Inflammation of hair bulbs
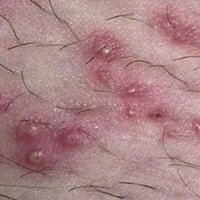
Folliculitis is an inflammation of a hair bulb caused by infection with white or golden Staphylococcus aureus. Most often the disease develops with neglect of personal hygiene measures. Microtraumas and cracks occurring in the hair follicle area can occur.
Reasons for
There are many reasons for the development of bulb inflammation. And although most often folliculitis develops with inadequate observance of elementary measures of personal hygiene. This reason is far from leading. Friction of the skin, for example, about clothes in the same place can cause micro-trauma. They, in turn, are open gates of penetration of staphylococcus into the hair follicle.
In addition, inflammation of the bulb can occur with a sudden hypothermia, malnutrition and some diseases. Most often, the development of folliculitis contributes to diabetes, anemia and chronic liver disease.
Depending on the cause of the disease, the disease takes one of numerous forms. Physicians distinguish:
- parasitic folliculitis - inflammation caused by bacteria( more often localized in the area of the mustache and beard);
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa - occurs after contact with water in saunas and baths with poor disinfection, as well as after contact with bath accessories of general use;
- Gram-negative folliculitis - caused by prolonged intake of hormonal drugs for the treatment of acne;
- other forms.
Folliculitis can be superficial and deep, single and multiple. In addition, inflammation of bulbs can develop and as a professional disease in people who constantly work with various lubricants. They affect the skin fatal, regularly contaminating it. Under certain conditions, ordinary folliculitis can develop into acute furunculosis.
Symptoms of
With superficial folliculitis, the disease usually proceeds easily. There is an appearance of an abscess with a size of up to 5 mm. In the location of an inflamed hair bulb. At the same time, the pain sensations are either insignificant or absent altogether. Over time, the abscess dries up on its own, forming a dark scaly crust and a slight pigmentation of the skin.
Deep folliculitis differs in appearance on the skin of large( up to 100 mm) diseased nodules, the center of which is located in the hair follicle itself and a noticeable abscess in the upper part. The abscess gradually matures and is opened, forming a yellowish crust as it heals.
With professional folliculitis, inflammation often develops on areas of the skin that are often contaminated: forearms and hands. The peculiarity of the formation of a professional folliculitis is the primary formation of a plug in the area of hair entering the inside of the hair follicle. This leads in the future to the development of suppuration.
Treatment of
Treatment of folliculitis consists in a neat puncture of the abscess and removal of pus coming out with a sterile cotton swab. The skin around the site of inflammation should be lubricated with antiseptic solutions daily, several times. For example, an alcohol solution of brilliant green or fucorcin.
With deeper folliculitis, it is recommended to apply a compress to the inflamed hair bulb with ichthyol ointment or ichthyol. It is desirable to change such a compress several times a day. When the problem is repeated or the chronic course of the disease, immunotherapy and antibiotics are recommended. The chronic course of folliculitis always indicates a decrease in the immune status of the human body.
Prevention of
Preventing folliculitis is simple: you must observe only a few simple rules of personal hygiene.
Rule 1. When entering the pool or sauna, be interested in the pH level of the water, as well as the degree of its chlorination. The proportion of chlorine in water should be at least half a gram per 1 liter, and the pH should not drop below 8. Correct parameters ensure that there are no conditions for rapid breeding of Pseudomonas bacteria. This can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Rule 2. You should never use other people's towels, hygiene products, washcloths and other bath accessories.
Rule 3. Avoid traumatic skin lesions. Especially damage caused by wearing tight underwear and clothes.