Gingivitis
 Gingivitis is a gum disease caused by local symptoms and general changes in the body, which proceeds without breaking the dentogingival joint. The frequency of occurrence of gingivitis is quite high, most often children, pregnant women and young patients under 30 years suffer from this ailment. Gingivitis gum refers to a group of periodontal diseases, tk. The gum enters the periodontal complex of tissues.
Gingivitis is a gum disease caused by local symptoms and general changes in the body, which proceeds without breaking the dentogingival joint. The frequency of occurrence of gingivitis is quite high, most often children, pregnant women and young patients under 30 years suffer from this ailment. Gingivitis gum refers to a group of periodontal diseases, tk. The gum enters the periodontal complex of tissues.
order not to be in the number of patients complaining of gingivitis in adults, it is necessary one every six months to visit the doctor periodontist, abide by the rules and regularity of individual tooth brushing, and at the first signs of gingivitis( swelling, redness, bleeding) to seek dental care.
Causes of gingivitis
The causes of gingivitis are divided into general and local. Common aetiological factors include a decrease in immunity, GI disease, cardiovascular disorders, endocrine disorders( diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease, pregnancy, puberty), hypovitaminosis, allergic conditions.
Against general disorders exacerbated by the influence of local factors: poor oral hygiene, the accumulation of pathogenic microorganisms, the presence of plaque and anomalies and deformation periodontal systems, mechanical injury, radiation damage and traumatic injury gums( trauma, burns, incompetent dentures) injuriousHabits( smoking), use of medicines( oral contraceptives), work on production with heavy metals( mercury, lead).The products of vital activity of microorganisms accumulate on the surfaces of teeth with unsuccessful hygiene of the oral cavity, in the place of accumulation of a soft plaque, a plaque is formed which, over time, becomes mineralized and turns into tartar. To remove these deposits, it is necessary to perform professional cleaning with ultrasonic devices to remove hard dental deposits, as well as removal of pigmented plaque by the Air flow apparatus. Mandatory grinding and polishing of surfaces with special pastes and brushes. On the smooth surface of the tooth, microorganisms are much harder to attach, hence the teeth will keep their purity longer. It is shown that deep fluoridation is carried out with special gels containing active fluoride, which reduce the permeability of enamel of the teeth, have anticarious activity, and reduce the number of pathogenic microorganisms on the surface of the teeth. But of course you should not go for individual cleaning of teeth at home. It is necessary to teach the patient the proper cleaning of teeth. Proper brushing of teeth implies underneath sweeping movements, made from the gum to the tooth edge by a manual brush on all segments of the teeth for 2-3 minutes. Teeth need to be cleaned 2 r. / Day, the first time after breakfast, the second time before going to bed. The brush should be individual for each member of the family, stored in a special glass with a bristle up. The toothbrush is recommended to be changed every three months. Patients with signs of gingivitis should acquire brushes with soft bristles. There are brushes with colored bristles that decolorize, signaling you to replace the brush with a new one. It is very convenient for those who forget to do it. It is desirable to alternate the paste and do not use whitening. People with periodontal disease should better use pasta with medicinal herbs and preparations. Such pastes should be purchased at pharmacies in your city. Use of mouth rinsers and dental floss( floss) is welcome. However, the dentist should explain and show on the model how to properly use the dental floss. It is important to avoid additional injury to the gums while cleaning the interdental spaces. Movements should not be sharp, without pressure.
Symptoms and signs of gingivitis
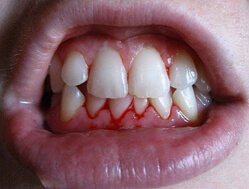
As mentioned before, gingivitis manifests itself more often in young people. Morphological and clinical signs of inflammation are found. Abundant dental deposits, bleeding gums when probing, the absence of periodontal pockets, with hypertrophic gingivitis may have a false periodontal pocket.
