling of constriction in the projection of pectoral muscles;
- discharge from the nipple;
- enhanced pigmentation areola;
- increase in the volume of soft tissue in the pectoralis muscles.
The patient also notes the accumulation and sagging of adipose tissue in the chest area. Externally, the male body begins to resemble a female body( noticeable mammary glands form).
Usually, the changes are bilateral, that is, the right and left glands are hypertrophied. If the increase occurs only on one side( Figure 5), the risk of a malignant process is higher.
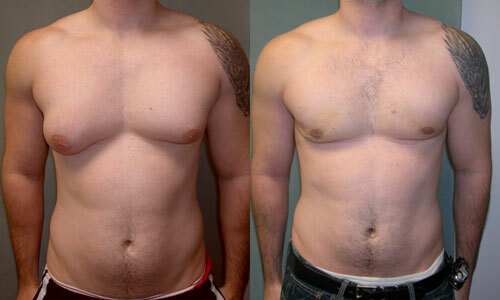
Fig.5 - Uneven hypertrophy of the mammary glands may indicate a malignant process.
Examination for mastopathy in men
Young men and men with a newly developed gynecomastia must undergo a comprehensive examination. Usually this condition is benign and safe for health. In many cases, it does not require treatment. Nevertheless, there are situations in which mammary hypertrophy occurs due to malignant neoplasms or other serious diseases requiring immediate medical intervention.
Diagnostics can be performed by a general practitioner, therapist, surgeon, endocrinologist, andrologist, oncologist, etc.
A standard examination includes:
- information collection( anamnesis);
- inspection;
- palpation( feeling);
- ultrasound;
- hormonal profile;
- biochemical blood test;
- mammography;
- tomography;
- puncture.
A comprehensive approach allows you to clarify the presence, nature and extent of gynecomastia, as well as its causes.
Treatment of mastopathy in men
Physiological gynecomastia usually passes independently and does not require special treatment. In adolescence, some patients require a consultation with a psychologist, to adapt to the characteristics of growing up and changes in one's own body.
If endocrine diseases( thyrotoxicosis, hyperprolactinaemia) have led to hypertrophy of the mammary glands, then the patient is recommended first of all for the treatment of these pathologies.
If gynecomastia is due to hypogonadism, then the patient may be prescribed hormone replacement therapy with testosterone.
Surgical treatment is performed:
- with a pronounced cosmetic defect;
- for breast fibrosis;
- for nodal forms of the disease;
- for suspected oncological process.
The operation includes mastectomy( removal of the gland) and liposuction( removal of adipose tissue).
Endocrinologist Tcvetkova IG
Recommended for viewing: