Eczema in a child: causes, symptoms, treatment
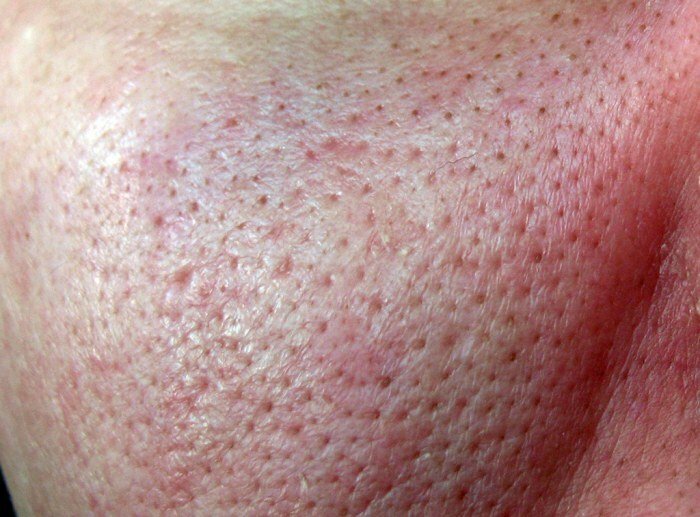
 Eczema is a skin disease( dermatosis) that is characterized by a chronic course with recurrent exacerbations( relapses).With this pathology, an inflammatory process develops in the superficial layers of the skin.
Eczema is a skin disease( dermatosis) that is characterized by a chronic course with recurrent exacerbations( relapses).With this pathology, an inflammatory process develops in the superficial layers of the skin.
This type of dermatosis is a polyethological disease, i.e. occurs due to the combined effect of external and internal damaging factors.Endogenous causes include metabolic, endocrine and immune disorders, as well as pathologies of the digestive system.The cause of microbial eczema is the introduction of streptococcal or staphylococcal microflora on the background of a decrease in resistance( resistance) of the body.
Table of contents: Forms of eczema in children Causes of eczema Symptoms of eczema Diagnosis of eczema Treatment of eczemaForms of eczema in children
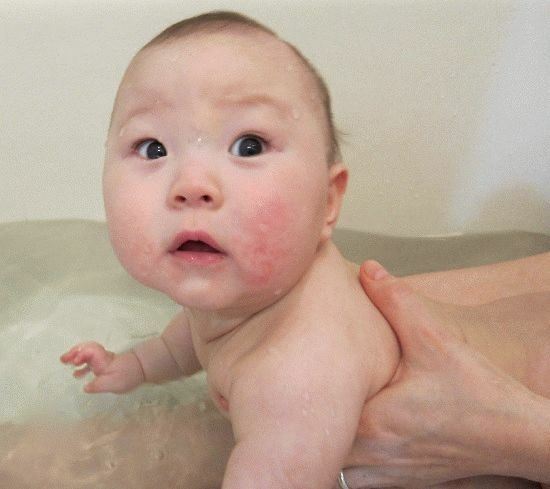
 Important: eczema in children often develops at the earliest age against atopic dermatitis or diathesis.
Important: eczema in children often develops at the earliest age against atopic dermatitis or diathesis.
A characteristic clinical manifestation of pathology is the formation on the skin surface of multiple primary elements in the form of vesicles, which then merge and open.In their place there are dying foci of inflammation or crusts are formed.
