Diabetes mellitus type 2 - symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Type 2 diabetes mellitus( DM 2) is the most common disorder in the metabolism of carbohydrates. Hyperglycemia in this disease occurs due to 2 factors:
- decrease in insulin production by beta cells of the pancreas;
- worsening the sensitivity of tissues to the action of this hormone.
It is believed that in patients with excessive weight, the leading cause of diabetes is insulin resistance. Because of obesity, cells lose receptors to insulin and cease to react to its presence in the blood. The decrease in the sensitivity of tissues can be compensated for a long time by increased production of the hormone. But when the reserve capacity of the pancreas is depleted, diabetes still manifests.
In a smaller group of patients, the primary disorder is the pathology of insulin secretion. These patients usually have normal body weight. They insulin resistance is attached after a while, as the disease progresses.
Content
- 1 Epidemiology
- 2 etiological factors
- 2.1 Unfavorable heredity
- 2.2 Perinatal disorders
- 2.3 Obesity
- 2.4 Physical inactivity
- 3 pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes
- 4 Symptoms
- 5 disease survey for diabetes
- 6 Treatment of diabetes type 2
Epidemiology
The incidence is constantly increasing. The World Health Organization( WHO) predicts a long-term increase in the number of people with diabetes in the world to 300-350 million in 15-25 years. This is explained by a change in the age composition of the population, and constant urbanization.
Critical figures for the spread of type 2 diabetes are observed in developed countries. The north of the geographical latitude, the more patients with a violation of carbohydrate metabolism.
National peculiarities of morbidity are revealed. Thus, the incidence of Pima Indians and Mexicans is especially high. In any population, older people are more likely to get sick. Among all adults, hidden or overt diabetes is detected in 10% of the examinations. In people after 65 years of prevalence reaches 20%.A critical increase in the incidence is observed after 75 years.
In recent years, another dangerous trend has been noted - a significant "rejuvenation" of the age of the manifestation of type 2 diabetes mellitus. If before the disease was practically not met in people under 40 years, now they regularly diagnose cases of illness of adolescents and even children.
In men, type 2 diabetes is less common than in women.
Etiological factors
Several etiological factors play a role in the appearance of a clear metabolic disorder. Diabetes occurs because of:
- genetic predisposition;
- of intrauterine development disorders;
- of the elderly;
- obesity;
- hypodynamia;
- redundant power supply.
Adverse heredity of
It is proved that heredity determines morbidity by 50-70%.If a patient has type 2 diabetes, one of the parents was ill, then the chance to encounter the same problem reaches 1: 2.The risk of disease in monozygotic twins reaches 1: 9.
Diabetes is predetermined by a combination of different genes. Each of the markers increases the risk of getting sick by 5-15%.Patients may have very different combinations of genetic loci linked to type 2 diabetes mellitus.
The genes:
- , which determine the synthesis and secretion of insulin, influence the development of the disease;
- responsible for the sensitivity of tissues to insulin.
It is already known that 35-147% increase the risk of diabetes with unfavorable markers for genes:
- KCNJ11;
- ABCC8;
- TCF7L2;
- SLC30A8.
All these loci are primarily responsible for the synthesis and secretion of insulin.
Perinatal disorders
The intrauterine period is reflected in a person's health throughout life. It is known that if a boy was born with a low body weight, then chances of getting 2 types of diabetes are quite high. If the weight at birth is more than normal, the likelihood of violations of carbohydrate metabolism in adulthood is also increasing.
Low weight of a newborn( up to 2.3-2.8 kg) often indicates insufficient nutrition in the intrauterine period. This factor affects the formation of a special "economical" metabolism. Such people initially have higher insulin resistance. Over the years, "economical" metabolism leads to the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis and hypertension.
Overweight at birth( more than 4.5 kg) indicates a violation of carbohydrate metabolism in his mother. Such women transmit unfavorable genes to their children. The risk of type 2 diabetes in a child is up to 50%( throughout life).
