Oligospermia - what are the causes and treatment
Although the term "oligospermia" literally means a decrease in the volume of seminal fluid, practitioners generally refer to this term as reducing the number of spermatozoa( oligozoospermia).Since in clinical recommendations the volume of ejaculate is considered only in conjunction with other changes, this article will focus mainly on oligozoospermia.
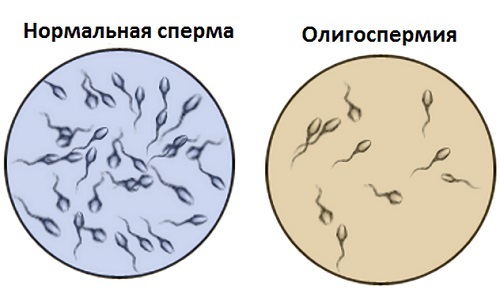
Fig.1 - Oligozoospermia - decrease in the number of spermatozoa.
Content
- 1 oligospermia
- 2 Oligozoospermia
- 3 reasons oligozoospermia
- 3.1 insufficient function of the testis
- 3.1.1 congenital deficiency of testicular functions
- 3.1.2 Acquired deficiency functions testicular
- 3.2 duct obstruction
- 3.3 mixed form
- 3.4 idiopathic form
- 3.1 insufficient function of the testis
- 4 TreatmentOligospermia
- 5 Conclusions
Oligospermia
Normally , the volume of ejaculate should exceed 2.5 ml of ( half a teaspoon and more).If it is below 1.5 ml, you can talk about oligospermia. This can be permanent and temporary.
Causes of temporary decrease in ejaculate volume:
- Long-term abstinence( see "Sexual abstinence for men is good or bad?").
- Excessive sexual activity.
- Stress state and other effects on the psychoemotional sphere.
- Incorrect power.
- Diseases of the prostate. Injury of the testicle or its epididymis.
The last two factors can cause permanent oligospermia, since prostate diseases often take a chronic course, and trauma can reduce the functionality of the testicle. To the number of reasons leading to a constant decrease in the volume of sperm, we must add a hereditary predisposition.
As for the treatment, it is obvious that neither the nature of sexual activity nor the lifestyle need specific therapy - it is enough to adjust the regime of the day and nutrition. Moreover, it is impossible to influence hereditary factors. Treatment of diseases of the prostate and genital tract injuries is necessary regardless of the volume of the ejaculate.
All these factors lead to the fact that in practice it is not much attention paid to the volume of sperm. Most often it is considered in conjunction with oligozoospermia.
However, if oligospermia is detected, post-urinary urinalysis is recommended. If spermatozoa are found in the urine, this indicates retrograde ejaculation, a condition in which ejaculate instead of the urethra enters the bladder.
Causes of retrograde ejaculation:
- Neurogenic( spinal cord injury, multiple sclerosis);
- Violation of the functions of the urethra( narrowing of the urethra, enlargement of the seminal tubercle, urethral valve);
- Dysfunction of the neck of the bladder( birth defects, complication after resection of the prostate);
- Drugs( antidepressants, antihypertensives, antipsychotics, alpha-1 adrenoblockers).
Oligozoospermia
Oligozoospermia is a decrease in the number of spermatozoa in seminal fluid. The European Association of Urologists in its recommendations indicates that the in the norm of 1 ml of sperm should contain more than 15 million spermatozoa .A smaller number of them in one milliliter of ejaculate is called oligozoospermia. But, as already mentioned, the concept of "oligospermia" is often used in clinical practice. This condition is rarely found in isolation, usually combined with asthenozoospermia( reduced sperm motility) and teratozoospermia( change in the shape of spermatozoa).This combination is called OAT-syndrome and is the main cause of male infertility.
Until recently, the RF Ministry of Health considered the norm the content of spermatozoa & gt;60 million / ml, and isolated several degrees of oligospermia, linking the severity with the probability of conception. In modern Russian clinical recommendations, created on the basis of the recommendations of the European Association, these norms and the division into degrees are absent.
Since spermatogenesis disorders can be caused by temporary causes( stress, testicular overheating, eating disorders), it is recommended to perform two spermograms at 2-3-month intervals before drawing any conclusions( read about how to properly prepare for spermogram).In any case, if there are changes in the spermogram for two or more indicators, a complete andrological examination is necessary.
Causes of oligozoospermia
Insufficiency of testicular functions
May be congenital and acquired.
Congenital insufficiency of testicular functions
Appears in the following pathologies:
- congenital absence of testicles( anarchy);
- testicular dysgenesis( hypoplasia of one testicle);
- gene mutations.
Acquired insufficiency of testicular functions
The cause may be:
- conditions caused by egg pathology: varicocele( third among infertility patients), testicular torsion, cryptorchidism( the later surgery is performed, the rougher changes in testicular tissues);
- testicular overheating: work in hot shops, addiction to baths, general fever( fever);
- systemic diseases( cirrhosis, kidney failure).Diabetes mellitus( oligospermia occurs in 30% of patients due to disease caused by vascular disease of the microcirculatory bed);
- effects of inflammation of the testicles( orchitis);
- hypergonadotropic hypogonadism: a violation of the normal ratio of hormones, when an increase in the level of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormones( stimulating the production of testosterone) is accompanied by a low level of testosterone itself.