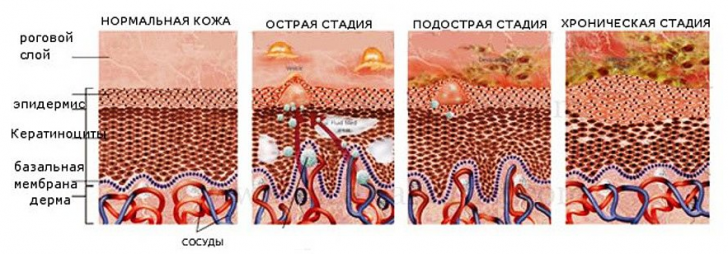
Eczema stages
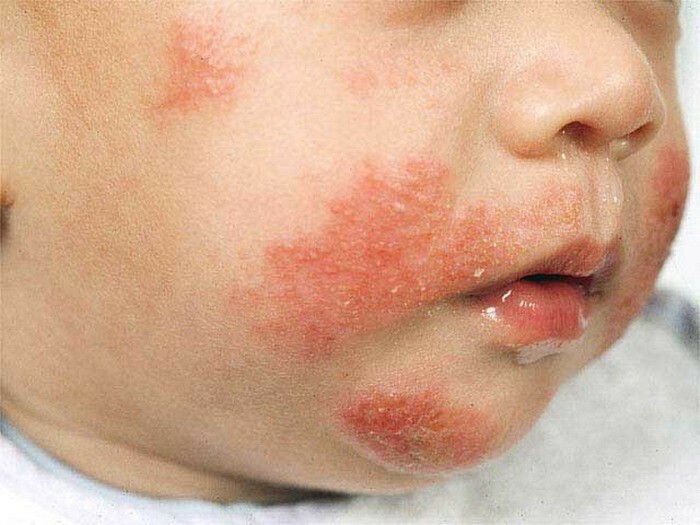
For eczema, the child is characterized by a primary localization of the rashes on the skin of the face and neck, as well as a lesion of the scalp.Vesicles can also appear with eczema on the legs, hands and in the groin-femoral and gluteal folds.As chronic eczema progresses, the primary elements gradually spread to other parts of the body.
The following varieties of this kind of dermatoses are distinguished:
- true eczema;
- seborrheic form;
- microbial eczema;
- dry eczema( dermatitis);
- is a dyshidrotic eczema.
Causes of eczema
The developing inflammatory process is allergic in nature.Great importance in the development of eczema in children has a genetically determined( hereditary) predisposition.
The most frequent direct cause of pathological changes are severe eating disorders and metabolic disorders due to diseases of the liver and gastrointestinal tract.To the number of eczema triggers are also hypersensitivity reactions( allergies) to children's hygiene products and severe stresses, leading to functional disorders of the nervous system.The development of pathology contributes significantly to the reduction of general and local immunity.
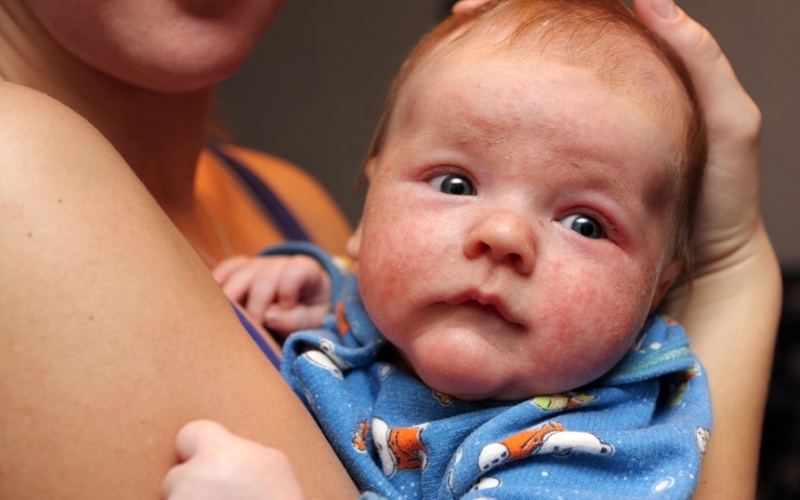
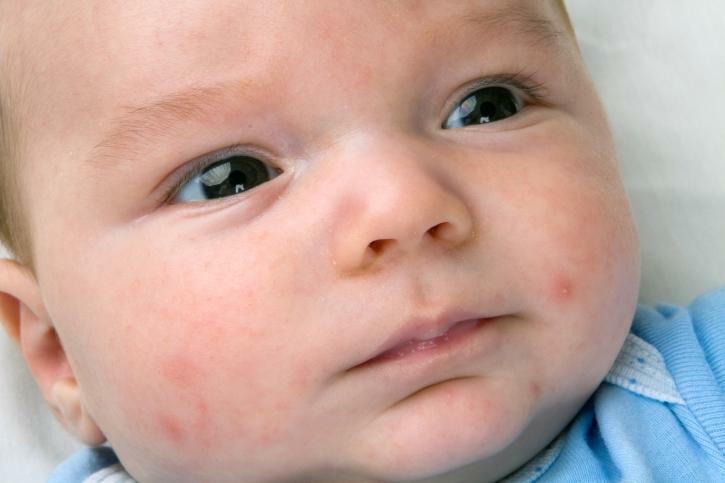 Please note: rashes on the skin especially often develop in the first six months of life, because at this age the skin of the baby is particularly sensitive, and the digestive system is not completely formed.In older children and adolescents, the metabolic and hormonal alteration of the body can become a peculiar impetus to the appearance of eczema.
