Skin cancer: external signs
 Skin cancer is usually the result of too much sun exposure. Although skin cancer is the most common form of cancer, many types of it are treated.
Skin cancer is usually the result of too much sun exposure. Although skin cancer is the most common form of cancer, many types of it are treated.
Skin Cancer:
external signs of skin cancer is divided into four types:
- Basal cell carcinoma( CCL) is the most common form and is 90% of all skin cancers. It begins in the basal cells, in the lower part of the epidermis( the outer layer of the skin), which is caused by prolonged exposure to direct sunlight. This is easily treated.
- Squamous cell carcinoma( RCC) is the second most common type. It begins in the epidermis, eventually spreads over the entire skin, if not treated. It is easily treated if the cancer is detected at an early stage, but in a small percentage of cases, the cancer has spread( metastasized) to other parts of the body.
- Malignant melanoma( 3M) is the most severe type of skin cancer and is responsible for most deaths. However, it can be cured if it is diagnosed and removed at an early stage.
- Kaposi's Sarcoma( CK) is caused by the herpes family virus. This form of cancer affects about one-third of all people with AIDS.
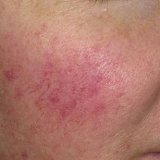
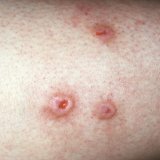
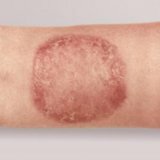
Symptoms and signs of skin cancer
Basal cell carcinoma:
- Sunstroke( pearl or transparent)
- flat, flesh-colored lesions that appear anywhere on the body
Squamous cell carcinoma:
- solid, red nodule on the face, lips, ears, neck, hands
- flat lesion with a scaly surface
Melanoma:
- Change the color, size, shape or texture of moles
- skin lesion with uneven borders
- common skin lesions
- large brown spots with darker CrappieKami
- solid, dome-shaped bumps anywhere on your body
only way to know whether the moles or spots on the skin be cancer, it is necessary to consult a doctor.
Causes of the disease:
- Exposure to ultraviolet( UV) radiation from the sun is the main cause of skin cancer. Skin cancer can also be associated with genetics( heredity) or radiation therapy.
- The virus that causes Kaposi's sarcoma.
Who is at greatest risk?
People at risk for developing skin cancer may have the following conditions and characteristics:
- Light skin
- Finding plenty of sun exposure
- Sunburn
- Family history of skin cancer
- Large number of moles
- Large dark moles known as congenital melanocytic nevus
- Precancerous lesionsthe skin, such as actinic keratosis
- HIV( human immunodeficiency virus) - the risk of Kaposi's sarcoma
Diagnosis Your doctor will examine your skin growths, changesI or unusual moles. This may include the use of a dermatoscope, which is used to closely examine the growth of the skin. If your doctor suspects cancer, a skin sample( biopsy) will be taken. A biopsy can confirm whether or not you have skin cancer.
Warning
In most cases, skin cancer can be prevented. If you are at greatest risk, avoid exposure to the sun. Being in the sun, use a sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30. You should also undergo regular check with your doctor or dermatologist.
Treatment of
The main objectives of treatment are to remove a cancerous tumor and prevent the spread of the disease.
Kaposi can be treated with chemotherapy. In addition, in cases where the cancer is found only in the upper layers of the skin, creams or lotions containing chemotherapeutic drugs are used.
Surgical procedures
Skin cancer can be removed surgically. Cryotherapy( freezing) and chemotherapy are also used. If the cancer is on or close to the surface of the skin, in such cases, photodynamic therapy( laser) is used.
Complementary Therapy
Alternative treatment will focus on prevention, not on the treatment of skin cancer. In addition, some methods can reduce the side effects of conventional treatment, such as chemotherapy. You should never rely on alternative methods to treat skin cancer.
Nutrition
There are certain foods that can help prevent skin cancer. It is difficult to verify the role of nutrients in the prevention of various forms of skin cancer but antioxidants( including vitamin C, vitamin E, beta-carotene, zinc and vitamin A), folic acid, fats and proteins, and a variety of natural products help keep the body in good shape. Foods such as fish, beans, carrots, beets, squash, cabbage, broccoli and vegetables containing beta-carotene and vitamin C, can help protect the skin. Lignans, substances contained in products such as soybeans and flaxseed, to help in the fight against cancer as a whole, including the proliferation of melanoma from one body part to another.
Other substances found in plants, protect your skin from the harmful effects of the sun:
- apigenin flavonoids found in fruits and vegetables, including broccoli, celery, onions, tomatoes, apples, cherries and grapes
- Curcumin, contained in the spices turmeric
- Resveratrolcontained in the grape skins, red wine and peanuts
- quercetin, flavonoids contained in apples and onions
Selenium has been touted as an antioxidant that can help prevent skin cancer. In one study, it is suggested that selenium can actually increase the risk of squamous cell carcinoma. Talk with your doctor before taking selenium.
balanced, healthy diet that consists mainly of fruits, vegetables, low-fat dairy products and whole grains can help your body cope with the effects of chemotherapy or other cancer treatments. Avoid foods high in fat and sugar, they can cause inflammation.