Fracture of the tooth
 A fracture of a tooth is a tooth injury, which is manifested by a fragmentary or continuous fracture of the crown, displacement and fracture of the radix. Fracture of the tooth causes a stroke, a drop, a sharp bite on the solid particles of food, during extraction and is manifested mainly by a defect in the socket, fractures of the alveolar process and jaws. In the correlation from the localization, the injuries of the crown and radix are isolated. Traumas crowns are divided into correlations from grazing hard tissues and opening the pulp chamber. Injuries to the root are divided into connectivity from the anatomical structure. Dentin, cement, and the neurovascular node are affected. The radius of the radix is transmitted by partial dislocation. In the clinic, the patient notes the sensitivity of the teeth, the change in color, mobility, aching pain, the appearance of scratches on the mucosa or skin. More often fracture of the tooth has a localization in the anterior incisors, rarely in the lower and others. Today, fractures are calculated more often. This is due to the promotion of sports games with a strong character( hockey, football, boxing, etc.).More often there are fractures in boys. Verified using clinical examination data, electrodontometry, transillumination method, radiography.
A fracture of a tooth is a tooth injury, which is manifested by a fragmentary or continuous fracture of the crown, displacement and fracture of the radix. Fracture of the tooth causes a stroke, a drop, a sharp bite on the solid particles of food, during extraction and is manifested mainly by a defect in the socket, fractures of the alveolar process and jaws. In the correlation from the localization, the injuries of the crown and radix are isolated. Traumas crowns are divided into correlations from grazing hard tissues and opening the pulp chamber. Injuries to the root are divided into connectivity from the anatomical structure. Dentin, cement, and the neurovascular node are affected. The radius of the radix is transmitted by partial dislocation. In the clinic, the patient notes the sensitivity of the teeth, the change in color, mobility, aching pain, the appearance of scratches on the mucosa or skin. More often fracture of the tooth has a localization in the anterior incisors, rarely in the lower and others. Today, fractures are calculated more often. This is due to the promotion of sports games with a strong character( hockey, football, boxing, etc.).More often there are fractures in boys. Verified using clinical examination data, electrodontometry, transillumination method, radiography.
Reasons for a tooth fracture
Inadequate dental intervention in different specialists often causes a fracture of the tooth. Therapeutic healing, in which the pin is incorrectly installed, is an extensive seal( inconsistency of the IRPC).Orthopedic: installation of non-removable structures not along the tooth line. Surgical action is the leading cause of the fracture. Normally, at the time of extraction, a preliminary detachment of the circular ligament( periodontal ligament located in the space between the gingival tissues and the neck) is made, the forceps are placed along the axis( the axis is the direction taken along the middle part of the crown and root), fixed in the cervical region, Corresponding to the number of roots( initially luxe( rocking) and then rotation( circular motions) in single-root teeth), luxation in multi-rooted) and at the end traction( withdrawal).
Fracture of the tooth is possible during the stages of luxation and rotation with the use of excessive force, with traction - with a sharp seizure, a fracture of the alveolar process occurs, or when the upper incisors are extracted during traction, a blow to the lower incisors leads to fracture of the latter.
In correlation with the non-dental agent, the following causes of tooth fracture are distinguished: physical impact from the outside( impact, fall, bad habits( nail bending)) and from the inside( trauma by hard particles with active chewing).In the connection with the course and the power of the impact of the traumatic moment, the scale of the fracture will manifest itself. The concomitant factors of the fracture will be a long carious process, which destroyed the crown, mobility, bite anomaly, anatomical organization( thin, curved, short roots).More often is revealed by fracture of the crown from the oral side, less often from the vestibular.
Symptoms of a tooth fracture
A jaw fragment with a tooth in it is marked as a segment. The segment is reconstructed from the tooth, lunochka, from the adjacent area of the jaw, covered with a mucous membrane, the ligamentous apparatus connecting the tooth in the hole, vessels, nerves. The base of the fragment is determined by the alveolar process. Radix is fixed by means of connective tissue fibers, which together with the collagen tissue, cellular particles form periodontium. Fractures of the tooth distinguish incomplete( bypassing the opening of the pulp apparatus) and complete( with the opening of pulp( open and closed)).In the direction of transverse, oblique, longitudinal. Incomplete fractures of the tooth are based on the boundaries of two strong tissues: enamel and dentin. Accordingly, cracks are isolated, an edge fracture in the edges of the enamel, enamel and dentin. When the lateral influence of the applied force in the direction of the tooth is more likely to edge fracture. In order to cause a trauma to the neurovascular bundle, a considerable force must be applied and the presence of predisposing factors is necessary. A full open fracture is characterized by the inclusion of tissues located within the boundaries of the crown: enamel, dentin, pulp. A complete closed fracture is indicated by a fracture within the boundaries of the cement of the root, dentin, pulp. Fracture occurs at various levels of organization( neck, root, apex radix) and with a differentiated direction of the fracture. A combination of fracture of the crown and radix is possible at the same time.