There is no structural change in the bone tissue of the alveolar process, the general condition of the patient does not suffer, the indices of hygiene and manifestations of gingivitis are interdependent. The symptoms of gingivitis gum is gum swelling, soreness, which most patients complain primarily bleeding when cleaning the teeth or the use of solid food, redness, possibly bad breath from the mouth.
Types and forms of gingivitis
Gingivitis is divided into catarrhal, hypertrophic and ulcerative forms. Based on clinical signs: acute and chronic. Depending on the degree of severity - light, medium and heavy. On a phase of a current - acute and chronic. By localization - papillary, marginal, diffuse. On etiology - traumatic, chemical, gingivitis of adolescents, gingivitis during pregnancy. In its prevalence - focal and generalized.
Hypertrophic gingivitis is quite common. In the etiology of generalized forms of hypertrophic gingivitis, an important role is played by infectious, chronic traumatic effects, metabolic disorders( pregnancy, pubertal period, endocrinopathies);Defeat of the central nervous system, taking contraceptive medications;Systemic pathologies of the circulatory system and others.
Occurrence of localized forms of gingivitis is promoted by an anomaly of occlusion( deep, cross, open bite), anomaly of the location of the teeth( congestion of the front group, supercomplete teeth).The process is most pronounced in the interdental gingival papillae and the marginal protrusion of the anterior group of teeth in the region of the second and third teeth. Microscopically, the tissues are edematic, full-blooded, abundantly infiltrated by lymphocytes, plasmocytes with an admixture of macrophages. The epithelium responds com- monly, which leads to a change in its vertical differentiation( increase in the number of layers, para- hyperkeratosis, acanthosis).Inflammation initiates the active division of fibroblasts with subsequent collagenosis, which facilitates fibrosis( consolidation) of the gum tissue. Exacerbation of chronic gingivitis is accompanied by an increase in exudative reactions.
The fibrotic and edematous forms of hypertrophic gingivitis are distinguished by the nature of clinical and morphological manifestations. With inflammatory( edematic) form the gingival margin and papillae are sharply hyperemic, edematous, cyanotic. The mucous gum sometimes grows so much that it closes the crown of the tooth, forming deep gingival pockets. Pockets contain the remains of food, tartar, bacteria, which leads to suppuration. Taking solid foods causes pain, bleeding. In fibrotic form, a slowly progressing neoplasm of connective tissue leads to a thickening of the gums, they bleed, painful, cyanotic. An additional mechanical stimulus leads to a pronounced growth of the interdental papillae and the formation of gingival polyps.
Atrophic gingivitis is a chronic disease that causes a loss of gums. It arises due to abnormalities of blood circulation and tissue trophism( deeply adapted bridges, clasps, pressure of hard dental deposits, etc.).The mucous membrane of the gums is dull, pale pink, the gingival papillae shorten, and then disappear altogether. The edges of the gums are thickened, the gingiva reduces the dimensions in the volume. Cervical teeth are exposed, hypersensitivity to temperature agents is shown. In the inflammatory process includes alveolar process and marginal periodontium, their atrophy leads to the denudation of the root of the tooth, they are shortened, and then disappear altogether.
Acute gingivitis
Causes of acute serous gingivitis can be temperature, infections, trauma, allergic and toxic-allergic factors. Acute gingivitis can accompany measles, SARS, influenza, metabolic disorders, etc. Also, poor hygiene( dental plaque, dental calculi) causes a local decrease in the immunity of the tissues of the oral cavity.
The risk of acute gingivitis in children is much higher, since up to 6-7 years of immunity is not yet fully formed, finally it is formed by 14-15 years. Observance of proper brushing of teeth in children is very important at an early age. Localized lesions of 1-2 teeth are caused by the accumulation of microorganisms, carious cavities on the contact surface, defects in seals, non-compliance with the clinical requirements of the seals. With gingivitis, the integrity of the dentogingival attachment is not impaired.
The mild degree of gingivitis is the defeat of the marginal gingiva, with the middle and severe forms being affected by the marginal and alveolar gums. When examined, there is diffuse reddening, swelling of the gingival tissue, light bleeding is possible during probing. The general state of health does not suffer. The interdental papillae are rounded, hang over the tooth tissue, dentogingival pockets are deepened. Pockets of food remain in the pockets, rotting, which aggravates the condition. On the mucous membrane of the lips, cheeks, tongue, there are fingerprints of the teeth, which indicates their edema. Increased salivation, there is a bad smell from the mouth.
Among acute forms of periodontal disease: necrotic gingivitis, specific, viral, gingival abscess. Acute necrotizing gingivitis( ulcerative) is characterized by severe pain of the gingival papillae, their necrosis. The general condition is disturbed and is manifested by the rise in temperature, the increase and soreness of the lymph nodes. In case of neglected cases, ulcers may form on the alveolar part of the bone, which communicates with the jawbone. If the process is not treated, it can lead to tissue loss or death.
Acute specific gingivitis occurs against the background of specific lesions of the body: tuberculosis, actinomycosis, syphilis, candidiasis. Acute viral gingivitis: the cause of its development is the herpes simplex virus, surrounding herpes and cytomegaly. A gingival abscess is the melting of the gingival papillae, the formation of pustules, accompanied by strong pain sensations. Acute local gingivitis is treated, and if local and general factors are eliminated, it is possible to prevent the manifestation of this ailment.
Diagnosing acute gingivitis is simple, based on complaints and clinical manifestations, the diagnosis is made quickly. The patient's young age, high indexes of Green-Vermilion hygiene, gum bleeding during probing, presence of cervical caries, sharp edges of seals, no changes in interdental septums, general condition of patient without deviations( except ulcerative forms of gingivitis).
Chronic gingivitis
Etiology, pathogenesis and symptomatology of chronic gingivitis does not differ from acute gingivitis. Chronic gingivitis can be atrophic, catarrhal, hypertrophic.
Chronic catarrhal gingivitis occurs with some periodicity, manifesting itself as a slight reddening and swelling of the gum. Its feature is a long and dull current. Complaints made by patients are not expressed. The process is limited and diffuse, with damage to the interdental papillae and marginal gingiva.
Chronic hypertrophic gingivitis is the enlargement of the gingival papillae, which can cover the entire outer surface of the tooth with the formation of a false periodontal pocket. There is pain when eating, bleeding. With prolonged course of any of the forms of gingivitis, atrophic gingivitis may develop, in which the gum decreases in size, is injured when taking solid food, becomes thin.
Atrophic gingivitis extends to the interdental papillae, they look like cut, marginal gums also flatten. Atrophic gingivitis is the storehouse of infection, it can provoke the development of exacerbation of the disease of internal organs.
Chronic gingivitis is divided into simple, hormonal, medicamentous, idiopathic, specific gingivitis.
Chronic simple gingivitis is caused by hard dental deposits in the adult population and in children in which the products of vital activity of microorganisms are concentrated. Hormonal gingivitis occurs most often in adolescents on the background of puberty, as well as in women during pregnancy or when taking oral contraceptives. Possible development of chronic gingivitis during treatment with steroid drugs.
Specific gingivitis is caused by Candida albicans, Actinomyces israelii and Treponema pallidum - causative agents of candidiasis, actinomycosis and syphilis. The degree of gingivitis depends on the degree of tissue damage. Chronic gingivitis is a precursor of periodontitis. Acute forms are amenable to treatment, and chronic ones are not, it is only possible to maintain them at the same level, without the occurrence of exacerbations.
When examining the oral cavity, reddening of the gums with a bluish tinge is evident. The gingival papillae are enlarged in size and thickened. During the period of exacerbation of chronic gingivitis, the gingiva becomes bright red, swells, bleeds when touching. On the surface there is a corresponding amount of dental deposits, the gingival joint is not destroyed, pockets are not detected. There is a huge number of tests to determine gingivitis before the manifestation of its first signs. These include the measurement of the amount of gingival fluid, the pH of the gingival fluid, the Kulazhenko sample( the time of formation of the hematoma on the gum), the gum bleeding index, gum thermometry, microbiological examination, X-ray examination, photoplethysmography, reoparodontography, polarography and many others.
Gingivitis in children
Children suffer from gingivitis quite often. The causes of this pathology in children can be external and internal. To external causes of gingivitis in children is the eruption of teeth, during which there is a natural trauma to the mucous membrane of the oral cavity. In the infancy, preschool and early school years, children have a habit of "trying to tooth", taking in mouth various things that can damage the mucosa and be the source of infection.
Also the cause of gingivitis in children may be a seal that does not meet the clinical requirements, the sharp edge of the decaying temporary tooth. External signs include various infectious diseases, the presence of carious cavities. Diseases associated with diabetes, tuberculosis and nephropathy. Wearing orthodontic equipment, which is an additional retention point for delaying microbes with unsatisfactory brushing of teeth.
The internal causes of gingivitis in children are: abnormal teething, which injures the gum, insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals in the child's body, unbalanced nutrition, reduced immunity. Gingivitis can be an additional symptom of the disease, but it can also act as an independent pathology. According to inflammatory signs, gingivitis in children is divided into catarrhal, hypertrophic, ulcerative and necrotic and mixed. Each of them has a sharp and chronic form.
Quite easily when examining the oral cavity of a child is determined by acute gingivitis of the gums. The child often refuses to eat, he is crying and irritable, does not sleep well. Manifestations are well expressed in the oral cavity: gums are red, edematous, bleeding is determined, the amount of plaque is increased. The clinical picture of the chronic form of gingivitis is blurred. The most common form of gingivitis among children is hypertrophic gingivitis. It is also called juvenile or pubertal gingivitis. The main complaints in children for pain, bleeding at meals, aesthetic disadvantage. Such changes after puberty disappear. It is possible to remove proliferation surgically.
At an early age in children, the second most common form is catarrhal gingivitis. It is manifested by gingival inflammation, bleeding and an unpleasant odor from the mouth. The consequence of catarrhal gingivitis is ulcerative gingivitis on the background of a decrease in the body's defense system. General health of the child is disrupted( temperature, increase in submandibular or occipital lymph nodes), children refuse to eat, crying, sluggish. In the oral cavity picture of ulcerative gingivitis: soreness, bleeding, the presence of dental deposits.
The most severe form is ulcerative necrotic gingivitis, in which necrosis of interdental papillae, marginal gums occurs. Ulcers are covered with a touch, they are gray, saliva is viscous, a putrid smell comes from the mouth. Due to inadequate dental treatment, development of atrophic gingivitis is possible. Inflammatory phenomena do not prevail, patients do not provide complaints, the dentist can diagnose it on a preventive examination.
Treatment of gingivitis
Treatment of gingivitis should first of all be complex, that is, it should be aimed at eliminating etiological, pathogenetic, symptomatic factors.
In the presence of sharp edges of the seal, correction of the filling or setting new at the same place, correction of established prostheses, restoration of the destroyed teeth with sharp edges with filling material or crown is necessary. If the cause of gingivitis is the eruption of the eighth tooth, it is necessary to prescribe rinsing with solutions of weak anesthetics( chamomile, sage), a solution of soda. In case of difficulty gum eruption is surgically opened to facilitate eruption.
The orthodontic treatment of gingivitis shows the appointment of professional hygiene every 3 months, rinsing with solutions of antiseptics, the appointment of fortifying agents for surgical intervention. In diseases of internal organs( cardiovascular system, gastrointestinal tract, nephropathy, endocrine system disorders, etc.), appropriate therapy should be prescribed directed at the treatment of the main focus.
Medication gingivitis occurs with the abolition or replacement of antibacterial drugs. Long-term use of antibiotics causes an imbalance in the normal microflora of the oral cavity. Reception of lactobacilli normalizes the maintenance of microbes in an oral cavity. It is necessary to examine adjacent specialists for health control, and the appointment of immunocorrective therapy and vitamins. For the appointment of immunosuppressors and other drugs that stimulate the immune system, it is necessary to consult an immunologist. Only after his examination, the administration of drugs is possible.