Please note: rashes on the skin especially often develop in the first six months of life, because at this age the skin of the baby is particularly sensitive, and the digestive system is not completely formed.In older children and adolescents, the metabolic and hormonal alteration of the body can become a peculiar impetus to the appearance of eczema.
Symptoms of eczema
The leading symptoms of eczema in children are:
- rashes affecting extensive areas;
- skin itching;
- burning.
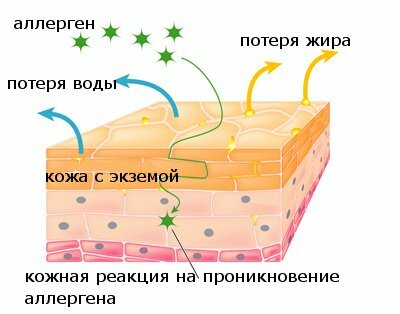
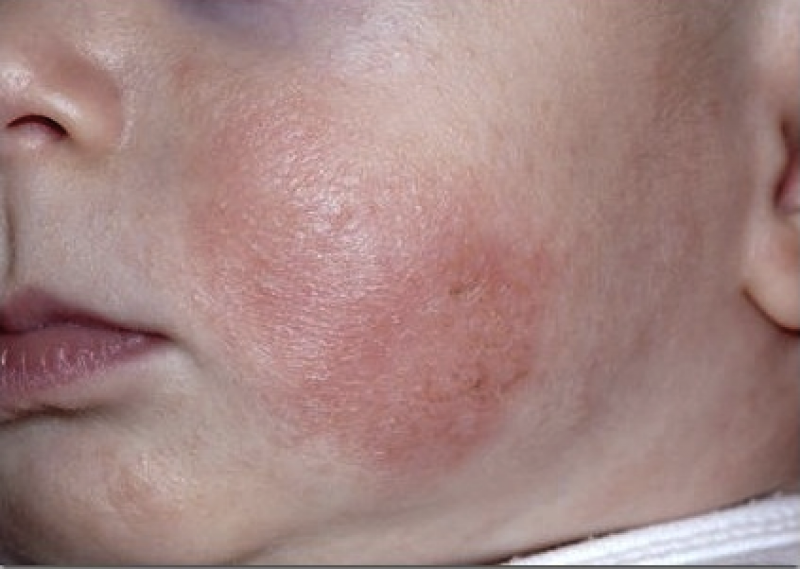
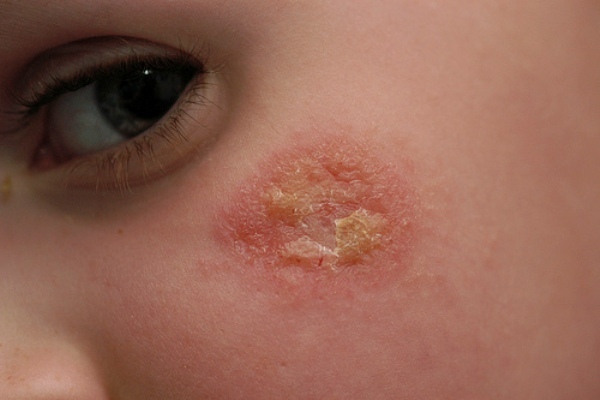 In most cases, the acute is diagnosed as a true( idiopathic) form of .Most often it develops at the age of 2 to 6 months.Already in the initial stage of eczema of this species on the skin appear multiple primary elements of bright red color.Vesicles with serous contents are localized first on the face, and then spread to the limb folds( mainly knee and elbow).On the spot of the bursted bubbles, secondary morphological elements are formed - point erosions, which are covered with scales and crusts.The subacute process is characterized by hyperemia of the epidermal layer of the skin, the appearance of swelling and wetting erosions( so-called "wet eczema").Foci of inflammation in a number of cases acquire a pink-cyanotic shade.Clinical manifestations in such a flow can spontaneously disappear, and then reappear.
In most cases, the acute is diagnosed as a true( idiopathic) form of .Most often it develops at the age of 2 to 6 months.Already in the initial stage of eczema of this species on the skin appear multiple primary elements of bright red color.Vesicles with serous contents are localized first on the face, and then spread to the limb folds( mainly knee and elbow).On the spot of the bursted bubbles, secondary morphological elements are formed - point erosions, which are covered with scales and crusts.The subacute process is characterized by hyperemia of the epidermal layer of the skin, the appearance of swelling and wetting erosions( so-called "wet eczema").Foci of inflammation in a number of cases acquire a pink-cyanotic shade.Clinical manifestations in such a flow can spontaneously disappear, and then reappear.
True chronic eczema has the property of exacerbating in the autumn-winter period and early spring due to a decrease in the number of vitamins coming with food and the associated weakening of immunity.
For seborrheic eczema , more often developing in infants and adolescents during puberty, is characterized by localization of inflammatory foci in those parts of the body where the skin has the largest number of excretory ducts of the sebaceous glands.The greatest number of specific primary elements is noted in the face area and on the hairy part of the head.They are covered with fatty scales yellow-brown plaques, rising above the skin.
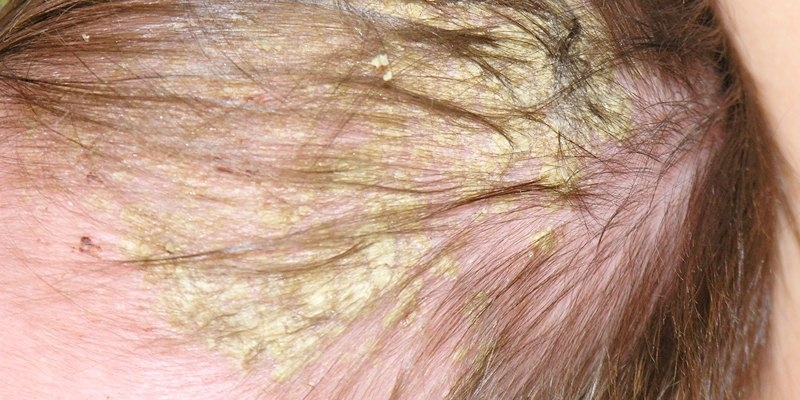
Microbial eczema , which develops against the background of infection with staphylococci or streptococci( usually with specific or nonspecific immunodeficiency), is characterized by the appearance of multiple crusted erosive lesions of diverse localization.
Dry eczema ( dermatitis) occurs with increased dryness of the skin.This form is characterized by seasonal exacerbations in winter, when the humidity level of the ambient air is lowered.
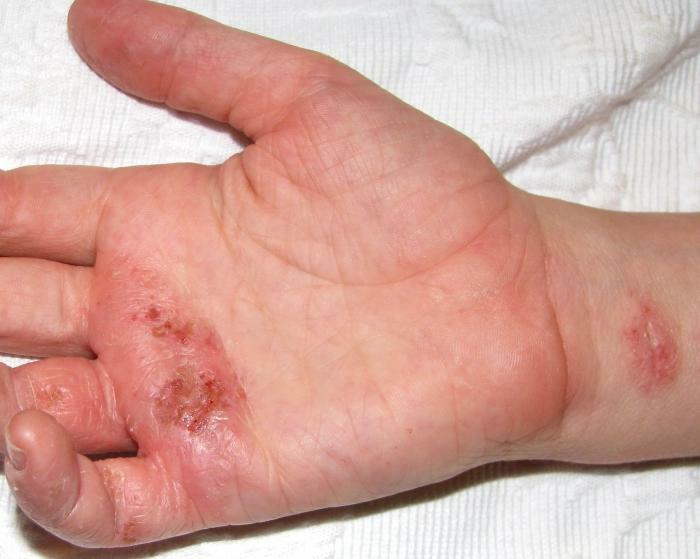
Dyshidrotic eczema , which develops as a result of endocrine and immune disorders( often against a background of genetic predisposition), is manifested by the fact that in the deep layers of the epidermis of the skin bubbles up to 5 mm in diameter are filled with transparent serous contents.The appearance of primary elements is accompanied by intense itching.
Diagnosis of eczema
The diagnosis of any of the varieties of eczema, as a rule, does not cause difficulties.Of paramount importance is the external examination and careful collection of anamnesis( including - allergological).