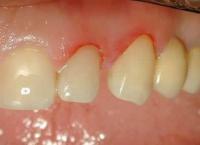
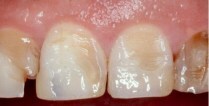
Symptoms of tooth fracture are caused by the level of damage, the degree of combination of tissues, mobility. With incomplete fracture, the patient notes cosmetic dissatisfaction, sharp edges, sensitivity during thermal and mechanical actions. Visually, a break occurs( more often a corner);On the mucosa due to trauma: abrasions, hemorrhage, hematomas. Occasionally on the tongue or cheeks, there are signs of prolonged contact with sharp edges in the form of ulcers. When the enamel breaks off, sensitivity increases with the action of various stimuli. With a fracture of dentin, the severity of the pain is stronger.
When complete fracture, manifested rupture pulp marked spontaneous pain, increasing at nakusyvanii, color change( pink color( due to a defect of the neurovascular bundle, wherein the erythrocytes penetrate into dentinal tubules), later yellow( hemoglobin is oxidized and transformed into hemosiderin)).The patient marks acute pain, which increases with opening and closing;Can join the fracture of the socket or even the jaw. Possible mobility, displacement, violation of occlusion. Pathology occlusion as one of etiological causes moments in trauma anterior movement of one or a plurality, spall alveolar bone or the fracture of the jaw. Probably damage to neighboring soft tissues, bleeding. The manifestation of symptoms is due to the age of the patient and the existence of conditions. The nature of the traumatic defect in children is determined by the age-specific features( unformed roots, the presence of the growth zone, etc.).
fracture
tooth root fracture of tooth root fractures attributed to complete( with the opening pulpovovoy camera).Fracture occurs in the well and belongs, preferably, to closed-type fractures. In the relationship of anatomic defect length of the root is isolated fractures in the neck region, the radix in the middle zone, the middle and interm tip radix in the apex region. A combination of fracture of the crown and radix is also possible.
The longitudinal fracture of the tooth is caused by the crown-root fracture and extends along the vertical facet. Injury caused parallel to the vertical line, the introduction of the pin greater in size than the channel lumen, and occasionally during endodontic operations in the process of curing.
Fracture follows through cement, dentin, vascular bundle. In correlation with the direction of the fracture, the following are distinguished: transverse, longitudinal, oblique. Often a longitudinal fracture of the root occurs in the chewing teeth, where the filling takes up more than half of the surface. After the fracture there are two thin walls, between which there was a seal. A comminuted type of fracture is indicated by reconstructing two or more fracture lines.
Fracture of the tooth neck, as an intermediate tooth is characterized by a fracture passing through the enamel, dentin, radix cement. There is a fracture of the entire crown in the middle of the enamel-dentine facet. Fracture of the neck of the tooth goes with a curved orientation, penetrating the gum: from the oral direction of the tissue, they split off at an acute angle, from the backward under the straight. Occasionally, the crown of the tooth remains fixed to the radix due to the residues of the circular ligament.
Radical root fracture is usually accompanied by a dislocation of the crown, which is manifested by characteristic features. Symptoms of fracture of the root of the tooth are determined by the level of the defect. Patient notes regular aching pain, increasing with biting. The tooth is transformed in coloring( pink coloration, later yellow), mobile. The mobility increases toward the line of the fracture near the neck of the radix. The tooth is sensitive to all kinds of irritants. Percussion gives a painful reaction. At a palpation inspection diagnose a dislocation and fracture. Defects and hemorrhages are likely on the mucous membrane.
Diagnosis of a tooth fracture
At a clinical medical examination it is necessary to calculate the line of the tooth fracture, alveoli, revealing a change in tooth tone, damage to occlusion, regional tissues. The tone is pink or dark. This is due to the destruction of the vascular-nerve bundle, the release of red blood cells into the dentin canals, oxidation, pulp necrosis. When the fracture teeth palpation helps calculate mobility fragments swelling that is formed when the alveolar bone fracture or tooth movement.
Mobility is calculated with tweezers support, moving the tooth in four directions:
I mobility level is vestibular;
II - vestibuloral and mediodistal;
III - vestibuloral, mediodistal and vertical;
IV - all kinds and circular motility.