Obesity
Weight and body proportions in many ways affect the development of type 2 diabetes.
The normal weight is determined by the body mass index( BMI).
The normal body weight corresponds to an index of 18.5 to 24.9 kg / m2.If the BMI is 25-29.9 kg / m2, then talk about the excess body weight.
Next come 3 degrees of obesity:
- 1 degree( 30-34.9 kg / m2);
- 2 degree( 35-39.9 kg / m2);
- 3 degree( more than 40 kg / m2).
BMI in men can be applied with small restrictions. It can not determine obesity in the elderly and in athletes with a large mass of muscle tissue. For these categories of patients, it is more appropriate to use the technique of calculating the percentage of fat tissue using caliperometry.
After 30 years, many men gain excess weight. Usually representatives of the stronger sex pay less attention to the calorie content of food and even to sports. Traditionally, a small excess of weight is not considered a disadvantage in an adult male.
For the development of diabetes, the physique plays a big role. Most men are predisposed to abdominal obesity. With this option, fatty tissue is mostly deposited in the abdomen. If a man has a waist larger than 96 cm, he is diagnosed with abdominal obesity. People with this physique have a risk of diabetes 20 times higher than the average.
Low physical activity
Hypodinamy is one of the characteristic features of the urban way of life. Men are most often engaged in mental work.
Physical activity is lower than necessary:
- due to lack of free time;
- low popularity sports;
- high availability of public and private transport.
The average rural resident needs 3500-4500 kilocalories per day. It is this amount of energy a man spends in the village on daily work. For a city dweller, the need for energy is much less. Usually, an office worker spends 2000-3000 kilocalories a day.
Physical activity helps maintain normal metabolism. It is known that within 12 hours after training, an increased number of receptors for insulin on cell membranes is retained. Tissues increase their sensitivity to insulin, as their need for glucose increases.
The pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes
Normally, insulin acts on most body tissues.
At the cell level it:
- stimulates glucose uptake;
- enhances the synthesis of glycogen;
- improves the capture of amino acids;
- increases the synthesis of DNA;
- supports ion transport;
- stimulates the synthesis of protein and fatty acids;
- inhibits lipolysis;
- reduces gluconeogenesis;
- depresses apoptosis.
Insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency lead primarily to an increase in the level of glycemia. This metabolic disorder is the main symptom of type 2 diabetes mellitus. A high level of glucose in the blood leads to the overcoming of the renal threshold and glycosuria. Abundant osmotic diuresis provokes dehydration.
All tissues in conditions of type 2 diabetes mellitus do not receive the right amount of energy. The deficit is partially closed due to the breakdown of proteins and fats. But in the body with this form of the disease, at least a small residual secretion of insulin is always preserved. Even the minimum level of the hormone is able to suppress the synthesis of ketone bodies( ketogenesis).Therefore, for type 2 diabetes mellitus, ketosis is not characteristic( energy supply of the organism due to ketone bodies) and metabolic acidosis( acidification of the body due to the accumulation of acidic products in tissues).
A diabetic coma with a high sugar level at type 2 is a relatively rare occurrence. Usually, this condition occurs due to severe dehydration with diuretics or cardiovascular disasters( heart attack, stroke).
A more frequent consequence of diabetes is late complications. These organ damage is a direct consequence of chronic hyperglycemia. The longer the blood sugar is raised, the more massive the damage to cells.
In type 2 complications can be detected at the same time as the underlying disease is detected. This is due to the fact that such a diabetes often lasts for a long time is hidden. Asymptomatic current complicates early diagnosis.
Symptoms of the disease
Usually, two types of diabetes in men are found accidentally. A slight deterioration in the state of health, which usually accompanies the onset of the illness, can rarely induce patients to consult a doctor. Complaints usually occur with severe hyperglycemia.
Diabetes is characterized by the following symptoms:
- severe thirst;
- skin dryness;
- skin itching;
- dry mouth;
- abundant and frequent urination.
In the early stages of the disease, patients may have spontaneous hypoglycemia. The fall in blood sugar is associated with hyperinsulinism.
These episodes manifest themselves:
- with severe hunger;
- trembling in the hands;
- rapid pulse;
- pressure increase;
- sweating.
Sometimes patients for a long time ignore all the symptoms of the disease. Seeking a doctor can cause them to form complications.
For men, erectile dysfunction is one of the most important reasons for consulting with health professionals. Initially, the patient can associate a decrease in potency with chronic stress, age and other causes. When examined, such patients can be diagnosed with severe hyperglycemia and insulin resistance.
Other complications of type 2 diabetes are manifested:
- impaired vision;
- decreased sensitivity in the fingers and toes;
- by the appearance of non-healing cracks and ulcers;
- chronic infection.
Diabetes can be detected for the first time and when hospitalized for a heart attack or stroke. These conditions are themselves a consequence of metabolic disorders. Complications could be prevented with early diagnosis of type 2 diabetes.
Diagnosis for diabetes
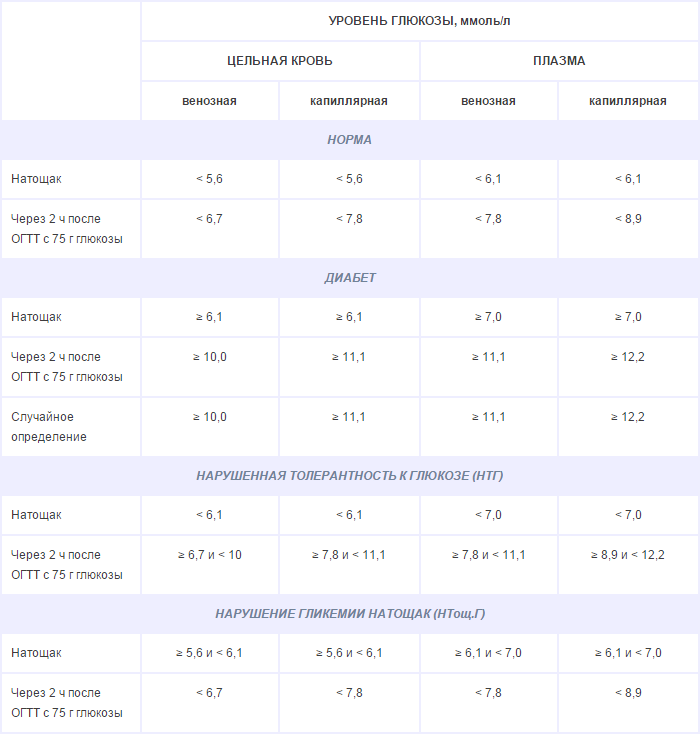
Diagnosis of type 2 diabetes includes primarily confirmation of hyperglycemia. To do this, take samples of blood sugar on an empty stomach and 2 hours after eating. In the morning, glucose should be within the limits of 3.3-5.5 mM / l, in the daytime - up to 7.8 mM / l. Diabetes is diagnosed when hyperglycaemia is detected from 6.1 mM / L fasting or from 11.1 mM / l throughout the day.
If glucose values are intermediate, an oral glucose tolerance test( "sugar curve") is performed.
The patient should come to the clinic on an empty stomach. First he is given the first measurement of blood sugar. Then give a drink of sweet water( 75 g of glucose per glass of water).Further within 2 hours the patient is in a state of physical rest( sits).During this time you can not drink, eat, smoke, or take medicine. The blood sugar is then measured again.
The test results can be used to diagnose:
- norm;
- diabetes;
- impaired glucose tolerance;
- hyperglycemia on an empty stomach.
The last two states are classified as prediabetes.15% of patients with impaired glucose tolerance develop diabetes throughout the year.
