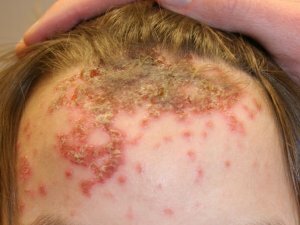
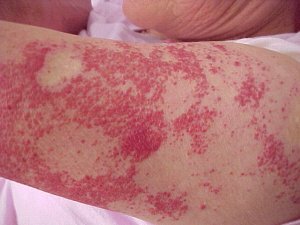
Atopic dermatitis
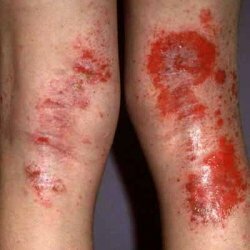 Atopic dermatitis is an allergic skin disease characterized by genetic condition, prolonged and poorly curable flow and a number of typical symptoms, the most common of which is skin itching.
Atopic dermatitis is an allergic skin disease characterized by genetic condition, prolonged and poorly curable flow and a number of typical symptoms, the most common of which is skin itching.
Currently, atopic dermatitis is the most frequent and most severe allergic skin disease, it affects more than 12% of the population.
As a rule, atopic dermatitis begins in childhood( 6-12 months), in some cases, the first symptoms of the disease can manifest later, from year to 5 years, sometimes the disease appears already in adulthood.
Atopic dermatitis may be concealed under the diagnosis of neurodermatitis, eczema, diathesis or allergic dermatitis.
Causes of Atopic Dermatitis
The symptoms of atopic dermatitis were first described in 1844, but there is still no consensus on the causes of atopic dermatitis. It is believed that this allergic disease, non-contagious, chronic, occurs as a reaction of the immune system to the external environment. One of the most significant factors in the onset of the disease is a hereditary burden.
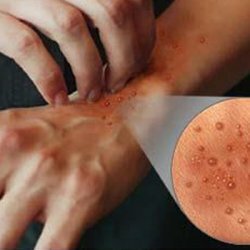 At the heart of the mechanisms of development of atopic dermatitis is immediate type hypersensitivity( lgE-dependent immune response), manifested as an immediate, in a matter of minutes, very rarely a clock, the reaction of immunity to an allergen that has entered the body.
At the heart of the mechanisms of development of atopic dermatitis is immediate type hypersensitivity( lgE-dependent immune response), manifested as an immediate, in a matter of minutes, very rarely a clock, the reaction of immunity to an allergen that has entered the body. Allergic predisposition goes into atopic dermatitis under the influence of the following factors:
- toxemia during pregnancy;
- smoking;
- drinking alcohol;
- digestive disorders( dysbacteriosis, enzyme deficiency, lack of breastfeeding, early lure, etc.);
- infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- reception of antibiotics;
- contact with animals, pollen of plants, household chemicals, and other allergens;
- frequent infectious diseases in the child, as well as the presence of parasites.
Allergens that cause the development of atopic dermatitis:
- food allergens - found in food;
- household allergens - are contained in house dust, book dust, in pillows( feather, tongs);
- epidermal allergens - found in pet hair, feathers of birds, pet food;
- is the algae contained in the pollen of plants.
Symptoms of atopic dermatitis
- The disease occurs at an early age( about half of the infants who are sick);
- the next of kin has allergy symptoms;
- dry skin;
- skin rashes. Can have both a local character, especially in the folds of the skin, and spilled;
- itching itch.
The following variants of the clinical course of atopic dermatitis are distinguished:
- Infant form. Occurs in a period of up to two years, in the form of vesicles( vesicles) on the skin, merging into the wet areas, subsequently forming crusts. Foci of inflammation are localized mainly on the face, limbs, on the neck, wrists, folds of the skin.
- Children's uniform. In children older than two years, atopic dermatitis is manifested by the following symptoms: peeling, dry skin, cracking, lichenization, inflamed skin areas are clearly localized, usually in the area of knee and elbow joints, in folds of the skin, on the neck. After healing of the inflammation foci, hyperpigmentation is retained in their place.
- Adolescent-adult form. At this stage, in the absence of effective therapy, inflammation can spread throughout the body and take a chronic form. The skin of the face, neck, back and chest is affected. Skin is dry, scaly, cracked, with traces of scratching. It is also possible hair loss on the occiput and the appearance of a fold on the lower eyelid( "Morgan's syndrome").In the period of remission, atopic dermatitis can manifest as scaly areas of the skin in pink, as well as cracks in the ears.
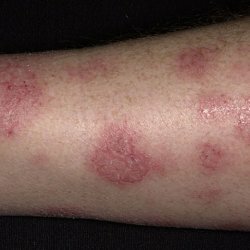 Atopic dermatitis can have a severe, moderate and mild course. In 70% of patients with complex therapy, the symptoms of the disease disappear by age 17.In other cases, relapses may subsequently occur. In the chronic form the disease passes in cases of early onset, severe course, often complicated by infection. You should not independently treat the atopic dermatitis, especially if there are suppurations in the inflamed areas, puffiness, increased body temperature - it is better to seek help from a doctor!
