How to use a contraceptive patch?
 To date, many different methods have been invented to prevent the onset of unwanted pregnancy. However, each method has its advantages and disadvantages. The most reliable is a condom. He is able to protect not only from unwanted pregnancy, but also from sexual infections. In spite of this, girls prefer to use other methods, for example, a special contraceptive patch.
To date, many different methods have been invented to prevent the onset of unwanted pregnancy. However, each method has its advantages and disadvantages. The most reliable is a condom. He is able to protect not only from unwanted pregnancy, but also from sexual infections. In spite of this, girls prefer to use other methods, for example, a special contraceptive patch.
This type of contraception is relatively young, but has already proved itself positively, because in addition to protection from pregnancy, it is able to restore the hormonal background of a woman.
How to use a contraceptive patch?
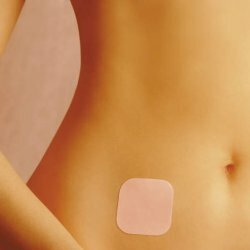
Externally, the contraceptive patch is no different from the usual. It is flesh-colored and measures about 20 centimeters. The patch should be pasted on the first day of menstruation on clean skin. Replacement of the patch is done every seven days. Adhesive patch is necessary in the area of the shoulders or abdomen, buttocks or scapula. That the plaster operated effectively, it needs to be changed every seven days, not later. During the month, you have to change three patches, after which you need to make a week break. But the break should not exceed seven days.
So that the skin does not have any allergic reaction or irritation, the adhesive needs to be glued to a new place every time. If you are going to use the plaster for the first time, then you need to glue it on the first Sunday from the beginning of the month. However, during the first week after the start of its use, it is still worth using other contraceptives, for example, condoms.
How the contraceptive patch works
The principle of the contraceptive patch is very simple. In the blood of a woman through the skin come the artificial analogues of sex hormones, which prevent the onset of ovulation. As a result, the ovaries do not produce eggs ready for fertilization. It is worth noting and the fact that this plaster has an effect on the mucous membrane of the cervix, so that the sperm can not penetrate into its cavity. This equates the chances of getting pregnant to zero. However, for the adhesive to function effectively, it must be on the body around the clock.
Many studies have been conducted, during which it became clear that the adhesive patch is almost never peeled off. However, if this happens, then you need:
- With a partial peeling off the adhesive, you need to try to paste it back. To do this, you need to press on it with your palm for 15 seconds, and then make sure that the edges are tightly adhered. If this manipulation did not help, then the plaster needs to be changed to a new one.
- If the adhesive is completely detached and can not be glued back, then replace it with a new one. However, the replacement must be carried out throughout the day. If it takes more time, then pregnancy may come, so you need to use a condom and start a new countdown.
Advantages and disadvantages of the contraceptive patches
One of the main advantages of the contraceptive patch is that it is very convenient to use. It is perfectly attached to the skin and is not affected by water or sun. Therefore, even if the girl leads an active lifestyle, she can not be afraid that the adhesive will come unstuck. With a band-aid you can visit the swimming pool, swim at the sea, go to the gym. Unlike other ways to protect against unwanted pregnancy, a band-aid does not need to be monitored every day. With a band-aid, you can not interrupt sexual intercourse.
Unlike tablets, the plaster does not enter the digestive tract and does not cause digestive disorders or diarrhea. It helps to restore the regularity of the cycle and helps reduce pain during menstruation. In addition, the plaster facilitates the symptoms of premenstrual syndrome. The patch is safe, as it reduces the risk of oncological and gynecological diseases.
However, no matter how good a contraceptive patch is, it also has its drawbacks. The disadvantages can be attributed to the fact that the patch is noticeable on the skin. Sometimes it can provoke irritation of the skin and discomfort on the skin. At first, the use of the patch may have side effects: dizziness, nausea, drowsiness, mood swings, spotting from the vagina, chest pains and others. However, all these symptoms disappear on their own in 1.5-2 months. Also it is worthwhile to understand that birth control patches protect only from unwanted pregnancy, but not from sexual infections. Therefore, if you are not sure about your partner, it is better to use a condom.
What side effects can occur from the plaster?
From the use of the contraceptive patch, side effects occur very rarely. However, it is worthwhile to understand that each of us has an individual organism, so no one is immune from side effects. If you notice a manifestation of at least one side effect, then you should immediately consult a doctor. The list of possible risks:
- From the nervous system: sleep disorders, migraine, dizziness, depression, anxiety.
- From the cardiovascular system: edema, high blood pressure, heart palpitations, varicose veins.
- From the digestive tract: gastritis, increased appetite, constipation, anorexia, abdominal pain, diarrhea, vomiting, meteorisms.
- On the part of the genitourinary system: pain during intercourse, breast enlargement, vaginitis, mastitis, abnormal ovaries, cyst, cystitis.
- Sometimes there are skin irritations: a rash, itching, hives, acne, dry skin.
- There may be pain in the back and legs, muscle weakness, convulsions.
- Possible metabolic disorders.
- Possible deterioration of vision.
All these symptoms are very dangerous, so a doctor's consultation is mandatory. Do not start using a patch yourself.
Contraindications to the use of the contraceptive patch
Contraceptive patches can not be used for certain diseases. If there is venous or arterial thrombosis, as well as the presence of serious diseases( diabetes mellitus, hypertension, etc.), then the band-aid should be abandoned. Also, it can not be used if there is a predisposition to a quantitative and qualitative violation of the composition of blood lipoproteins.
The plaster can not be used for cancer, as well as for benign formations. If there are problems with the hormonal background, menopause, uterine bleeding, then it is worthwhile to look for other methods of contraception. Doctors do not recommend using plaster during pregnancy, during lactation, and also during the first four weeks after childbirth.
If a woman has bad habits( smoking, alcohol dependence), then the band-aid may not be effective. Sometimes there is an individual intolerance to the components of the drug, so there may be an allergy to the patch.
If the weight of a woman is more than 90 kg, then this reduces the effectiveness of the patch. Therefore, doctors do not recommend using this method of protection against unwanted pregnancies to full girls. It should be understood that the contraceptive patch is a hormonal drug, using which you need to be very careful. During the use of the patch you need to be under the supervision of a doctor.