Table 1 - Criteria for diagnosis of diabetes and other disorders of carbohydrate metabolism( WHO, 1999).
For the diagnosis of hyperglycemia in recent years, the analysis on glycated hemoglobin is increasingly being used. This indicator shows the average level of glycemia in the last 3-4 months. Normally, glycated hemoglobin is 4-6%.With the manifestation of diabetes, this parameter increases to 6.5%( minimum).
Additional tests are performed to confirm insulin resistance and relative insulin deficiency. It is necessary to examine the blood for insulin, C-peptide, blood and urine for ketone bodies. Sometimes for differential diagnostics with 1 type of patient it is recommended to pass specific antibodies( to GAD, etc.)
For 2 types of disease it is characteristic:
- high or normal level of insulin;
- high or normal C-peptide level;
- low level or absence of ketone bodies in urine and blood;
- lack of high antibody titer.
Insulin resistance indexes( HOMA and CARO) are also calculated. An increase in HOMA values of more than 2.7 indicates an increase in insulin resistance. If the CARO index is less than 0.33, this indirectly confirms the low sensitivity of the tissues to the beta-cell hormone.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes
For the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, men use a diet, exercise, special drugs in tablets and insulin preparations.
The diet corresponds to the 9 table for Pevzner. The diet should reduce the number of animal fats and simple carbohydrates( see Figure 1).It is desirable to organize meals regularly, in small portions.
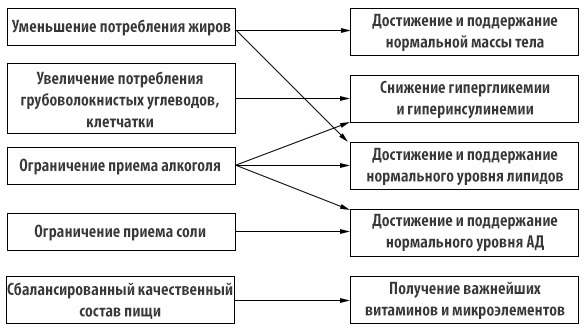
Fig.1 - Principles of dietary recommendations for diabetes 2.
A man needs to know approximately his energy needs during the day and take into account the calorie content of food. Do not overeat. It is especially important to limit food in the evening hours.
Physical activity is selected according to age and concomitant illnesses.
Table 2 - Physical activity in the treatment of diabetes 2.
| INTENSITY | TIME, min | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | |||
| 20 | |||
| 10 | |||
| Very heavy | 5 | Swimming |
Treatment starts immediatelyHow is diabetes diagnosed. First, one drug or combination of tablets is usually used. If this is not enough, then insulin is added to the treatment.
For patients with type 2, the same insulin solutions are recommended as for type 1 patients. Differences in therapy:
- is sometimes sufficient only for basal insulin;
- no obvious need for pump therapy;
- doses of insulin are quite large;
- good effect give mixed preparations. Read more «Insulin in the treatment of diabetes mellitus».
Table 3 - Therapeutic tasks for type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
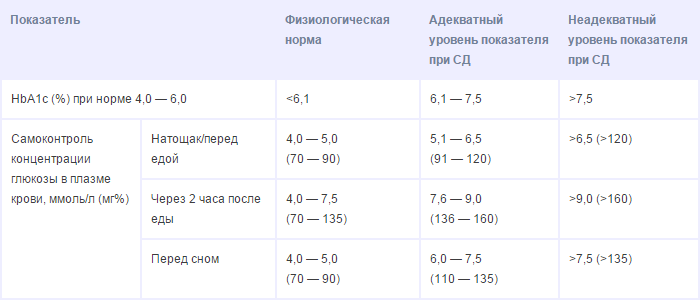
Treatment of type 2 diabetes is carried out by an endocrinologist. All patients should be on dispensary records. A full survey is required once a year. Inpatient treatment - according to indications.
Doctor-endocrinologist Tsvetkova IG
Recommended for viewing: