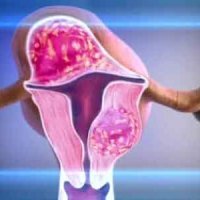
Polycystic ovary: symptoms, causes and treatment
 Polycystic ovaries - a serious chronic disease of the reproductive sphere, which does not ovulate and infertility arises due to pathological changes of female genital glands structure.However, the inability to conceive a child is only the tip of the iceberg, polycystic ovary leads to serious hormonal and metabolic disorders, and also does not better reflect the appearance of the woman.
Polycystic ovaries - a serious chronic disease of the reproductive sphere, which does not ovulate and infertility arises due to pathological changes of female genital glands structure.However, the inability to conceive a child is only the tip of the iceberg, polycystic ovary leads to serious hormonal and metabolic disorders, and also does not better reflect the appearance of the woman.
Polycystic ovaries: the causes of
Normally in the ovary of healthy womenMonthly grows 5-6 follicles with ovules, but ripens and bursts during ovulation only the one that contains the most vitalbnuyu egg.All other follicles under the influence of hormones are amenable to reverse development.If the hormonal balance is disturbed( estrogens and androgens are released in excess, and progesterone is not synthesized enough), immature follicles instead of being resolved, are transformed into cysts.From cycle to cycle, the number of these cysts increases, so over time, the ovaries are almost completely covered by them.This is the polycystosis.
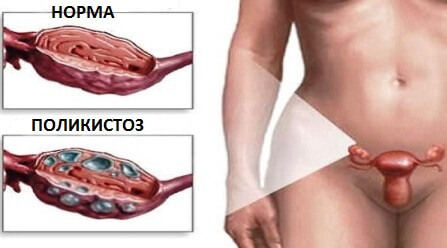
The exact cause of the occurrence of polycystic ovary is not known to date.However, scientists believe, a role in this process, the following factors are:
- Reduced tissue sensitivity to insulin and a compensatory overproduction of the hormone by the pancreas.Under the action of insulin, female gonads begin to actively synthesize estrogens and androgens, which is manifested by a violation of ovulation.
- Failure in the hypothalamic-pituitary regulation of the functioning of the female reproductive system.
- Inflammatory diseases of the ovaries.
- Dysfunction of the cortical gland of the adrenal gland, which synthesizes androgens.
Polycystic ovary occurs both in adolescent girls and in adult women giving birth.An impetus to the development of the disease can be severe stress, a serious infectious disease, an autoimmune process, a sharp change of climate.
symptoms of polycystic ovarian
Due to the fact that with polycystic ovary in women occur multiple lesions, the clinical picture of the disease can be considered a very different set of both clinical symptoms and their severity.For example, some patients may not even know about their condition until they begin to actively seek the cause of infertility.In others, on the contrary, the symptoms are so pronounced that women seek medical help immediately after the appearance of the first signs of ailment.
The main symptoms of polycystic ovaries include:
- Violations of the menstrual cycle - long delays and prolonged menstruation.
- Chronic pain in the lower abdomen of the , pelvic area, lower back.
- Hyperproduction of secret by sebaceous glands( from this skin and hair become fat ).
- Acne rash .
-
 Excessive hairiness legs, arms and appearance of hair growth in places that are not typical for women( on the chest, on the chin), alopecia, male pattern of the head.This is all the result of excess in the body of the female male sex hormones( androgens).
Excessive hairiness legs, arms and appearance of hair growth in places that are not typical for women( on the chest, on the chin), alopecia, male pattern of the head.This is all the result of excess in the body of the female male sex hormones( androgens). - Significant weight gain .Fat deposits appear mainly in the waist( like an apple).The development of obesity in polycystic ovaries is associated with impaired glucose tolerance and excess in the blood of insulin.
- The inability to conceive .
- Constancy of basal temperature .Women, protected by the natural method or, on the contrary, trying to become pregnant, can note that the basal temperature does not change during the cycle, which indicates the absence of ovulation.
In addition, during the laboratory and instrumental research also characteristic for polycystic ovary signs are also revealed:
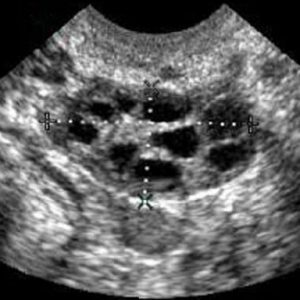
- By ultrasound - an increase in the sex glands in sizes 2-3 times, visualization of cysts, thickening of the endometrium.
- According to laboratory tests - increased concentrations of androgens, estrogens, insulin, luteinizing hormone and other pathological changes.
. Implications of polycystic ovary
Polycystic ovary is a very insidious disease that besides infertility entails a lot of undesirable consequences for the health of women. In particular, it is proven that patients with polycystic disease are at increased risk of developing the following conditions:
- Hyperplasia of the endometrium and uterine cancer.
- Malignant breast tumors.
- Diabetes of the second type.
- Obesity.
- Atherosclerosis.
- Thrombosis.
- Cardiovascular diseases( hypertension, stroke, myocardial infarction).
Diagnosis of polycystic ovary
A survey of a woman with suspected polycystic ovary should include:
-
 Interview and general examination( it is important for the gynecologist to determine the type of body, the presence of excess weight, the condition of skin and hair).
Interview and general examination( it is important for the gynecologist to determine the type of body, the presence of excess weight, the condition of skin and hair). - Gynecological examination.
- Ultrasonic scanning of the pelvic organs.
- Laboratory tests.It is necessary to assess the level of hormones of the pituitary gland, ovaries, adrenals.In addition, it is necessary to determine the level of glucose, insulin in the blood and the lipid profile.
- Diagnostic laparoscopy.It is conducted in controversial cases, for example, when the results of examination and laboratory tests indicate polycystosis, and ultrasound has no characteristic signs of an ailment.
The diagnosis of "polycystic ovary" is based on the presence of a woman at least two of the criteria listed below:
- Menstrual irregularities and lack of ovulation( as a result, the inability to become pregnant).
- Clinical or laboratory evidence of hyperproduction of male sex hormones.
- Signs of polycystic ovary change, obtained with ultrasound scanning.
Thus, only ultrasound for diagnosis is not enough( unfortunately, many women are diagnosed with polycystosis in this way).The ultrasound picture of the disease in question can be confused with the picture of multifollicular ovaries - an ailment that has significant differences with true polycystosis.
Methods of treatment of polycystic ovary
 It is almost impossible to completely cure polycystic ovaries. Gynecologists can only minimize the manifestations of the disease and thus help the woman achieve the main goal( this is, as a rule, the conception and birth of a healthy child). However, to get what you want, you can not delay visiting a doctor.The sooner a diagnosis is made, the easier it will be to normalize the hormonal background and restore the proper functioning of the reproductive system.
It is almost impossible to completely cure polycystic ovaries. Gynecologists can only minimize the manifestations of the disease and thus help the woman achieve the main goal( this is, as a rule, the conception and birth of a healthy child). However, to get what you want, you can not delay visiting a doctor.The sooner a diagnosis is made, the easier it will be to normalize the hormonal background and restore the proper functioning of the reproductive system.
The treatment of patients with polycystic ovary with conservative methods - drug therapy , which involves the use of several groups of drugs:
- Hormones and their antagonists .Selection of hormonal drugs is carried out in accordance with the detected violations of the hormonal background.One patient is prescribed ovulation stimulants, others - progesterone, dexamethasone, antiandrogen preparations, oral contraceptives or other hormonal medications.
- Sugar-reducing drugs ( most often metformin).The expediency of using these remedies is explained by the need to increase the sensitivity of tissues to insulin and thus to reduce the concentration of insulin in the blood and stop its stimulating effect on the ovaries.
- Vitamins, which favorably affect the functioning of the sex glands( in particular vitamins E, C and group B).
Complex medication is prescribed for up to 6 months.If her result is unsatisfactory( no pregnancy comes), gynecologists resort to surgical treatment of .Modern laparoscopic equipment allows for such interventions with the least traumatism for a woman - already 3-4 days after the operation the patient is discharged home, and on her body there are only a few practically invisible scars.
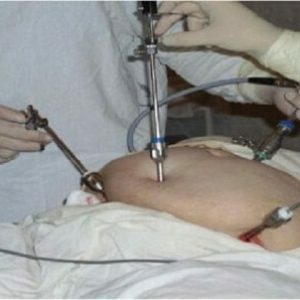 In polycystic ovaries, two surgical techniques are commonly used:
In polycystic ovaries, two surgical techniques are commonly used:
- Visional resection is the removal of part of the ovary most affected by the cysts.
- Cautery - cauterization of cysts on the surface of the gonads.
As a result of such operations, ovulation and the production of sex hormones by the ovaries are normalized.However, the disease can return, so gynecologists recommend that patients already in the first or second cycle after a surgical procedure try to conceive a child.
Diet and physical activity in polycystic ovary
Because excess weight creates serious obstacles to the normalization of the hormonal background, weight loss for patients with polycystic ovary is not less important than medical or surgical treatment. Patients can help their body to lose weight and cope with the disease with the help of diet and physical activity ( regular hiking and jogging, fitness, etc.).
The diet for women with polycystic ovary should be based on the following principles:
- Reducing caloric intake by reducing the consumption of fast carbohydrates and fats.
- Fractional power supply.
- Eating lots of vegetables and fruits.
- Complete refusal of alcohol.
- Restrictions in the diet of fried, smoked, pickled, spicy dishes.
Pregnancy and polycystic ovary
 Polycystic ovaries are by no means a verdict or an excuse to put a "cross" on the desire to have children. Correctly selected treatment in most cases helps a woman conceive a child.However, after the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, one should not forget about the disease.Such future mothers need drug support( mostly hormonal) and a very careful attitude to their condition, since there is a high risk of miscarriage.In addition, patients with polycystic ovary should be under special control of doctors in view of the possibility of developing gestational diabetes, increasing blood pressure and other complications of pregnancy.
Polycystic ovaries are by no means a verdict or an excuse to put a "cross" on the desire to have children. Correctly selected treatment in most cases helps a woman conceive a child.However, after the onset of a long-awaited pregnancy, one should not forget about the disease.Such future mothers need drug support( mostly hormonal) and a very careful attitude to their condition, since there is a high risk of miscarriage.In addition, patients with polycystic ovary should be under special control of doctors in view of the possibility of developing gestational diabetes, increasing blood pressure and other complications of pregnancy.
It is also worth noting that pregnancy can become a cure for polycystic ovary. Many women with this condition had a normal menstrual cycle after childbirth, and there were no problems with conception in the future.
Zubkova Olga Sergeevna, medical reviewer, epidemiologist