With specific lesions of the gums, prescribe antibiotics and antifungals, antiseptic rinses.
Treatment of acute catarrhal gingivitis is aimed at eliminating adverse factors, normalizing the reactivity of the body, and showing desensibilizing therapy. The dentist needs to teach the patient proper personal hygiene of the oral cavity, perform antiseptic treatment of the oral mucosa( 0.06% with Chlorhexidine solution, 1% peroxide solution), apply a bandage with an ointment containing corticosteroids.
For chronic catarrhal gingivitis, rinse 1% with tannin solution, decoction of oak bark, sage infusion. Irrigators, vibrating massage or gum auto-massage are recommended. Irrigator - a special device that delivers water from a thin tube under a slight pressure. Included with the irrigators are replaceable nozzles. Irrigator allows not only to perform massage movements, stimulating microcirculation in the bloodstream, but also cleans interdental spaces.
Treatment of ulcerative necrotic gingivitis consists of general and local treatment. The general treatment consists of taking antibiotics, antihistamines and anti-inflammatory drugs, taking high-calorie shredded foods, limiting the intake of solid and irritating foods. Local treatment is carried out on an outpatient appointment with a dentist for a week or longer. It is necessary to carry out anesthesia of the affected mucosa. Applied anesthesia with gel anhydration or infiltration anesthesia( Lidocaine, Septanest, Ultrakaine).Further, removal of dental deposits, both hard and soft, removes the sharp and overhanging edges of the seals. Mechanically or with the help of proteolytic enzymes( trypsin, chemotripsin), remove necrotic gingival tissue. Apply the enzyme to the cotton swab and apply to the affected area for 10 minutes, repeating the procedure 2-3 times per reception. Then, antiseptic treatment of ulcers with peroxide solution, chlorhexedin, potassium permanganate or Furracillin is carried out. For better and faster healing of ulcers, keratoplastic preparations are applied( Solcoseryl ointment, Metiluracil ointment).
Treatment of gingivitis in children is similar to that in adults, but since gingivitis in children occurs without pronounced changes in the general state of the body and without a vivid clinical picture in the oral cavity, it is sufficient only to conduct occupational hygiene and use of antiseptic agents. Tartar removal is carried out by ultrasonic devices, the Air flow system, grinding and polishing with pastes, as well as deep fluorination. At home, children can rinse the mouth with a 0.06% solution of Chlorhexedin( 2 times a day for 30-40 seconds lasting 10 days).There are gels "Holisal", Metrogil denta, which have anti-inflammatory and antiseptic effects. When hypertrophic forms of gingivitis in children after the restoration of the hormonal background, the size of the gingival papillae normalizes. If they are kept in the same volume, surgical excision, cryodestruction, and gingivoplasty are possible.
The use of physiotherapeutic treatment for gingivitis contributes to a speedy recovery. This includes intraoral cellular electrophoresis( eg potassium iodide), UVO in an oligothermic dose, laser therapy. The course of therapy lasting 7-10 days for 10 minutes will have a positive effect on the recovery of the patient.
When removing dental deposits from false periodontal pockets, open and closed curettage of periodontal pockets is performed. Closed curettage is the removal of hard tooth deposits by means of hooks, excavators, curettes. When the curettage is open, a gum incision is made and the stones from the tooth surfaces are also removed, seams are applied and protected with a bandage or a diplenic film.
If the recommendations of the dentist are observed by adults and children, the teeth are cleaned properly about two times a day after meals, the complete treatment of acute forms of gingivitis occurs. A prolonged course of gingivitis can cause chronicization of the process and the development of periodontitis of the teeth. The correct selection of a brush with a soft bristle, the use of toothpastes with medicines, the timely replacement of brushes has an important preventive value.
It is necessary to come to the dentist no less than once every six months for carrying out preventive examinations. Any dental disease is easier to prevent than to start and then long to treat.