Differential diagnostics is performed with pathologies such as Dühring dermatitis and diffuse neurodermatitis.
Treatment of eczema
 The treatment strategy is determined by a dermatologist after setting an accurate diagnosis and identifying the etiologic factor of the disease.A prerequisite for successful therapy is the elimination or minimization of the patient's contact by the stimulus.
The treatment strategy is determined by a dermatologist after setting an accurate diagnosis and identifying the etiologic factor of the disease.A prerequisite for successful therapy is the elimination or minimization of the patient's contact by the stimulus.
Basic treatment tactics
If the disease developed in an infant, then first of all the mother needs to adjust the diet and adhere to the hypoallergenic diet until the end of the lactation period.
Note: , women planning a pregnancy, you need to take into account that to prevent the development of eczema, the baby needs to eat right during the gestation period.
Babies who are on artificial feeding, require the replacement of milk mixtures with analogues.For older children, it is required to exclude from the menu products that may be allergens( chocolate, nuts, citrus fruits, etc.), and so-called.Gistaminoliberators - strong meat broths and cocoa.

 Special attention should be paid to the clothes of the baby.It is necessary to exclude the contact of synthetic tissues with the skin - the underwear should only be cotton.It is important to ensure that the seams are not in contact with sensitive areas of the body.Do not wear tight clothing;The wardrobe should be updated regularly as the child grows.For washing, it is important to select special children's hypoallergenic powders.
Special attention should be paid to the clothes of the baby.It is necessary to exclude the contact of synthetic tissues with the skin - the underwear should only be cotton.It is important to ensure that the seams are not in contact with sensitive areas of the body.Do not wear tight clothing;The wardrobe should be updated regularly as the child grows.For washing, it is important to select special children's hypoallergenic powders.
It is important to ensure that the baby sweats as little as possible.For this, the room should maintain the optimum temperature and humidity.
Children need to cut their nails shortly to prevent skin trauma when combing.
Medical methods for treating eczema in children
Drug medications are selected according to the type of eczema and the nature of the associated pathologies.When choosing therapeutic tactics, the individual constitutional features of the patient must be taken into account, as well as the nature and severity of the disorders from the immune, nervous and endocrine systems.
The main groups of medicines prescribed for the therapy of eczema:
- soothing( sedative);
- antiallergic( desensitizing and antihistamines);
- is an anti-inflammatory;
- antipruritic;
- immunomodulators.
In the child's body, the level of calcium is relatively low, and the permeability of blood vessels is high.In view of these features, the use of calcium-containing drugs in combination with antihistamine and anti-inflammatory agents, as well as vitamin complexes is indicated.
 Calcium in the form of glycerophosphate, lactate or gluconate for children is given orally in dosages of 0.25-0.5 g per reception( depending on age) as a solution( 2-5%).Multiplicity of reception - 2-3 times a day.
Calcium in the form of glycerophosphate, lactate or gluconate for children is given orally in dosages of 0.25-0.5 g per reception( depending on age) as a solution( 2-5%).Multiplicity of reception - 2-3 times a day.
To reduce the level of sensitization and reduce inflammation, sodium thiosulfate is recommended.For oral administration, the drug is prescribed 0.25-0.5 g 2-3 times a day.10-20% solution can be used for IV infusions every other day for 5-8 ml.The course requires 8-10 injections.
As a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent, a 1-2% solution of sodium salicylate is indicated, the dosage of which is determined at the rate of 0.1 g per kg of baby weight per day.The daily dose is divided into 2-3 doses.Children who have reached the age of 2 years, the drug gives 0.25 g for each year of life.
Dosages of antihistamines are determined according to the age of the child.They are appointed by short courses( from 1 week to 10 days).
Among the most effective antihistamine drugs, which additionally possess antiserotonin and anti-bradykinin properties, are:
- Dimedrol;
- Suprastin;
- Sandosten;
- Diazolin;
- Tavegil;
- Fenkarol;
- Peritol;
- Peritol.
Note: parallel reception of ascorbic acid allows to reduce the dosage of antihistamines somewhat, since vitamin C is their synergist.
The long-lasting persistent course of the disease requires the appointment of sedatives( meprobamate, Andaxin).If there are neurotic disorders and / or vegetovascular dystonia, drugs with anticholinergic and anxiolytic properties( Tazepam, Amizil) are shown.
With the development of impetigo ( pustular skin lesion) against the background of idiopathic and seborrhoeic forms, as well as with microbial eczema, antibiotic therapy with broad spectrum drugs is indicated.
The most effective and safe are the following antibacterial agents:
- semi-synthetic antibiotics of the penicillin series( Oxacillin, Ampicillin);
- macrolides( Erythromycin).
Important: a child under 9 years of age is not recommended to give tetracycline-based drugs, as they have a negative effect on osteogenesis( formation of the skeleton) and have the property of accumulating in hard dental tissues.
Treatment of eczema in the hands of a child in the persistent course of the disease often requires the use of hormonal drugs for topical use( for example, ointments with hydrocortisone).
In severe eczema hormones from the group of glucocorticoids can be administered orally( Dexamethasone, Prednisolone or Urbazone).
With sluggish or latent and long-term manifestations of eczema with a tendency to develop neurodermatitis, plasma and hemotherapy are often required.
 Important: All medications must be prescribed by a doctor, self-medication is dangerous to your child's health.Before using drugs, you should carefully study the instruction - there are contraindications and age restrictions.
Important: All medications must be prescribed by a doctor, self-medication is dangerous to your child's health.Before using drugs, you should carefully study the instruction - there are contraindications and age restrictions.
Treatment of eczema in children with folk remedies
When treating eczema with folk remedies, decoctions of the following medicinal plants are shown at home:
- motherwort;
- sequence;
- valerian( root);
- hawthorn;
- chamomile.
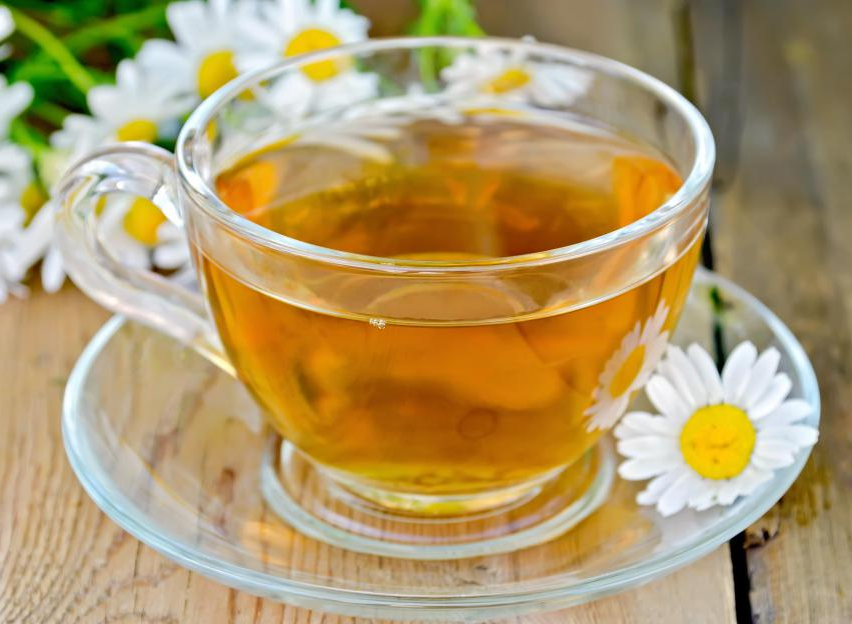 Please note: herbal decoctions are prepared from the calculation of 5-10 g of dry vegetable substrate per glass of water.Accept ready phytopreparations for 1 tbsp.L.3-4 times a day.
Please note: herbal decoctions are prepared from the calculation of 5-10 g of dry vegetable substrate per glass of water.Accept ready phytopreparations for 1 tbsp.L.3-4 times a day.
Non-drug methods also use ultraviolet irradiation.The technique can be used only in the phase of regression of rashes, i.e., without exacerbation of the disease.A good effect is also possible to achieve such physiotherapeutic procedures as UHF procedures and phonophoresis with hydrocortisone.
Children over 3 years of age are shown sanatorium treatment( during the period of acute eczema symptoms).
About the symptoms of eczema in children, the mechanisms of the development of the disease and the methods of its treatment tells the dermatovenereologist:
Konev Alexander, the therapist