- hypogonadotropic hypogonadism: decreased hormonal background.
- iatrogenic factors( caused by medical procedures): taking certain medications, including antibiotics( cause reversible oligospermia) and chemotherapy, radiation therapy.
Obstruction of the
ducts Or a communication disorder between different parts of the vas deferens. It can also be congenital, caused due to incorrect development of the vas deferens, or acquired. The causes of acquired obstruction:
- cysts, prostate tumors;
- infections that caused narrowing of the ducts due to edema. Include inflammation of the epididymis or the vas deferens themselves. They are considered as a reversible cause of infertility, and should be cured, but there is still no reliable relationship between them and a violation of sperm quality: with pronounced inflammation, normal spermatogenesis may be present. Nevertheless, long-term untreated infections can cause cicatricial narrowing of the vas deferens and, as a consequence, oligospermia.
- iatrogenic: ducts are damaged during hernia repair, operations on the scrotum, bladder neck.
Mixed form
Proteins of spermatogenic( sperm) epithelium are perceived by the body's immune system as foreign. Therefore, there is a so-called hematotestick barrier, through which neither immunocompetent cells nor antibodies penetrate, and the proteins of the testicles, respectively, do not enter the circulating blood. If the outflow of secret is broken, this barrier can become permeable, which can cause autoimmune inflammation of the testicle and its appendages and, as a consequence, the development of oligospermia.
Idiopathic form of
In about 40% of cases of oligospermia, it is not possible to identify the specific cause that caused this condition. Perhaps, in this involved factors such as
- obesity( fat tissue produces female sex hormones in men - estrogens);
- eating disorders: a deficiency of vitamin A( involved in the synthesis of male sex hormones - androgens), zinc, selenium( involved in spermatogenesis).
Treatment of oligospermia
The method of treatment of oligospermia depends on the causes that caused it.
oligospermia induced retrograde ejaculation treated or surgically corrected urethra when anomalies, or by drugs. These include Ephedrine, Midodrin, Brompheniramine, Imipramine, Desipramine. The doctor chooses the specific agent and its dosage. If medication is ineffective use IVF or ICSI( sperm injection obtained by needle biopsy or microsurgical operation eggs, egg inside).
Oligospermia caused by a disorder of testicular development and chromosomal by mutations of does not respond to treatment.
Varicocele or varicose veins of the spermatic cord .Perhaps both conservative treatment( sclerotherapy) and surgical( dressing or removal of varicose veins).After the operation, the quality of the sperm is usually restored.
Non-obstructive oligospermia .The only officially recommended by the European association of urologists is the method of infertility treatment - ICSI, which is necessary to conduct a genetic study of spermatozoa. Nevertheless, in 27% of pairs with oligospermia, observed for 2 years, there was an independent conception. But it is not recommended to tighten with supervision: the probability of conception directly depends on duration of infertility, falling to the fourth year up to 5%.When
obstructive oligospermia caused hypogonadotropic hypogonadism , when the reduced production of hormones that stimulate the production of testosterone( FSH and LH) and, consequently, decreases the level of the hormone, are often effective hormonal drugs.
These drugs can be divided into 2 groups:
1. Anti-estrogens. Embedded in the hormonal metabolism at the central level, increasing the synthesis of follicle stimulating and luteinizing hormones, and as a consequence, increasing testosterone levels, which amplifies spermatogenesis( sperm production).This group includes drugs such as clomiphene and tamoxifen.
2. Gonadotropins. Synthetic analogues of hormones stimulating the production of testosterone and spermatogenesis:
- analogues of luteinizing hormone: Luveris;
- analogues of follicle-stimulating hormone: Gonal-F;
- analogues of chorionic gonadotropin: Ovitrel, Bigagonil, Ovitrel, Prophase, Horagon, Pregnil, Gonadotrophen. Normally this hormone is absent in men, its drugs act similarly to the luteinizing hormone, but stronger and longer.
See in more detail: "Gonadotropic hormones - luteinizing, follicle-stimulating".
idiopathic oligospermia recommended to start with the normalization of the regime of the day, eliminating stress factors, food enriched with protein, vitamins, trace elements. It is also possible to use previously described hormonal drugs.
Obstructive oligospermia. Obstruction of the ducts inside the testicle, unfortunately, is not corrected. In other cases, the patency of the ducts can be restored surgically. Or it is possible to extract spermatozoa using a puncture biopsy and conduct ICSI.
Inflammatory processes. require treatment with antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, the choice of the drug will depend on the identified pathogen, so the antibiotic should appoint a doctor. Often used funds from the group of tetracyclines, fluoroquinolones.
Conclusions
Oligospermia is a condition that can be caused by many causes. Having found out in the spermogram a change in two or more parameters, it is necessary to undergo a complete andrological examination. But to come to any conclusions, let alone begin treatment oligospermia need not earlier than after the re semen, since many changes may be caused by external transient factors.
Methods of treating oligospermia can be both conservative( therapeutic) and surgical. Unfortunately, some factors that cause this state are not amenable to correction. In this case, conception with assisted reproductive technologies is recommended: IVF or ICSI.
Recommended for viewing: