Pathogenesis of cholelithiasis
 Traditionally, it has been found that cholelithiasis most often affects the adult population, especially middle-aged and overweight women. About what the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis is from itself, and will be discussed below.
Traditionally, it has been found that cholelithiasis most often affects the adult population, especially middle-aged and overweight women. About what the pathogenesis of cholelithiasis is from itself, and will be discussed below.
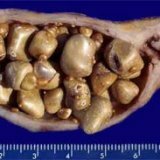
Under cholelithiasis is meant a disease in which the formation of sand and stones begins to appear in the bile ducts or in the cavity of the gall bladder itself. Unfortunately, this is not a rare occurrence. For example, in the Americas and Western Europe, a quarter of the male and a third of the female population suffer from cholelithiasis.
Causes of cholelithiasis
The process of occurrence of stones is usually caused by an increase in the concentration of salts in the bile due to disturbed metabolism, as well as stagnation in the gallbladder of bile.
Gallstone disease can occur for the following reasons:
- if there is a violation of the periodicity of food - during fasting, overeating, irregular meals;
- when taking contraceptive drugs based on hormones;
- during pregnancy;
- for prolonged sitting;
- with excess weight;
- for abnormalities in the pancreas;
- for dyskinesia of the biliary tract.
Processes occurring in the body during the period of
disease The pathogenesis of the disease indicates that the appearance of gallstones occurs as a result of precipitation of bile particles with high density. Most of the stones of this type include calcium salts, a special bile pigment - bilirubin, and cholesterol. Stones prevent the normal operation of the gallbladder, which is a kind of bile supporter.
When overeating, when riding and shaking, stones have the ability to go out into the mouth of the duct, it is also called biliary colic, after which it is blocked. This entails a violation of the process of outflow from the gallbladder bile, an increase in the walls of the gallbladder in size. The person begins to experience the strongest pain. It can develop into an inflammatory process in the gallbladder - acute cholecystitis. Also, the organs that are nearby can be inflamed - namely the pancreas, stomach and duodenum.
Symptoms of the disease
If the stones are not located in the duct, but in the gall bladder, the person with the disease may not even know that he is sick. One of the first symptoms, indicating the appearance of cholelithiasis, is a strong feeling of bitterness in the mouth, nausea and the urge to vomit, as well as the appearance of gravity on the right side under the ribs.
It happens that the stone comes out of the gall bladder into the bile ducts. In this case, an attack of biliary colic is inevitable, when a sharp pain is felt in the upper part of the abdomen or in the hypochondrium. It can "give" in the back, in the right arm or in the right collarbone. Symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, which do not bring any relief, and bitterness in the mouth may appear.
If the stone is small and could easily pass the ducts, it enters the duodenum and colic ceases on their own. Then the stone simply leaves the body together with the feces. If the stone itself is not removed from the body, there is a blockage of the biliary tract and begins the development of both subhepatic( mechanical) jaundice, as acute cholecystitis.
Diagnostic measures
They should be performed only by a doctor - specialist gastroenterologist. The diagnosis can be made based on complaints from the patient or on the conduct of some specialized studies. The pathogenesis of the cholelithiasis pathology of this particular patient should also be studied in detail.
The patient is first subjected to ultrasound examination of the abdominal organs. In more difficult situations, it may be possible to refer the patient to an X-ray scan with a preliminary input of the contrast medium. It can be administered both intravenously and through the oral cavity. Sometimes a contrast agent is injected directly into the bile ducts when an endoscope is used or when a thin needle is punctured. When these procedures are carried out, it is possible to rid the bile duct from small stones.
Treatment of cholelithiasis
For the treatment of this ailment, both therapeutic methods and surgical intervention are used. Traditionally, treatment begins with the application of non-surgical methods of action.
The first of these is a strict diet. It is important to exclude from the daily diet all fried, fatty foods, carbonated drinks, chocolate, and also spicy. You can not eat fatty meat, all kinds of smoked meat, you need to exclude alcohol, and use of irritating seasonings. It is advisable to include in the menu sour-milk products and food of vegetable origin. Wheat bran is also very useful.
The second step to cure is the removal of stones from the gallbladder with special preparations. These acids are chenodeoxycholic and ursodeoxycholic. However, this method is used only when removing stones from cholesterol or single stones of small sizes - no more than two centimeters. The course of treatment lasts from a year to a year and a half.
The third step is the use of a method called extrapolar shock wave lithotripsy. This is the procedure for the destruction of stone formations by means of a shock wave, which appears when the special technique is applied. Indications for the use of this type of treatment - the presence of stones from cholesterol, not exceeding three centimeters. When using this method, the stones are broken into pieces of small size( no more than two millimeters), after which they leave the body together with feces. This is a fairly painless treatment that can be carried out on an outpatient basis.
Surgery is the last resort. Its essence consists in the operative removal of the entire gallbladder from the body. This operation is performed in two ways:
- Classical cholecystectomy. This operation consists in carrying out an incision of sufficiently large size and removing the bubble. The seam after this operation has a size of twelve centimeters.
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy. It is carried out with the help of a special instrumentation, introduced into the abdominal cavity through small holes( up to one centimeter).After such an operation, there are practically no traces on the skin. This method is less traumatic, in addition, the patient needs a shorter period of stay in the hospital.