With the fracture of one tooth, percussion of closely located teeth is invariably performed. Vertical percussion confirms the height of the defect of periapical tissues, as a variant of a local periodontal tissue cut or limited dislocation. Carefully conducted horizontal percussion, showing a periodontal rush in the vestibulo-orientation, hemorrhage, pulpal edema. When assessing the percussion echo in the area from healthy to causal, the sound changes from distinct to blunt. Clinical technique that calculates the edges of the fracture: with a right hand brush, small swings of the crown in the antero-posterior trend are carried out in a small sweep, the second finger of the left hand, located on the vestibular side in the radix region, will feel the movement of the broken radix. This gives, undoubtedly, a fracture line. When the outer edge of the hole breaks, when the tooth is tilted orally, palpating, the sharp edge of the fracture is determined. Symptoms of fracture of the root of the tooth will be unreliable in the fracture in apex.
The leading additional method in diagnosing a fracture of the tooth is radiography. The X-ray diffraction data will show the direction of the fracture, the presence of hammering, periapical transformations, the lumen of the pulp chamber, the stage of formation of the root system, the width of the dentin between the face of the fracture and the cavernous tooth, the deformation of the periodontal, the growth zone of the apex of the root, and the presence of foreign inclusions. Fracture on the roentgenogram will be in the form of enlightenment. The next instrumental method of examination will be electrodontometry( the medical examination method to calculate the level of pulp sensitivity to electric current).With apex fracture, sometimes the neurovascular bundle does not collapse. With a fracture near the crown, the pulp near the apex retains its viability. Primarily the information may be incorrect, but the correction in subsequent visits allows you to determine the tactics in healing. With unformed radii of permanent teeth, the data will be inaccurate in view of the immaturity of the nerve fibers of the pulp. Also, the EOM data will be lowered when pulpal edema is detected, the injury of the neurovascular bundle, periodontal disease. The transillumination method uses flexible fiber-optic light guides. With the help of illumination, minor damage( cracks, breaks) is revealed.
Treatment of tooth fracture
Treatment of fractures of the crown, the neck of the tooth, the root is carried out by therapeutic, orthopedic and surgical methods. Healing of injured teeth in the region of the crown consists in the restoration of the lost tissue of the crown without extirpation or with the removal, in correlation from the clinic. All patients have a pronounced pain symptom, so anesthesia is performed prior to manipulation. The choice of the method of healing is determined by the defect index of the tooth tissues. With a crown fracture without opening the tooth space, a restoration is performed, a light composite is used for restoration, with a dentin fracture, an insulating liner is first applied, then restored with light material. With the fracture with the opening of the pulp chamber, trepanation, removal of the pulp, filling with the use of in-channel pins, restoration of the crown are performed. The most effective restorations are using a cap. When changing the color of the tooth, not in the acute period, whitening is performed.
Fracture of the neck of the tooth requires orthopedic correction, if the fracture passes above the tooth-gum junction, it is advisable to expose the radix stump by cutting off the mucous remains. Recover lost tissue KShV( cultic pinned tab), crown. If the orthopedic intervention is not possible, an extraction is performed.
Treatment of root fracture of the tooth is based on the types of fractures and the depth of the fracture line. The least favorable are longitudinal, oblique and fragmented fractures, in which radixes can not be used for support, extraction is performed and a calculation is made about replacement of a dental defect. With a transverse fracture, much determines the level of the fracture. The transverse fracture in the middle, between 1/3 and the middle part is favorable for depulpation, filling of the channel with the use of zinc phosphate cement( "Unifas"), establishment of in-channel pins. Initially, the pin is selected from the channel clearance, if there is no displacement of the fragments, then the pin should easily penetrate into the apical part. In case of displacement, when adjusting the pin installed in the channel, it is necessary to make the swinging movements of the crown, the feeling of failure will be a sign of falling into the apical part. The pin is removed, the phosphate cements are lubricated, injected and fixed.
Treatment of tooth root fracture between the median and apical parts is determined by removal of the neurovascular bundle, filling with zinc phosphate cement( "Phosphacap"), the apex area is left unchanged. Vital pulp in the apex zone is monitored by EOM.With the fact of necrosis of the neurovascular bundle, resect the tip of the radix. With the radius of the radix without displacement, the tooth is immobilized with a kappa tire for 4 weeks or with a smooth staple bar( fix with plastic).When initially displaced, the tooth is re-inserted, then immobilized with a tire. After sealing, it is important to place the tooth in the exact location and to remove the risk of injury when closing the jaws. After the necessary time, the coronal part is filled with orthopedic intervention. An alternative to intermaxillary healing is the re-implantation: the root is removed, sealed, sealed with a pin and zinc-phosphate cement and re-implanted.
Treatment of tooth fracture should be carried out in a short time, because in the absence of proper healing, if there is no contact with the tooth, the antagonist moves the injured fragment, which will require orthodontic intervention before prosthetics;Change the color of the tooth. After healing for a few days, the patient is recommended painkillers( Ketorol, Naise) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs( Claritin, Suprastin).