Disease skin disorder
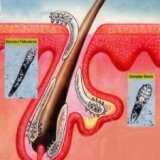
Demodex is a disease that is accompanied by a skin lesion with a microscopic tick. This mite is called Demodex folliculorum. For many people, the presence of a tick on the surface of the skin is considered a normal factor, it does not cause any human anxiety. The tick feeds on the dead cells of the upper layer of the skin. But still, if the body weakens, the tick immediately penetrates into the deeper layers of the skin, which causes an inflammatory process. As a rule, demodex is located in the sebaceous glands and hair follicles, feeding on the contents. The tick especially prefers places where salo is high.
At first glance, the skin disease of demodex is similar to acne and rosacea. The combination of demodex with these diseases is due to the fact that in both cases, acne vulgaris and pink, which depress the protective functions of the skin.
To develop the disease can at any age, but still frequent cases are observed in adolescents, in pregnant women and in people who have suffered emotional stress. Independently the disease does not go away, it is necessary to fight it. The skin is affected first in some areas, then in others, which creates both certain disadvantages for both men and women. With a long course of the disease, acne appears on the chest, and even on the back. Acne with demodex can not be suppressed in any case, because it can lead to an exacerbation of the infection. When crushing acne, the mite, which is in the liquid, is pressed deeper.
This skin disorder is accompanied by such signs:
- Acne. It can be pink acne, a rash, youthful acne, acne, a different plan for sores, etc., on the face. It is pimples that are a manifestation of demodicosis disease. The protracted shape of this process promotes the development of acne on the skin of the back, in the chest area and even on the hips.
- Red spots that are mostly located on the face.
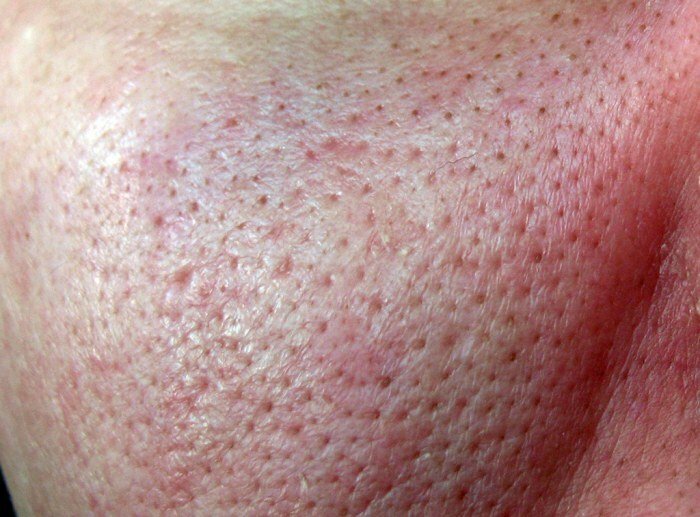
- Increased skin fatness, while the pores of the skin are particularly enlarged. Plague-infested areas have a certain appearance. The skin becomes more moist, greasy, and has a characteristic luster. As a rule, the skin on the nose and on the cheeks suffers.
- A pale or earthy-gray hue of the face.
- Bumpy facial skin. In the thickness of the skin is formed a fairly coarse "scar" tissue, as well as many small hard lumps of calcium. This leads to a deterioration of complexion and develops tuberosity of the skin.
- Difficulty in movement of facial muscles.
- The size of the nose increases. Sometimes the increase is significant and the nose resembles a huge blue-red plum( rhinophyma).
- Itching, there is a slight tickling and crawling on the skin. People sometimes do not notice the tickling, and they scratch automatically. Itching with demodex usually intensifies toward evening and lasts throughout the night. At night, the period of the most active life of ticks begins, usually at this time their mating takes place.
- Itching of the scalp, in some cases, hair loss. Hair loss can also be associated with the active activity of the demodex mite.
- Itching of the eyelashes. Loss of eyelashes is observed. Most often, this is due to the vital activity of the tick of demodicosis, which is in the roots of the eyelashes. During the disease, the bases of the eyelashes begin to itch, at which time the eyelashes become thinner and gradually fall out.
- Itching of the auricles.
To diagnose demodex, scraping is taken on the affected skin areas and microscopic examination is performed. If a mite-demodex is found in the scrapings, then the demodicosis is diagnosed.
In the inflammatory process, antibiotics are prescribed. The main priority is the antibiotics of tetracycline. Metronidozole or titeral are also used, and sedatives are also used. These are substances that increase the activity of neutrophils. In especially severe cases, roalsutan is used. As antiparasitic agents, trichopolum is also used. The course of treatment is from four to six weeks. Ornidazole is used in a cycle of 8 to 10 days. As antiparasitic agents, sulfur preparations are used. Including in the treatment of demodex( skin disease), angioprotectors, antiserotonin and antihistamines are used. Antihistamines are loratadine, terfenadine, ebastin, etc. For topical use, vasoconstrictive drugs, for example, aqueous adrenaline-resorcinol solution, as well as ointments that contain antibiotics mupirocin. Assign also fuzidinovuyu, erythromycin or tetracycline ointment. Anti-inflammatory preparations containing sulfur, metronidazole, naphthalene-indomethacin, butadione, orthophane ointment. Skin covers lubricate with preparations containing vitamin A - it can be retinoic ointment, retin A or airol. In the eye area, alcohol ester mixtures, sodium sulfapyridazine, tricholate cream and other preparations are used.
Excellent properties for skin disease demodex, has the drug "Spregal."This preparation contains a solution of esdepaletrin and piperonyl butoxide. This drug is rubbed into the affected areas of the skin 3 times a day. In 87% of cases, there is an improvement in the clinical picture and a complete recovery. This drug is well tolerated and does not cause side effects.
The main emphasis is on improving immunity, selecting the drugs individually in each case. As for external therapy, it is aimed at effective cleansing of the skin, and pathological aspects should be taken into account. During treatment it is recommended to reduce contact with water as much as possible. For washing, special lotions and emulsions should be used.
An integrated approach to cure demodex disease will help to cope with the ailment that has arisen. First of all, it is necessary to restore the protective functions of the skin, and on the other hand, treatment should be aimed at suppressing the activity of the tick.