Atopic dermatitis can have a severe, moderate and mild course. In 70% of patients with complex therapy, the symptoms of the disease disappear by age 17.In other cases, relapses may subsequently occur. In the chronic form the disease passes in cases of early onset, severe course, often complicated by infection. You should not independently treat the atopic dermatitis, especially if there are suppurations in the inflamed areas, puffiness, increased body temperature - it is better to seek help from a doctor!
Diagnosis of atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is located at the intersection of two medical specialties - a dermatologist and allergologist-immunologist, some uncomplicated forms of atopic dermatitis can be treated by a pediatrician, although the most effective treatment for a doctor is a specialist.
- gastrointestinal diagnosis;
- analysis of feces for dysbiosis;
- coprogram;
- ultrasound of the abdominal cavity;
- feces analysis on egg worm;
- blood test for antibodies;
- endocrinologist consultation;
- consultation of a neurologist and orthopedist( if inflammation is located in certain places to exclude possible pathology of the spine);
- allergic tests;
- blood test for LgE-specific immunoglobulins E;
- crops on microflora and fungi( in case of purulent discharge from affected skin areas);
- test for sensitivity to antibiotics;
- immunogram( if atopic dermatitis is aggravated simultaneously with viral and catarrhal diseases);
The main difficulty in planning successful therapy of atopic dermatitis is to identify the factor that is the main cause of the disease. The causes that trigger the mechanism of the disease and complicate its course can lie not only in the immune field, but also in the plane of the nervous and endocrine systems. Unfortunately, without revealing the true cause of atopic dermatitis, it is practically impossible to achieve a stable remission.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis
- diet, aimed at removing the allergen from the patient's body;
- antihistamines;
- detoxifying( cleansing) agents;
- means that reduce the sensitivity of the body to the allergen( hyposensitizing);
- anti-inflammatory drugs( corticosteroids);
- antiseptics;
- sedative( sedative) remedies;
- enzymes that support pancreatic function;
- antibacterial agents;
- prebiotics;
- antiviral drugs( in case of concomitant viral infection).
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in the acute stage differs somewhat, it includes complex medical therapy:
- topical glucocorticosteroids - relieve the symptoms of exacerbation. Have a number of contraindications, it is necessary to take only under the supervision of a doctor;
- drugs that include glucocorticosteroids, antibiotics and an antifungal component are effective against concomitant infection;
- zinc-containing preparations;
- antihistamine preparations of the 2nd and 3rd generations;
- sorbents.
During remission, atopic dermatitis, like any chronic disease, needs maintenance treatment:
- use of medical cosmetics;
- treatment of concomitant diseases of the zhkt, nervous, endocrine system, etc.
Folk remedies for atopic dermatitis
 Positive dynamics in the treatment of atopic dermatitis is observed when used in traditional medicine. In uncomplicated forms of the disease, you can use soothing preparations, take baths with decoctions of herbs, make lotions and compresses.
Positive dynamics in the treatment of atopic dermatitis is observed when used in traditional medicine. In uncomplicated forms of the disease, you can use soothing preparations, take baths with decoctions of herbs, make lotions and compresses.
However, it must be borne in mind that medicinal herbs can trigger an allergic reaction.
Treatment of atopic dermatitis in pregnancy
Atopic dermatitis, as a rule, is first manifested in early childhood, so during pregnancy, you can face exacerbations of a chronic disease.
In general, the treatment of atopic dermatitis during pregnancy is the same as in standard cases, but special attention should be paid to medications( it is advisable to use the latest generation of drugs as the safest), limit the use of cosmetics, do not use drugs that are contraindicated during pregnancy.
Prevention of atopic dermatitis
- primary - is aimed at preventing the disease - the mother's diet during pregnancy, the exclusion of allergens from the diet, the use of medicines only in case of emergency, compliance with the rules of breastfeeding and complementary feeding.
- secondary - is aimed at achieving long-term and stable remission - compliance with the temperature regime in the room( not more than + 24 degrees, humidity - about 60%), wet cleaning, dieting, avoiding contact with animals, household chemicals, excluding allergens contained inPollen of houseplants, wearing clothes from cotton fabric, use of hypoallergenic cosmetics, refusal of sunburn. Also, an important role in the prevention of atopic dermatitis is played by the therapy of concomitant chronic diseases, the use of vasoconstrictive, sedative drugs, vitamins.
Features of nutrition in atopic dermatitis
 Compliance with hypoallergenic diet is the most important element of therapy of atopic dermatitis.
Compliance with hypoallergenic diet is the most important element of therapy of atopic dermatitis. Hypoallergenic diet for atopic dermatitis
Excluded during acute exacerbation of atopic dermatitis products:
- citrus;
- nuts;
- seafood;
- chocolate;
- fish;
- coffee;
- mayonnaise;
- seasonings;
- tomatoes;
- milk;
- eggs;
- mushrooms;
- soda;
- sausage;
- strawberry;
- pineapple;
- honey;
- alcohol.
Allowed for atopic dermatitis products:
- boiled beef;
- olive and sunflower oil;
- potatoes;
- buckwheat porridge, rice, oatmeal;
- sour-milk products;
- cucumbers;
- green apples;
- tea.
Complications of atopic dermatitis and prognosis of recovery
With adequate therapy and elimination of aggravating factors, the prognosis is favorable.
Complications of atopic dermatitis:
- concomitant bacterial infection;
- pyoderma - the appearance of pustules on the skin;
- viral infection, herpes;
- fungal infection;